Exam 2 Study Guide - the Department of Psychology at Illinois State
advertisement

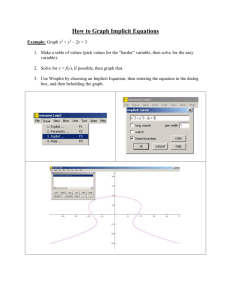
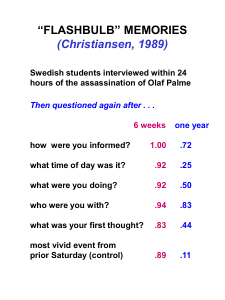
Cognitive Psychology (PSY 366) Spring 2004—Dr. Hund Exam 2 Review: Terms and Concepts Note: This is a guide, not a comprehensive list. Concepts not on the list may appear on the exam. Not all concepts on this list will appear on the exam. Exam 2 is worth 40 points. It will include 36 multiple-choice questions (1 point each) and 2 short-answer questions (2 points each). Chapter 6: Memory Acquisition and Retrieval Explicit memory: definition, examples of tasks Recall Recognition Implicit memory: definition, examples of tasks Priming Lexical decision Word stem completion Procedural knowledge Jacoby et al. (1989) How to become famous overnight study Source monitoring Processing fluency Activation account of implicit memory Multiple memory systems account of implicit memory Craik & Lockhart (1972) Levels of Processing: describe levels and types of tasks, results, role of intentionality Mnemonics: peg word, method of loci, first letter State-dependent learning (classic sea diver learning study) Retrograde amnesia Anterograde amnesia: HM and Korsakoff’s syndrome as examples Chapter 7: Memory Errors and Gaps Schema: definition, examples Selection Attention Ability to make inferences (reconstruction) Intrusion errors Factors that distort eyewitness testimony Suggestibility Source amnesia/confusion Weapon effect (Inattentional blindness) Verbal overshadowing effect Flaws in standard interviewing methods: repeated questioning, leading questions, misinformation Cognitive interview techniques Reinstate context Recall events from multiple perspectives Recall events in different orders Use open-ended questions False memory: definition, examples, Deese-Roediger-McDermott paradigm APA conclusions concerning repressed and recovered memories Causes of forgetting: decay, interference, retrieval failure (retention interval matters) Autobiographical memory Chapter 8: Long Term Memory Long term memory: limitless capacity and duration; metaphors; semantic information Serial position effects: primacy effect (LTM), recency effect (WM) How long will you remember information from this class? [see Ch. 7; Let’s hope so!] Semantic network models: main ideas—spreading activation, fan effect, Collins & Quillian (1969) Connectionist network models: main ideas—input layer, hidden layer, output layer, nodes, connections, connection weights, parallel distributed processing Acquiring memories effectively Practice Redundancy Spacing Elaboration Chapter 9: Categorization Traditional view of categories (evidence and problems) necessary and sufficient features Probabilistic views of categories (1) prototype theory (evidence and problems; Rosch; Posner & Keele) typicality effects, fuzzy boundaries, graded membership family resemblance (2) exemplar theory (evidence and problems) Theory-based view of categories [also called implicit theories in text] (evidence and problems; Keil) On-line view of categories: ad hoc categories (Barsalou), category flexibility (evidence and problems) Current ideas: mixed models Article E: Rosch (1978) Cognitive economy Three levels in the vertical hierarchy of categories subordinate basic level: What makes the basic level “basic?” superordinate Prototype Chapter 10: Language 4 components of language Phonology Semantics Syntax (can skim p. 315-324) Pragmatics Speech segmentation Categorical perception (of speech sounds) Generativity of language Aphasia Broca’s aphasia Wernicke’s aphasia Relation between language and thought Linguistic relativity Linguistic determinism (Sapir-Whorf hypothesis) Concepts/thoughts influence language Language acquisition [see lecture notes, these topics are NOT included in text] When does language emerge? Theories of language development Nativist accounts(Chomsky’s language acquisition device) Behaviorist account (Skinner) Interactionist account Word learning Quine’s problem What factors help children map words to referents? Joint focus of attention Perceptual features of objects (shape bias) Mutual exclusivity Context (syntax, infant-directed speech, prosody, prior knowledge)