Plant and Animal Classification Vocabulary
advertisement

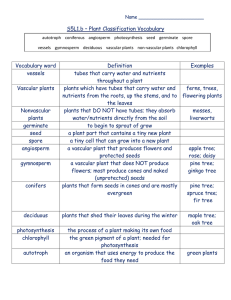
Amphibian A smooth skin animal Ex. frog, salamander Reptile An animal with scales (tiles) Ex. snake, turtle, alligator Mammal An animal with hair or fur Ex. person, cat, monkey Invertebrate An animal without bones Ex. bug, snail, octopus Vertebrate An animal with bones Ex. - any FARM Boy Mollusk A type of invertebrate, usually very slimy and mushy Ex. Snail, clam, jellyfish Vascular A plant with veins or tubes Ex. leaf, celery, tree, grass Nonvascular A plant with no veins or tubes Ex. moss Angiosperm A flower-bearing plant Ex. Apple tree, rose bush Gymnosperm A cone-bearing plant Ex. Spruce tree, Fir tree, Pine tree Spruce Tree A specific type of gymnosperm Ex. A Christmas tree Protist Single celled organisms Ex. Algae, paramecium Fungus One of the 5 types of living things Ex. Mushrooms, mold Answers Only Amphibian Reptile Mammal Invertebrate Vertebrate Mollusk Vascular Nonvascular Angiosperm Gymnosperm Spruce Tree Protist Fungus Art Center You will be drawing TWO pictures today in this center to help you remember the difference between an angiosperm and gymnosperm plant. You may look at Becka’s picture to help you with drawing ideas. Remember to add DETAILS to your pictures. You need to draw BOTH pictures before you begin to color. Angiosperm picture: Draw a girl named Angie. Hopefully you already know a person named Angie that you can use for inspiration. You may draw her in a dress with flowers, eating fruit, picking flowers, walking through a field of flowers, and fruit treed in the background. All of these things should help you remember that ANGIosperm plants always have flowers and fruits. But sometimes a plant holds its seeds inside a CONE instead of a FRUIT! These plants are called GYMNOSPERM. Gymnosperm picture: Draw your class in gym class. You may pick any game that you play in gym class that includes the use of balls. But in THIS picture, you are going to replace the balls with pine cones. This will help you remember that GYMnosperm plants are cone-bearing plants. When you finish, put this picture in your binder to help you study before the test. Flashcards It is very important that you drill your vocabulary words. You should get to a point where you don’t have to even THINK before answering the word “vascular” or “amphibian.” The more you practice saying your words out loud, the easier it becomes to remember them for a test. You may look at the tray for a FEW minutes and observe the moss and celery. They are examples of VASCULAR and NONVASCULAR plants. Then you need to practice your flashcards as a team. Pictionary It is very important that you drill your vocabulary words. The more you practice saying your words out loud, the easier it becomes to remember them for a test. It also helps you learn the definition of a word when you are forced to DRAW it instead of relying on the definition alone. Take turns playing Pictionary. Make sure that the picture has been drawing (or mostly drawn) before you shout out the answers. Learn 360 You will be watching a movie called “Science: Animals Without Backbones” on the back computer. It will take you 15 minutes to watch the video. The video begins by explaining the 5 types of living things (the 5 kingdoms) including plants, animals, and fungi. Then the video will go into more details about invertebrates, animals without backbones. When you are finished, come back to your seat and read a book quietly until it is time to rotate. Websites You will be working with several different websites on the large screen. Work from left to right on the tool bar. Many of the websites are multiple choice quizzes. Read the questions out loud together and discuss your answer before making a choice. Observe & Read You may take a few minutes to observe the items on the tray. Make sure to also read the explanations that are provided with them. When you are finished looking at each item, you may choose an A.R. book to read. Make sure you write down the title and author of the book so that you can take a test on it later. If you do not finish the book, I will keep them on my shelf for a few extra days to allow you time to finish. Celery is a vascular plant. Look at the area on the end of the stalk that has been cut. You should be able to see the tubes that run up and down the stalk carrying nutrients and water to the rest of the plant. Trees are also vascular plants. Look at the tubes on the back of the leaf. Don’t they look like veins? Tubes run up and down the entire tree carrying nutrients and water to all areas. Moss is a nonvascular plant. Moss will never grow very tall because it does not contain any tubes to carry water to the top of the plant. Moss is always found very low and flat. It soaks up water and nutrients directly from the area it is attached to. Lichens are a nonvascular plant. Lichens are often found on dead twigs and trees. They will not grow very tall because they do not contain tubes. Nutrients must be soaked up directly from the area it is growing on. The deer is a vertebrate. Its skull is a bone. Decomposers have eaten away at all of the soft tissues and organs on an animal and the only things left after the decomposers are finished are the bones. Turtles are also vertebrates. The turtle’s shell is a bone. The shell looks a little bit like the deer’s skull. Now look inside the shell. You can see where the turtle’s backbone was attached to the top of the shell. A snake is a vertebrate. Look at the bones inside the bag. Please be gentle as you handle these. Also look at the snake’s skin and observe the “tiles”. A tarantula is an invertebrate. It does not have any bones. It must shed its outer skin as it grows bigger and grow a new “shell” to help protect it.