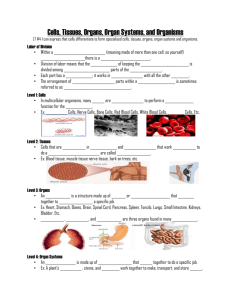
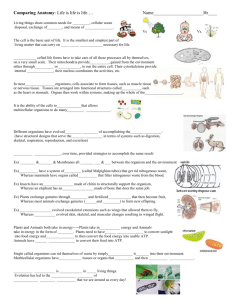
File - Mrs Morritt Science
advertisement
Biological Sciences Program 2013 Year 8 Science Understanding: Biological sciences: Multi-cellular organisms contain systems of organs that carry out specialised functions that enable them to survive and reproduce (ACSSU150) Science as Human Endeavour Scientific knowledge changes with new evidence. Scientific discoveries have changed people’s understanding of the world (ACSHE134) Science knowledge can develop through collaboration and connecting ideas across the disciplines of science(ACSHE226) Science and technology contribute to solutions to issues. They may impact on society and involve ethical considerations (ACSHE135) Science understanding influences the development of: industry, agriculture and marine and terrestrial resource management (ACSHE136) People use understanding and skills from across the disciplines of science in their occupations (ACSHE227) Scientific Inquiry Processes Identify questions and problems and make predications that can be investigated scientifically. (ACSIS139) Plan and conduct a range of investigation types, including fieldwork and experiments, ensuring safety and ethical guidelines. (ACSIS140) In fair tests, measure and control variables, and select equipment to collect data with accuracy appropriate to the task (ACSIS141) Construct and use a range of representations, including graphs, keys and models to represent and analyse patterns. (ACSIS144) Summarise data, and use scientific understanding to identify relationships and draw conclusions(ACSIS145) Evaluate the method used to investigate a question or solve a problem, including: the quality of the data. Identify improvements (ACSIS146) Use scientific knowledge and findings from investigations to evaluate claims. (ACSIS234) Communicate ideas, findings and solutions to problems using scientific language and representations using digital technologies (ACSIS148) VOCABULARY- these terms are important in conveying your understandings in the biological sciences Cell Vacuole Bladder External Fertilisation Organism Respiration Respiratory system Sperm Cell membrane Compound microscope Lung alveoli Ova Nucleus Cell specialization Capillary Pollen Cytoplasm Excretion Aquatic Ovule Mitochondria Excretory system Gill Anther Metabolism Kidney Operculum Stigma Ribosome Urea Sexual reproduction Ovary Chloroplasts Artery Asexual reproduction Seed Cell wall Vein Internal Fertilisation Vertebrate © Education Research Solutions T: 1300 669 810 E: contactus@educationresearch.com.au W: www.educationresearch.com.au This is an ERS plan and is NOT endorsed by ACARA. Green font is ACARA sourced materials. Go to: http://www.australiancurriculum.edu.au Biological Sciences Program 2013 Year 8 Cells Microscopy Classification Content Description Cells are the basic units of living things and have specialised structures and functions (ACSSU149) distinguishing plant cells from animal or fungal cells identifying structures within cells and describing their function examining a variety of cells using a light microscope, by digital technology or by viewing a simulation recognising that some organisms consist of a single cell recognising that cells reproduce via cell division describing mitosis as cell division for growth and repair Teaching Plan Homework and Assessment 6 Classification of Living Things 1. Recall that there are a number of characteristics that are associated with living things (MRS GREN) 2. Living things are classified according to their structural features 3. Recall all five Kingdoms of living things. 4. Identify the characteristics of the animal kingdom. 5. Distinguish between vertebrate and invertebrate animals and identify simple classes of invertebrates ( Poriferans, Cnidarians, Echinoderms, Annelids, Platyhelmiths, Molluscs, Nematodes and Arthropods). 6. Understand that vertebrates have a backbone and are divided into 5 main groups: Mammals, Reptiles, Birds, Fish and Amphibians. 7. Using and construct a classification key to identify living things. Reference & Questions SA1 Focus 1.4 pp17-19 SA1 Focus 4.8 pp195-201 SA1 Q4.8 p200 Practical SA1 P4.8 p200 Homework Book 4.8 Scientific Naming 4.9 Sifting and sorting Assignment Classification Poster 15% 7 Viewing Cells 8. Explain how early scientists used microscopes to extend their observations 9. Recall the main parts of a light microscope 10. Calculate magnification by reference to objective and ocular lens values 11. Use a microscope safely to observe prepared plant and animal cells and tissues and draw them scientifically. 12. Make wet mounted slides of plant tissues, observe and make scientific drawings. Reference & Questions SA1 Focus 4.1 pp161-166 SA1 Q4.1 p165 Practical SA1 P4.1 pp165-166 Homework Book 4.1 Using a Microscope 8 Single Celled Organisms 13. Identify and recall the 4 other kingdoms: Plants, Fungi, Monerans and Protists. 14. Realise there is a difference of opinion amongst scientists about how to group organisms at higher levels of classification. 15. Realize organisms can vary from unicellular to multicellular 16. Discuss single celled organisms and identify different types. 17. Understand the importance of singled celled organisms as decomposers and how they cause disease. 18. Define mitosis as a form of reproduction in single-celled organisms and growth and repair in multicellular organisms. Reference & Questions SA1 Focus 4.9 pp202-206 SA1 Q4.9 p205 Homework Book 4.10 Sorting Animals Term3 Week © Education Research Solutions T: 1300 669 810 E: contactus@educationresearch.com.au W: www.educationresearch.com.au This is an ERS plan and is NOT endorsed by ACARA. Green font is ACARA sourced materials. Go to: http://www.australiancurriculum.edu.au Animal and Plant Cells 19. Recall that cells are the basic structural unit of life 20. Describe in diagram form the features common to all cells 21. Recall the typical structure of an animal and plant cell. Terminology includes nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, vacuole, mitochondria and organelles. 22. Distinguish between an animal and a plant cell in diagrammatic form 23. Identify some observable differences between the structure of animal and plant cells Reference & Questions SA1 Focus 4.1 pp161-166 SA1 Q4.1 p165 Specialized Cells 24. Discuss how cells make up multi-cellular organisms – defining tissues, organs and systems. 25. Recognise that complex plants and animals have body systems 26. Identify systems in the human body and identify the tissues and organs that make up each system. 27. Different types of cells have different functions. 28. Examine the structure of specialized cells in familiar tissues such as kidney, muscle and nerves Reference & Questions SA1 Focus 4.6 pp184-189 SA1 Q4.8 p189 Practical SA1 P4.6 p189 Homework Book 4.6 Systems Investigation Test 25% The Musculoskeletal and Digestive Systems 29. Discuss the importance of bones and muscles and how they work together. Term4 30. Identify the organs involved in the human digestive system and recall the role and function of each component. 1 31. Compare similar digestive systems in different organisms and describe how these differences are linked to the organisms environment. Reference & Questions SA1 Focus 4.2 pp167-170 SA1 Q4.8 p169 Homework Book 4.2 Analyse this! The Respiratory and Excretory System 32. Recall that respiration occurs in every living cell (animal and plants) and sustains life 33. Describe the process of respiration in simple terms (word equation) 34. Identify the organs and overall function of the respiratory systems in a human 35. Describe the structure of the organ, tissues and specialised cells in the respiratory systems and relate its function to the overall function of the system 36. Compare similar systems in different organisms such as respiratory systems in fish and mammals and describe how these differences are linked to the organisms environment 37. Describe why lungs are unsuitable for gas exchange in water 38. Describe the structure of each organ in the excretory systems and relate its function to the overall function of the system Reference & Questions SA1 Focus 4.4 pp175-178 SA1 Q4.4 p177 Practical SA1 P4.4p178 Homework Book 4.4 Photosynthesis and Respiration Cells 9 Body Systems 10 Multi-cellular organisms contain systems of organs that carry out specialised functions that enable them to survive and reproduce (ACSSU150) identifying the organs and overall function of a system of a multicellular organism in supporting the life processes examining the specialised cells and tissues involved in structure and function of particular organs describing the structure of each organ in a 2 © Education Research Solutions T: 1300 669 810 E: contactus@educationresearch.com.au W: www.educationresearch.com.au This is an ERS plan and is NOT endorsed by ACARA. Green font is ACARA sourced materials. Go to: http://www.australiancurriculum.edu.au Body Systems Review system and relating its function to the overall function of the system comparing similar systems in different organisms such as digestive systems in herbivores and carnivores, respiratory systems in fish and mammals distinguishing between asexual and sexual reproduction comparing reproductive systems of organisms 3 4 The Reproductive System 39. Recall importance of reproduction methods in order to survive. 40. Distinguish between sexual and asexual reproduction. 41. State the lack of variation in offspring produced via asexual reproduction 42. Describe that sexual reproduction increases variation 43. Compare the structures involved in sexual reproduction for flowering plants and vertebrates 44. Examine the organs involved in the male and female human reproduction systems. 45. Examine the development of a child from fertilization to birth. 46. Compare similarities of plant repro parts to animal repro parts. Asexual reproduction in plants Reference & Questions SA1 Focus 4.5 pp179-183 SA1 Q4.8 pp182-183 Practical SA1 P4.5 p183 Homework Book 4.5 Strange Plant Sex Investigation Test 25% Revision and Reveiw Homework Book 4.11 Crossword 4.12 Sci-words Topic Test 25% 5 TEXT REFERENCES AND RESOURCES Student text: Science Aspects Book 1 (SA1) Homework activities: Science Aspects Homework Book 1 Year 8 Biology Assessment schedule 2013 Homework, class participation and quizzes (ongoing) Classification Poster (Term 3) Second hand data investigation test (Term 3 Week 10) End of Topic Biology Test (Term 4 Week 5) 10% 15% 25% 25% © Education Research Solutions T: 1300 669 810 E: contactus@educationresearch.com.au W: www.educationresearch.com.au This is an ERS plan and is NOT endorsed by ACARA. Green font is ACARA sourced materials. Go to: http://www.australiancurriculum.edu.au