Worksheet: Energy & Enzymes
advertisement

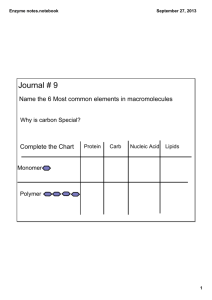
Name: Block: Date: Enzymes Enzymes are important biological macromolecules that do work in all living things. Plants, animals, and prokaryotes all depend on enzymes to break down large molecules or build new ones. Enzymes are made up of one or more proteins, and proteins are made based on information found in your DNA. There are even enzymes that make other enzymes! Once a reaction has been completed, the enzyme is free to be reused again and again in future reactions. In general, enzymes are a series of protein molecules (also called polypeptides) that must be folded in a specific three-dimensional shape in order to function properly. Certain environmental factors can change enzymes by breaking the hydrogen bonds that maintain their specific shape. These factors include things such as pH and temperature. If an enzyme's shape changes significantly and it can no longer function, the enzyme denatured. Step 1 1. Molecule C is a large molecule called a(n)___________________. 2. Molecules A and B are called substrates, and are usually _______________ or building blocks of larger macromolecules. 3. Molecule C is made of which of the four major biological macromolecules? ___________ Step 2 4. Molecules A and B are now bound to molecule C’s ______________ ______________. 5. Is molecule C breaking apart (decomposing) or building (synthesizing) a macromolecule? What is the name of this reaction? ___________________________________________ 6. If a solution is too acidic or basic, molecule C can ________________ or change it shape so that A and B will no longer fit. Step 3 7. What will happen to molecule C now that the reaction is complete? 8. What are two things that affect how fast molecule C works? 9. Molecule D is made of building blocks represented by A and B. If D represents a disaccharide, A and B would represent ___________________. 1) The enzyme pancreatic amylase is manufactured and secreted by the pancreas into the small intestine. Pancreatic amylase breaks down starch into a smaller sugar. Pepsin is an enzyme that is released by the stomach and functions to break down proteins into amino acids. The following graph shows the pH at which both pepsin and pancreatic amylase can function in the body. If the pH of the body falls above or below the graphs for each enzyme respectively, that enzyme will denature and no longer function. The higher the curve of the graph, the more productive the enzyme is. Which of the following statements is true with respect to Figure 1? a) Pepsin and pancreatic amylase could never function together in the same part of the body at the same time. b) Pancreatic amylase could function in the stomach with a pH of 1-2. c) The optimal pH for the functioning of pepsin is approximately 8.5 to 9. d) Pancreatic amylase is used in the small intestine. Normally, the small intestine must be slightly acidic in order for it to function. 2) Figure 2 depicts the activities of three enzymes. Remember that the average human body temperature is 37oC. Which curve illustrates the functioning of human DNA polymerase, which functions in the nucleus of cells? a) Enzyme A b) Enzyme B c) Enzyme C d) None of the above could represent the activity of human DNA polymerase. 3) Which curve illustrates the functioning of DNA polymerase from a shark (Hint: the body temperature of a shark is typically the same as water that surrounds it about 20oC)? a) Enzyme A b) Enzyme B c) Enzyme C d) None of the above, since sharks, like all fish, do not contain DNA polymerase. 4) At what temperature would enzyme B be completely denatured? a) 37°C c) 25°C b) 40°C d) 50°C