Homework # 4: Fats and Lipids
advertisement
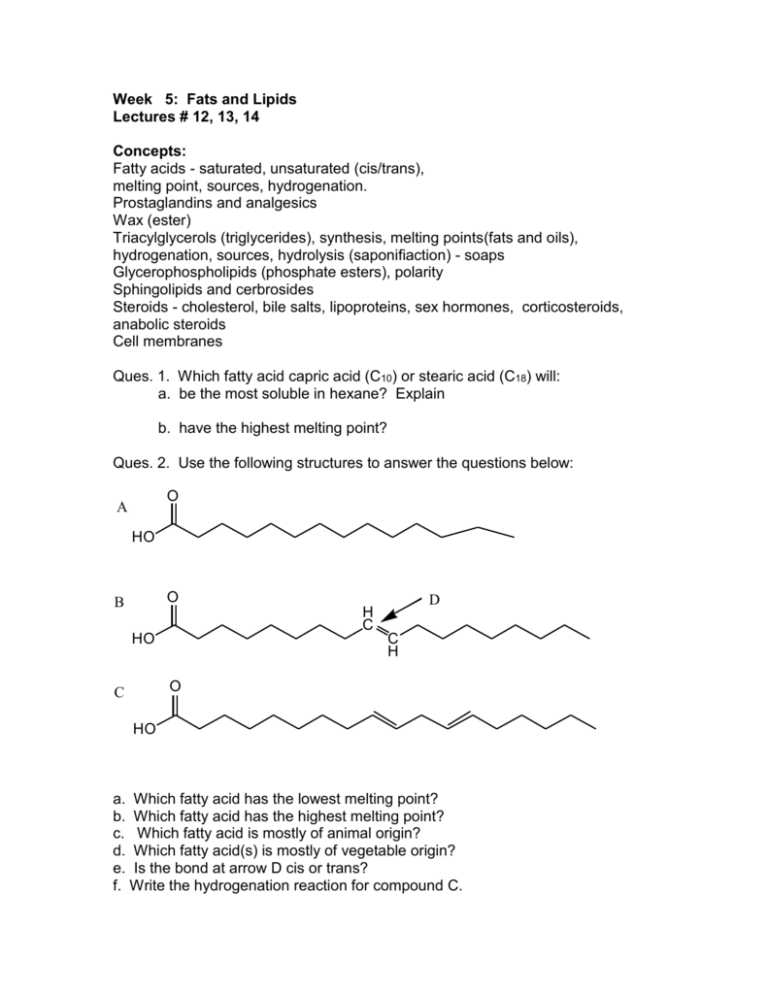
Week 5: Fats and Lipids Lectures # 12, 13, 14 Concepts: Fatty acids - saturated, unsaturated (cis/trans), melting point, sources, hydrogenation. Prostaglandins and analgesics Wax (ester) Triacylglycerols (triglycerides), synthesis, melting points(fats and oils), hydrogenation, sources, hydrolysis (saponifiaction) - soaps Glycerophospholipids (phosphate esters), polarity Sphingolipids and cerbrosides Steroids - cholesterol, bile salts, lipoproteins, sex hormones, corticosteroids, anabolic steroids Cell membranes Ques. 1. Which fatty acid capric acid (C10) or stearic acid (C18) will: a. be the most soluble in hexane? Explain b. have the highest melting point? Ques. 2. Use the following structures to answer the questions below: O A HO O B H C HO D C H O C HO a. Which fatty acid has the lowest melting point? b. Which fatty acid has the highest melting point? c. Which fatty acid is mostly of animal origin? d. Which fatty acid(s) is mostly of vegetable origin? e. Is the bond at arrow D cis or trans? f. Write the hydrogenation reaction for compound C. g. Before hydrogenation compound C is a _______(solid or liquid) at room temperature and after hydrogenation it is _______(solid or liquid) at room temperature. Ques. 4: Use the structures above to answer the questions below a: Which structure represents the most unsaturated fatty acid? b: Which structure represents the fatty acid with the highest melting point? c: Which structure represents the fatty acid with the lowest melting point? d. Which structure represents the fatty acid which is able to add one mole of hydrogen in a hydrogenation reaction? e. Which arrow shows the fatty acid with a cis alkene structure? f. Which arrow shows the fatty acid with a trans alkene structure? Ques. 5. Read the Health Notes on omega-3-fatty acids in fish oils and the Trans fatty Acids and hydrogenation. Explain the general issues of partially hydrogenating oils to make things like margarine. Relate to issue of why they would partially hydrogenate an oil, what are the health issues with trans and cis fats, and what are omega-3-fatty acids and how can they help. Ques. 6. Write the ester synthesis reaction to form a wax from a 30C alcohol and a 16 carbon fatty acid. Ques. 7. Write the ester synthesis reaction to form a triacylglycerol of glycerol and the fatty acids of: myristic, stearic, and oleic. Ques. 8: Use the two structures above to answer the following questions. a. Which triglyceride is most likely of animal origin? b. Which triglyceride is most likely of vegetable origin? c. Which triglyceride is most likely to be a solid at room temperature? d. Which triglyceride is most likely a liquid at room temperature? e. Which triglyceride is can be made into a margarine by the hydrogenation reaction? f. Which triglyceride is can undergo the acid hydrolysis reaction? Ques. 9. a. Write the basic hydrolysis or saponification reaction of the following triacylglycerol: O H2C CH O H C O H C O O H2C O H C C H C H C H H C C H b. What is the general name of the products form the basic hydrolysis reaction? Contrast the property of the product with that of a fatty acid. Ques. 10. What is olestra - a fat substitute? How does it work? What are the solubility issues with Vitamin A, D, E and K? Why those vitamins but not others such a B and C? Ques. 11: Use the structures above to answer the following questions: a. Which structure is a wax? b. Which structure is a salt of a fatty acid and thus is a soap? c. Which is one of the structures that results from the basic hydrolysis or saponification of structure "A" using sodium hydroxide? d. Which other the structure besides structure "A" may undergo the basic hydrolysis or saponification using sodium hydroxide? Ques. 12: Use the structures above to answer the following questions: a. Which triglyceride is a phospholipid? b. Which triglyceride is a lecithin? c. Which triglyceride is a cephalin? Ques. 13. For the following compare and contrast structural components or “parts lists”. Also give the function or use and any disease associated with missing enzymes. Lecithin Cephalin Sphingolipid Cerebroside Ques. 14. a. Write the structure of cholesterol. What functional groups are present? b. Compare and contrast the structures for the following. Include differences in functional groups, occurrence or uses. Bile Salts with cholesterol Steroid hormones with each other of: Testosterone Estrogen Progesterone Norethindrone Adrenal Corticosteroids: Cortisone with prednisone Anabolic Steroids Ques. 15. Draw a cross section of a cell membrane and explain the function of each part. Why are the “tail” of the phospholipids point into the center (use polar and nonpolar)? What are the purpose of any carbohydrate or protein parts?








