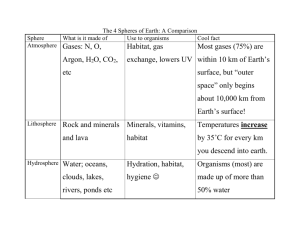
Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Look at the
advertisement

Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Ohio Standards Connection Technology Nature of Technology Benchmark A Recognize the characteristics and scope of technology. Indicator 1 Identify objects created within the human-made world (e.g., books, chairs, houses, buses) and objects that occur in nature (e.g., trees, flowers, rocks and rivers). Technology for Productivity Applications Benchmark A Understand basic computer and multimedia technology concepts and terminology. Indicator 1 Locate computer and multimedia technology in the classroom and identify it by name (e.g., computer, VCR, listening station). Indicator 2 Name the basic parts of a computer (e.g., monitor, keyboard, mouse, printer). Indicator 3 Use computer and multimedia technology with teacher assistance (e.g., computer, VCR, listening station). Lesson Summary: Students identify plants and animals that live together in forests, fields or waters in Ohio. They explore how animals depend upon plants and other animals for their needs. After using technology and other media resources for research information and images, students design and build a mobile of an Ohio habitat and share their understanding of the habitat with their classmates. This lesson brings together technology and science content and is designed for the elementary classroom. Estimated Duration: Five hours and 30 minutes Commentary: This lesson integrates the science concept of living things using their physical characteristics to survive and interact in their habitats with the technologically-based exploration of the natural and human-made worlds. Students use technology to research and present the findings to their class. Pre-Assessment: Use Attachment A, Human-made or Natural Worksheet, to differentiate between pictures of human-made and natural objects. Students should circle the natural objects. Then have students look at the circled (natural) things and mark an “L” beside the natural things that are living. Distribute Attachment B, Forest, Field, or Water?. Have students use a green crayon to circle animals and plants that could live in a field (rabbit, flower), a brown crayon for those that could live in a forest (owl, fir tree, squirrel) and blue for those that could live in water (fish, water plant). Note that some animals or plants could live in more than one habitat (rabbit, flower). You may want to point this fact out to the students before they do the worksheet. 1 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Technology and Information Literacy Benchmark A State what information is, and show where it can be found. Indicator 2 Identify places where information can be found and retrieve information from a specified location (e.g., classroom, school library, public library, the Internet, computer folder, hard drive, Web site, book). Science Life Sciences Benchmark A Discover that there are living things, non-living things and pretend things, and describe the basic needs of living things (organisms). Indicator 1 Explore differences between living and nonliving things (e.g., plantrock). Benchmark B Explain how organisms function and interact with their physical environment. Indicator 5 Investigate observable features of plants and animals that help them live in different kinds of places. Look at the plant and animal in each picture in Attachment C, Animals Need Plants. How does the animal in each picture need the plant? (Note that the eagle uses a tree for watching and nesting; a butterfly uses flower for food, spinning a cocoon, and a leaf for laying eggs; the fish uses plants for eating, hiding and laying eggs for protection) Pass out Attachment D, Parts of a Computer Worksheet, to each student. Ask the students to put a “1” by the picture of a keyboard, a “2” by the mouse, a “3” by the monitor and a “4” by the printer. As a class, orally name places to find information on plants and animals, using print material and information technology resources, like the Internet, a CD, DVD or a videotape. Scoring Guidelines: Use Attachment E, Pre-Assessment Checklist, to help determine student understanding. Post-Assessment: Based upon student observation during the project, use Attachment F, Post-Assessment Rubric, to evaluate each student’s level of understanding, skill and performance on the following criteria: Sorts pictures of objects into groups of living or non-living, natural or human-made and gives a logical oral explanation for their choice; Correctly identifies the basic parts of a computer system; Follows the correct order for turning on and off computers and using multimedia technology with teacher assistance; Runs a CD or other multimedia technology on animals and plants (i.e., videotape, DVD, presentation software); Names three different places to find information about animals and plants such as Internet, multimedia technology, encyclopedia, library book; Finds information on Ohio plants and animals using information resources with teacher assistance; Names ways the animal in their mobile depend upon plants and other animals in their habitat; 2 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Indicator 6 Investigate the habitats of many different kinds of local plants and animals and some of the ways in which animals depend on plants and each other in our community. Science and Technology Benchmark A Explain why people, when building or making something, need to determine what it will be made of, how it will affect other people and the environment. Indicator 1 Explore that objects can be sorted as “natural” or “human-made”. Constructs a mobile of one animal and one plant that live together in a common Ohio habitat (e.g., forest, field, water). Recognizes how animals and plants survive in a habitat. Scoring Guidelines: Use the Attachment F, Post-Assessment Rubric, to evaluate students upon completion of the project. Instructional Procedures: Day One Time: 45 minutes Instructional Tip: Before students start this project, have a habitat mobile assembled and on display. Use Attachment G, Model of a Habitat Mobile, to construct your model. Mount the pictures on tag-board, cut out and assemble as shown. Display the model in a prominent place in the classroom for a few days before you begin this lesson so students can see it, ask questions about, become motivated to do the project and can understand its assembly. 1. Complete the pre – assessment. Upon review of the results, modify instructional procedures to fit student needs such as using other resource materials, pictures, models and artifacts that may already be in the classroom or local field trip site. 2. Have student pairs sort pictures at their tables into stacks of natural and human-made objects. Have them discuss how they made their choices. 3. Ask each student pair to place one of their pictures on a bulletin board under the headings of Natural or Humanmade. Ask why they placed their pictures where they did. Instructional Tip: Observe and note student placements and reasons. Note the students having difficulty with the project; give individual or small group help later, perhaps during the research or construction phase of the project. 3 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Day Two Time: 60 minutes 4. Lead students in a discussion about the differences between living and non-living things. Have them consider what makes something living. Include the facts that living things move, eat, grow, change and reproduce. 5. Ask students to work in groups or individually to verbally identify or physically sort the Natural pictures into groups of "Living" and "Non-living" things on the bulletin board. Ask them to tell why they grouped them as they did to the class group discussion. 6. Give students Attachment C, Animals Need Plants. Ask them to identify the pictures of living things in a forest (tree and eagle), those that live in fields (butterfly and plant) and those that live in water (fish and water plant). Discuss with the students that plants and animals have features or parts that let them live in their habitat. In this example: The eagle has keen eyesight and a sharp beak for finding and tearing food and has claws for grasping food and tree branches. The tree that the eagle sits in is strong and tall so it can support the eagle and receive sunlight. The flower has leaves to capture sunlight and smell and color to attract insects. The butterfly has wings to fly and is light enough to sit on the flower. The fish has fins and gills to live in water. The water plant’s leaves and roots can survive under water. 7. Using pictures, help students identify other organisms that live together in a habitat, allow student pairs to match pictures. For example, students might put a raccoon and an ear of corn together and determine that they live in a field habitat. Then, have students identify features of each organism that help them live in the habitat, (e.g., a raccoon’s sharp claws lets it climb trees in a forest or corn needs a field for lots of sunlight and room to grow). Finally, help students decide how the animals might depend on the plant for its needs (e.g., the raccoon needs the corn for food). Day Three Time: 60 minutes 8. Explain to students that information means a collection of facts which can include words, numbers, sounds or pictures. Have students use both technological devices (Internet, CDs, DVDs) and traditional print resources (books, magazines) to locate information. Instructional Tip: Frequently restate or reinforce the idea of using technology to find answers to questions rather than focusing on technological resources as research instruments. 9. Attach labels to the monitor, keyboard, mouse and printer in the room. Be sure each label has both number and the component’s name on it. Point to each computer part and show the name of the computer part on the label attached to the part. Students should use Attachment D, Parts of a Computer Worksheet, to write the number of the part by the correct word and picture on the sheet. 4 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Instructional Tip: Remind students that in this lesson while the focus is on study of natural living and non living things, they will be using human made things to collect information and display their findings. 10. Students identify the parts of a multimedia device by naming the part. Then ask students to put a label with the part name by a picture of the part on a bulletin board (with assistance). Include keyboard, mouse, printer, projector, computer and DVD or VHS player. Instructional Tip: Ask volunteers to demonstrate the devices. Select students who have previous experience or are hands-on learners. 11. Ask students how we tell the technological system device what to do (type or press keys, use the mouse). Ask how we get information from this system (print, show a picture, look for things on the Internet). 12. Show a multimedia presentation such as videotape, DVD, electronic slide show on animals and plants in a habitat in Ohio. Instructional Tip: Ask volunteers to run the multimedia presentation to get them accustomed to using the technology. 13. Ask students to name some of the animals and plants in the presentation. Put up pictures of these organisms on the board with their name labels. Have them think of other organisms that they have seen or that they know that live in Ohio. Instructional Tip: Farm animals could also be considered as living in a habitat. 14. Have students identify what features they see on an animal or plant that would help that living thing survive in its habitat such as birds have different shapes of beaks and feet; frogs have skin that can repel water and legs to jump fast and far. 15. Discuss with students how the animals in the presentation depend upon other living things in their habitat to meet their needs such as raccoons eat fish, birds need trees for homes and insects need plants for food. Day Four Time: 60 minutes 16. Show students how to use select Web sites to locate local animals and plants. From those sites, have them work in pairs to locate and print out a local animal and a local plant from the same habitat. Consider the Ohio Department of Natural Resources Web site or its CDs as possible resources. 5 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Instructional Tip: Allow more than one pair of students to print out the same information about an animal or plant. 17. Ask students to save the pictures in file folders or plastic seal bags then label it with both their names. Instructional Tip: Show students the materials they will be using to construct their mobiles such as straws, pipe cleaners, paper clips and demonstrate techniques for working with these materials. Day Five Time: 60 minutes 18. Have students cut out their animal and plant pictures from similar habitats. Assist students as needed with cutting pictures. 19. Have them mount their pictures on tag-board or construction paper and cut them out. Instructional Tip: Provide other pictures from magazines on CDs for students to find and cut out, or as readyto-use pictures for students who have difficulty with cutting and pasting skills or who have been absent or not able to use a computer. 20. Have students examine the existing mobile. Have them recognize the materials used in making the mobiles. Why are straws used (light, easy to slip paper clips onto, inexpensive, straight)? Why are the paper clips used (to hold pictures to straws, can be linked together to make a chain)? Why are pipe cleaners used (to add strength to the straws)? Instructional Tip: Set up organized procedures or work station for distribution of mobile construction materials. 21. Ask students to tell why a mobile is a good way to display animals and plants in a habitat (attractive, clearly shows plants and animals that are in the same habitat, fun to make). 22. Have them look at the mobile. Point out how the pictures can be rearranged on the mobile by changing the length of paper clips or sliding the clips along the straw. 23. Have students lay their mobiles flat on the table so they will understand how they will go together before actually assembling them. 24. Students begin to assemble and display their mobiles. Instructional Tip: Hook the mobiles through the ceiling tile supports to display them. Just push up on a ceiling tile and hook a paper clip through a hole in the support frame. 6 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Day Six Time: 45 minutes 25. Require each pair to present their mobiles, naming the plant and animal and telling the features that let them live in their habitat. 26. Students tell how the animals in their mobile depend upon the plants or upon each other. Differentiated Instructional Support: Instruction is differentiated according to learner needs, to help all learners either meet the intent of the specified indicator(s) or, if the indicator is already met, to advance beyond the specified indicator(s). Students can work in groups to research and print out Ohio plants and animals. Students may use pre-cut pictures to group and assemble mobile. Challenge students to locate and take pictures of Ohio plants and animals to use for their mobile. Challenge students to create a multi-media presentation on Ohio plants and animals of interest. Extensions: Students could keep logbooks of a trip with their parents or class to a local habitat (state park, zoo, farm). Rangers, zoo officials or other wildlife managers would provide valuable resources and insight into Ohio habitats. Students could take photos or make drawings to create a new mobile to remember their trip. Students could create mobiles using materials and design of their choice. Home Connections: Students investigate their backyard or local park and find animals and plants that live together there. They discuss with family members the relationships that exist between the plants and animals they find, or they research the relationships at the public library or on the Internet. Materials and Resources: The inclusion of specific resource in any lesson formulated by the Ohio Department of Education should not be interpreted as an endorsement of that particular resource, or any of its contents, by the Ohio Department of Education. The Ohio Department of Education does not endorse any particular resource. The Web addresses listed are for a given site's main page; therefore, it may be necessary to search within that site to find the specific information required for a given lesson. Please note that information published on the Internet changes over time; therefore, the links provided may no longer contain the specific information related to a given lesson. Teachers are advised to preview all sites before using them with students. 7 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Note: Some Web sites contain material that is protected by copyright. Teachers should ensure that any use of material from the Web does not infringe upon the content owner's copyright. For the teacher: pictures of human-made and natural objects (be sure to include some living and some non-living things), pictures of plants and animals, pictures and labels of computer and multimedia parts, a computer, Internet websites of local plants and animals, a printer, a video of local animals and plants, a multimedia presentation device, a ready-made mobile For the students: computer for each pair of students, access to the Internet, printer for computers, straws, paper clips, pipe cleaners, tag-board, paste, scissors. Optional: publications featuring pictures of Ohio plants and animals Potential IMS linked lessons: Being Alike Is Also Really Being Different – Grade Kindergarten, Science, Life Sciences Characteristics and Structure of Life – Grade One, Science, Life Sciences Investigating Ohio’s Environment – Grade Two , Science, Life Sciences Our Grasslands – Grade Two, Science, Life Sciences Plants and Animals Around the Year – Grade Two, Science, Life Sciences Vocabulary: 1. Habitat terms field – an open land area free of woods and buildings forest – a dense growth of trees and underbrush covering a large tract habitat – the home, place or environment where a plant or animal naturally or normally lives and grows human-made – something made by people that is not naturally found in nature living – to be alive natural – something found in nature, such as wood, clay, gases non-living – something that has never been alive or part of something that was alive 2. Multimedia and information terms information – knowledge obtained from investigation, study, or instruction keyboard – set of keys which operates a machine or device monitor – a viewing screen for a computer mouse – a hand-controlled device printer – a device that will print text or graphics from a computer onto paper 8 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson 3. Mobile terms balance – when weights of the parts of a mobile are evenly distributed materials – substances that have weight and take up space (rocks, paper, liquids, air) mobile – a structure (as of paper or plastic) suspended so that it moves in a current of air CD and DVD Characteristics (of objects and living things) Computer Habitat Internet Mobile Ohio Paper clip Pipe cleaner Various animal and plant names found in Ohio Library Connections: In 2003, the State Board of Education and the Ohio Department of Education established library guidelines that represent a standards-based education approach to school library programs. Entitled Academic Content Standards K-12 Guidelines Library, Ohio’s library guidelines provide a variety of content-specific, grade-level indicators describing information literacy, literacy linked to library-based technologies, and media literacy experiences for students. Featured on pages 204-219 are sample activities for making library connections across academic content standards and disciplines. Also included are gradeband models for student research and specific information concerning copyright and fair use of materials laws. K-12 teachers are encouraged to utilize the library guidelines and collaborate with the school library media specialist (SLMS) whenever possible. Ohio’s library guidelines can be found under the heading of Library at www.ode.state.oh.us, keyword search Library. Library Guidelines Information Literacy Benchmark E Understand what information is and use a process to find information. Indicator 1 Identify what information is and recognize that it can be represented in a variety of ways (e.g., numbers, words, pictures, sounds). Indicator 2 Decide what information is needed. Indicator 3 Find the information with the assistance of the teacher or librarian (e.g., using books or observations). 9 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Indicator 4 Use the information by sharing ideas and experiences. Librarians should have books and other materials on Ohio habitats and Ohio plants and animals available for students to use for their research. Having Web sites already bookmarked would be extremely helpful. Librarians or information technology specialists may be called upon to help students learn the different names and functions of the computers and other multimedia devices being used to gather information for the lesson and how to print selected pictures. If available, the SLMS can introduce a copy machine as another man-made technological device. Make copies of animals from books to use in mobiles. This would also be a good time for the SLMS to reinforce the difference between fiction and nonfiction and show students where to find books on habitats and animals. The SLMS can act as an intervention specialist for struggling and/or gifted students. Research Connections: Marzano, R. et al. Classroom Instruction that Works: Research-based Strategies for Increasing Student Achievement. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development, 2001. 1. Identifying similarities and differences enhances students’ understanding of and ability to use knowledge. This process includes comparing, classifying, creating metaphors and creating analogies and may involve the following: Presenting students with explicit guidance in identifying similarities and differences; Asking students to independently identify similarities and differences; Representing similarities and differences in graphic or symbolic form. 2. Nonlinguistic representations help students think about and recall knowledge. This includes the following: Creating graphic representations (organizers); Making physical models; Generating mental pictures; Drawing pictures and pictographs; Engaging in kinesthetic activity. 3. Cooperative learning has a powerful effect on student learning. This type of grouping includes the following elements: Positive interdependence; Face-to-face promotive interaction; Individual and group accountability; Interpersonal and small group skills; Group processing. 4. Setting objectives and providing feedback establish a direction for learning and a way to monitor progress. This provides focus on learning targets and specific information 10 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson to allow the student to make needed adjustments during the learning process, resulting in increased student learning. Technology for All Americans Project, Measuring Progress: A Guide to Assessing Students for Technological Literacy, Reston, VA: International Technology Education Association, 2004. Standards-based student assessment supports the systematic, multi-step process of collecting evidence on student learning, understanding and abilities and using that information to inform instruction and provide feedback to the learner, thereby enhancing learning. Students should be assessed often using a variety of tools and methods. The design of student assessments should follow set principles, such as utilizing authentic assessment that provides students the opportunity to demonstrate their knowledge and abilities in real-world situations. Note: the complete publication and other resource materials are available online at the Ohio page of the ITEA Center to Advance the Teaching of Technology and Science [CATTS] web link: http://www.iteaconnect.org/EbD/CATTSresources/CATTSresourcesOH01.htm Additional Resources: Ohio Trees www.dnr.state.oh.us (Search for “Ohio Trees”) Ohio's Amphibians www.dnr.state.oh.us (Search for “Amphibians”) Animals in Ohio www.ohiohistorycentral.org (Select “Animals” under Basic Topics) A Closer Look at Wildlife www.hsus.org (Select “Wildlife” tab at top; Select “A Closer Look at Wildlife” on left margin) A First Look at Farm Animals www.hsus.org (Select “Farm Animals” tab at top; Select “First Look at Farm Animals” on left margin) Ohio Summer Wildflowers www.dnr.state.oh.us (Search for “Ohio Summer Wild Flowers”) Pictures of Ohio Animals www.dnr.state.oh.us (Search for Ohio Species) 11 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson General Tips: Search the Internet for a wildlife guide in your area. Attachments: Attachment A, Human-Made or Natural Worksheet Attachment B, Forest, Field, or Water? Attachment C, Animals Need Plants Attachment D, Parts of a Computer Worksheet Attachment E, Pre-Assessment Checklist Attachment F, Post-Assessment Rubric Attachment G, Model of a Habitat Mobile 12 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Attachment A Human-made or Natural Worksheet Photo Credits: US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration US Fish and Wildlife Service NASA 13 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Attachment B, Forest, Field, or Water? Photo Credit: US Fish and Wildlife Service 14 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Attachment C, Animals Need Plants 15 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Attachment D – Parts of a Computer Worksheet Name __________________________ ______ ______ ______ ______ 16 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Attachment E, Pre-Assessment Checklist Directions: Put a check in the box that indicates the level of the student’s ability or knowledge. Or write a brief comment in the appropriate boxes. Name ___________________Class _________________Date _____________ Task or Knowledge Mastery of Task or Knowledge Proficiency of Task or Knowledge Improvement Needed in Task or Knowledge Task or Knowledge Not Demonstrated Differentiates between natural and human-made objects Differentiates between living and non-living objects Knows the basic parts of a computer Recognize links between animals and plants in a habitat Recognizes how animals depend upon plants in a common habitat Recognizes organism’s features that helps them live in their habitat 17 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Attachment F, Post-Assessment Rubric Use the rubric as a guide to help determine each of your students’ level of skill, understanding and performance in the following criteria. The second page is a marking worksheet to calculate the final score. Skills, Understandings, and Performances Identifies natural and human-made objects 4 3 2 1 Sorts all pictures of natural and human-made things into correct groups Sorts most pictures of natural and humanmade things into correct groups Sorts some pictures of natural and humanmade things into correct groups Sorts no or few pictures of natural and humanmade things into correct groups Identifies living and non-living things Sort all pictures of living and non-living things into correct groups Identifies the monitor, keyboard, mouse and printer Name and locates a computer or multimedia technology in the classroom Names and locates computer or multimedia technology correctly with no teacher assistance Recognizes and retrieves information resources Correctly names and uses two different information sources such as library, Internet, computer, book, multimedia Sort some pictures of living and non-living things into correct groups Identifies two of the following: the monitor, keyboard, mouse and printer Names and locates computer or multimedia technology with some errors with some teacher assistance Correctly names and uses one information source such as library, Internet, computer, book, multimedia Sort no or few pictures of living and non-living things into correct groups Knows the basic parts of a computer Recognizes ways in which animals depend upon plants and each other in a common habitat Easily offers examples (without assistance) of animals which depend upon plants and each other in a common habitat Sort most pictures of living and non-living things into correct groups Identifies three of the following: the monitor, keyboard, mouse and printer Names and locates computer or multimedia technology correctly with some teacher assistance Correctly names and uses two different information sources such as library, Internet, computer, book, multimedia Offers examples other (without assistance) of animals which depend upon plants and each in a common habitat Recognizes how animals and plants survive in a habitat Easily recognizes features that help an organism survive in its habitat Names features of organisms that help them in the habitat Recognizes ways in which an animal depends upon a plant and/or other animals in a common habitat when shown a picture Tells how a given feature might help an organism in its habitat Fails to recognize ways in which an animal depends upon a plant and/or other animals in a common habitat, even when shown a picture Fails to understand how a feature might help an organism live in its habitat Identifies one or fewer of the following: the monitor, keyboard, mouse and printer Fails to name and locate computer or multimedia technology correctly even with teacher assistance Fails to use even one information source such as library, Internet, computer, book, multimedia effectively 18 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Attachment G, Model of a Habitat Mobile Mount the pictures below on tag-board or construction paper, cut them out and assemble the mobile as shown on the following page. Photo Credits: US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration US Fish and Wildlife Service 19 Habitat Mobile – Kindergarten Interdisciplinary Lesson Assembled Mobile A pipe cleaner has been inserted into the straw to add strength and stability to the mobile. 20