90453 Describe modification of livestock reproduction or plant
advertisement

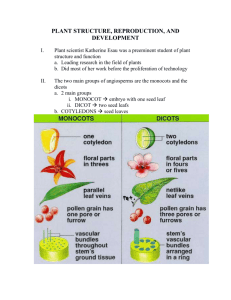
90453 Describe modification of livestock reproduction or plant propagation to improve productivity. PLANT PROPAGATION TO IMPROVE PRODUCTIVITY. Notes. 1. This Achievement Standard requires knowledge of reproductive process(es) of plants, and describing techniques used to modify reproduction or propagation of plants, and how these techniques modify reproduction and improve productivity. 2. This Achievement Standard is largely theoretical but practical experience is an important part and you need to build in as much as possible. THE EMPHASIS SHOULD BE ON COMMERCIAL PROPAGATION TECHNIQUES AND PRACTICES. 3. Aspects of this Achievement Standard may require to be skipped over or to be covered in more depth, depending on whether Horticulture has been taught as Year 11. 4. Notes accompany this scheme for depth and breadth of teaching. 5. Do the practical activities on the fine days and last periods and theory when the weather is no good or in the mornings. 6. Power point presentations are a good way to go on a field trip with out leaving the room if this is more suitable. 7. All videos are from the Growing Awareness series from VEA, if not otherwise stated. 8. Texts. There are no text books for this Achievement Standard. This text may be helpful. Yates Guide to Horticulture by Don Bramley from Heinemann 1985. The following biology texts and workbooks are useful for physiology of plants but not productivity. The Life of Plants by Martin Hanson, published by Longman Paul 1994. Year 12 & 13 Biology Student Resource & Activity Manuals from Biozone, are good for more detailed knowledge and activities on growth and reproduction. Year 11 Biology 1.7 NCEA Level 1 Workbook (from ABA Books Ltd), Year 11 Study Guide NCEA level 1 Biology & Human Biology (from ESA Publications New Zealand Ltd) & 24 hour Year 11 Biology / Human Biology Revision Notes (from ESA Publications New Zealand Ltd) can be utilised for basic concepts and activities, on growth and reproduction, if students have not done Year 11 Horticulture. 106760019 last saved 7/03/2016 8:21:00 AM Title Key outcomes Positioning in teaching programme Links to curriculum Time allowance Assessment Modification of Plant Propagation Describe the modification plant propagation to improve productivity Autumn/Spring terms Science and technology curriculum documents Approx 24 lessons (6 weeks) AS90453(version 2) All videos are from the Growing Awareness series from VEA, if not otherwise stated. Texts. There are no text books for this Achievement Standard. This text may be helpful. Yates Guide to Horticulture by Don Bramley from Heinemann 1985. The following biology texts and workbooks are useful for physiology of plants but not productivity. The Life of Plants by Martin Hanson, published by Longman Paul 1994. Year 12 & 13 Biology Student Resource & Activity Manuals from Biozone, are good for more detailed knowledge and activities on growth and reproduction. General references/texts/Equipment 106760019 last saved 7/03/2016 8:21:00 AM Year 11 Biology 1.7 NCEA Level 1 Workbook (from ABA Books Ltd), Year 11 Study Guide NCEA level 1 Biology & Human Biology (from ESA Publications New Zealand Ltd) & 24 hour Year 11 Biology / Human Biology Revision Notes (from ESA Publications New Zealand Ltd) can be utilised for basic concepts and activities, on growth and reproduction, if students have not done Year 11 Horticulture. 1 Specific Learning Outcomes Learning Activities Resources Introduce AS90453. AS90453.doc Glue AS90453 into books and use as title page. Highlight the key words in the excellence column (see below). Explain techniques used to modify plant propagation to improve productivity Explain how techniques used to modify plant propagation improve productivity Justify a technique used to modify plant propagation in a plant production system to improve productivity. Review with students what ‘Explain’ and ‘Justify’ mean/require. Review what was learnt in year 11 – Wordlist. 90453.1 Explain techniques used to modify plant propagation to improve productivity. 2 Students can: Define Propagation Define Physiology – refers to structures, functions, & control mechanisms involved in plant reproduction. Identify basic plant parts & layout. Identify the differences between the sexual & vegetative parts of the plant. Define the difference between sexual & asexual propagation. 106760019 last saved 7/03/2016 8:21:00 AM Highlight the labels on a plant structure diagram, 1 colour for vegetative & another for flowers fruit & seeds. Collect flowering weeds & dissect them in the lab to investigate in more detail. Define propagation and list the differences between sexual and asexual propagation (Homework Ex if time is short). Plant Propagation wordlist.xls Assessment 3 Specific Learning Outcomes The physiology of sexual propagation. Students can: Explain the cycle of events involved in sexual reproduction Initiation of flowers and growing to the point where they open Pollen formation Development of the ovary and ovules Pollination Fertilisation Seed (embryo) development Fruit development Seed dispersal Germination completes the process 4 5 Students can: Describe and explain pollination & fertilisation. Methods of pollen movement - insects, water, wind, animals. Self and Cross Pollination The difference between bisexual, monoecious, dioecious, parthenocarpic. Seed (embryo) development & Fruit development. Students can: Explain Seeds and Seed dispersal. What is a seed? Dicots & monocots. Seed parts. Methods of dispersal. 106760019 last saved 7/03/2016 8:21:00 AM Learning Activities This is intended to provide an overview of sexual reproduction. The detail /depth required is covered in the following lessons. Dissect as many different flowers as you can find under a binocular microscope & identify the parts. Investigate the diversity but focus on the parts they all have in common those parts that are labelled on the flower diagram worksheet. Copy cycle of events as notes in a list or as a flow chart. Class discussion and dissection of flowers and completion of the relevant questions on worksheet. In season, look at corn cobs to show the pollen tubes. Look at a variety of flowers & group them according to their method of pollination. Draw a diagram of the fertilisation process & label all the parts. Look examples of the different types of fruit development. Look at different types of seeds & groups them according to their method of dispersal. Look at methods to collect seeds before they disperse. Use these methods to collect seeds. Collect seed from the local area. Resources flower diagram worksheet.doc Video ‘Sexual reproduction in Plants’. Summary notes for AS90453 Propagation Pollination and Fertilisation.doc Video – Private Life of Plants – Travelling. Seed collection books. Assessment Specific Learning Outcomes 6 7 Learning Activities Students can: Explain the process of Germination and techniques used to enhance it. Factors affecting germination. Invisible changes inside the seed as the seed germinates. Seed viability and dormancy (e.g. scarification, stratification, removal of chemical inhibitors etc.). Students can: Explain the role of Plant hormones in the development of the plant. Id the key hormones and their role Auxins Gibberellins Cytokinins Ethylene 8 Introduction to sexual and asexual plant propagation techniques. 9 Students can: Explain the genetic basis to propagation techniques. F1 Hybrids Cross and Self Pollination 106760019 last saved 7/03/2016 8:21:00 AM sexual Resources Complete the germination worksheet. Carry out your favourite germination experiments. Look at seed packets, discuss viability & the reasons for their ‘sow before’ dates. (Seed dormancy and seed sowing experiments are carried out later in this scheme). Changes you cannot see during germination.doc. Germination.doc. At each stage of growth, identify which hormones are involved, where these are produced, what factors stimulate their production & what effect do they have on the plant’s growth. Complete worksheet on Plant Hormones, Growth and differentiation. Plant hormones, growth and differentiation.doc Extension: Carry out an experiment by spraying gibberellic acid on carnations & note changes in their growth. (refer also 2.5- Plant Growth and Development) Discuss general ideas that apply to all techniques about collecting material – timing, stage of growth, plant health, equipment used, etc. Visit local nurseries or view PowerPoint and get a feel for the sorts of places that they are and what goes on there. Review meiosis, F1 hybridisation and punnet squares. Discuss the Controlled pollination of plants to produce new seed/plants with improved characteristics. Examples to refer to include the forestry industry (breeding for a range of wood and tree characteristics) , fruit industries, new cultivars of flowers, etc. Using honey & pearl sweet corn, count the yellow & white seeds, then work out the ratio, as predicted by Mendel’s generation of offspring when crossing heterozygous genes. View power point of What nurseries look like. Plant breeding.doc Assessment Specific Learning Outcomes 10, 11 Students can: Explain seed germination requirements. Breaking seed dormancy. Optimal conditions for germination Understand the techniques of environmental control, such as protected environments, water, temperature, media etc (also covered in 2.2) 106760019 last saved 7/03/2016 8:21:00 AM Learning Activities Review the techniques for seed sowing and the need for water, oxygen, a suitable temperature. Discuss the role of light in the germination of seeds. Review the techniques for pricking out and potting up seedlings. Explain what seed dormancy is. Carry out breaking of seed dormancy activities.(stratification – Golden queen peach seeds, Scarification – Kowhai, etc) Construct a flow diagram that identifies and explains the stages in the germination of a seed. Students need to be able to understand why water, oxygen and a suitable temperature are requirements for germination to occur. Carry out seed sowing practicals. Carry out pricking out and potting up of seedlings. Resources Order some seeds from New Zealand tree seeds www.nzseeds.co.nz To get the correct dormancy breaking technique, use the table from the site GERMINATION INFORMATION.doc Video ‘Plant Propagation’ Assessment Specific Learning Outcomes 12 13 14 15 16 Students can: Explain the physiology of asexual propagation and asexual propagation techniques. Cuttings – stem, root, leaf Material selection for cuttings. Understand the techniques of environmental control for striking cuttings, e.g. bottom heat, moisture. Use of hormone applications to encourage rooting and callus growth. Learning Activities Use a microscope & prepared slides to investigate phloem, xylem, & cambium tissues first hand. Review the basic structure of the plant. Discuss the physiology of the stem, what tissues there are and what they do. Discuss the different natural propagation types, e.g. tubers, rhizomes, corms, bulbs, runner etc & ‘artificial’ propagation types e.g. grafting. Describe the sequence of events that occur when a cutting forms roots. Define adventitious roots. Complete worksheet on how plants grow by cuttings Carry out practical of the different types of cuttings, using hormones where appropriate. Show the different techniques of environmental control & place cuttings in these environments. Resources http://www.bestgardening.com/bgc/howto/prop001.htm http://www.bestgardening.com/bgc/howto/botany01.htm Mist Propagation.doc Video ‘Growth & Propagation’ or ‘Establishing New Plants’ Apple root stocks.doc T budding How Plants Grow from Cuttings Budding and Grafting. The qualities of rootstocks; e.g. dwarfing, disease resistance etc. Tissue culture. 106760019 last saved 7/03/2016 8:21:00 AM Discuss scion (budwood) selection & the reasons for using rootstocks. Carry out practical of budding (both ‘T’ and Chip) & grafting include; whip & tongue, cleft graft, bench & mechanical grafting. Students need to be able to list the steps and explain why they are done (Tabulate) Discuss tissue culture. Get the students to report on the following using these websites & worksheets; 1. The technique. 2. Hormone application and the other chemicals involved. 3. Examples from New Zealand. 4. The reason that we use tissue culture. 5. Advantages and Disadvantages http://www.jmu.edu/biology/biofac/facfro/cloning/cloning2.htm http://academy.d20.co.edu/kadets/lundberg/ptc/images/callus.gif Tissue culture.doc Assessment Specific Learning Outcomes 17 Students can: Explain the use of natural techniques of asexual propagation. Types of division, e.g. bulbs, tubers, rhizomes etc. Layering. Learning Activities Students to carry out different types of natural asexual propagation techniques. For each tabulate information on : Examples of plants used Time of year performed Steps taken Advantages/Disadvantages Resources Plant Propagation by Layering Try http://www.ces.ncsu.edu/hil/hil8701.html 90453.2 Explain how techniques used to modify plant propagation improve productivity. 18 19 20 Students can: Explain how techniques used to modify plant propagation improve productivity in large scale, commercial production. 106760019 last saved 7/03/2016 8:21:00 AM Discuss what Productivity is and common measures of it.( Eg the time taken to produce saleable plants, quantity or quality of plants, economies of production). Review propagation techniques (both sexual and asexual) and identify the critical steps within each propagation method. Link these steps/techniques to productivity. The summary sheet can be used as a template to guide the students. Use the Gyphsophila HortFACT to sort out the changes in production time.. Look at some specific examples of breeding programmes that have improved the genetics of a crop to improve time of production, quantity and quality of the end products, and the economics of production. Discuss the advantages & disadvantages of sexual & asexual propagation in regards to increasing productivity. SUMMARY SHEET - PLANT PROP TECHNIQUES HortFACT on Gyphsophila.doc berryfruit information .doc Comparison of asexual and sexual prop.doc Assessment 106760019 last saved 7/03/2016 8:21:00 AM 21 22 23 90453.3 Justify a technique used to modify either plant propagation in a livestock or plant production system to improve productivity. Review the requirement for ‘justification’ Students can: answers ie students need to explain why the selected technique is better and why the Justify a technique used to modify alternatives are not as suitable. In justification plant propagation in a plant the comparison of the relative pros and cons of production system to improve different techniques is vital. productivity. The decision on which technique to use should be made according to the best balance of all the factors that have discussed in this unit. Ask questions like, what is the best technique: To produce identical plants? To produce large numbers of plants? To produce plants in sufficient numbers at a low per plant cost? The selected method will differ from plant to plant and situation to situation. Eg a nursery growing Braeburn apples will graft their plants onto rootstocks whereas someone growing pinus radiata plants may raise their plants from seed, cutting or tissue culture depending on the situation. Issues to consider include: Quantity, quality or the time of production of the offspring. Time of production, quantity & quality of the end products & the economics of production. Careful selection of the plant varieties allows the maximum return from the market. Identical plants. Timing of propagation for production. Advancing productivity. Even germination. Profit The best way to prepare the students is to get them to do the questions from previous exams & to investigate the propagation methods used for specific crops & discuss the reasons for the techniques chosen. . Use past examination papers.. 23 Test. 106760019 last saved 7/03/2016 8:21:00 AM Y 12 Prop Test 2.4 Sample test 90453-exam 2003 90453 exam 2004.pdf 106760019 last saved 7/03/2016 8:21:00 AM