Chapter 2: The Earliest Human Societies pp
advertisement

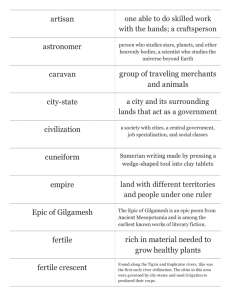
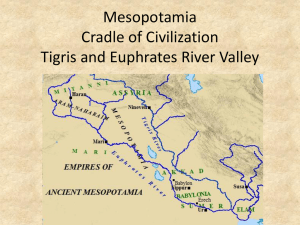
Chapter 3: Ancient Mesopotamia pp.78-107 Lesson 1: “Geography of Mesopotamia” pp.83-86 Key Terms & People: 1. Mesopotamia 2. floodplain 3. silt 4. semiarid 5. drought 6. surplus I Mesopotamia “land between the rivers” A. In Southeast Asia between 2 rivers 1. 2. a. start in mountains of b. flow through to B. Harsh environment with semiarid climate 1. Hot summers with little rain 2. Able to plant crops because of river valley a. rivers b. rivers II. Irrigation A. Unpredictable yearly floods 1. No reliable planting season starvation 3. By 6,000 B.C. farmers built irrigation system using canals a. III. Resources A. Area had few natural resources 1. Built with a. 2. Few mountains or natural barriers a. b. B. Traded for natural resources 1. C. Some jobs needed to be done continuously 1. Community leaders organized workers and projects Lesson 2: “The First Civilization” pp.88-95 Key Terms & People: 1. civilization 2. Sumer 3. city-state 4. ziggurat 5. polytheism 6. king I Rise of Civilization A. Agriculture Villages/Cities Civilization 1. Leadership was needed a. organize and lead public projects i 2. Leadership/ government + complex culture = a. 1st civilization = Sumer ~3300 B.C. B. Five Traits of Civilization 1. Advanced Cities a. advantages i 2. Specialized Workers a. specialization b. specialization 3. Complex Institutions a. examples: b. purpose: 4. Record Keeping a. keep track of details b. often involves 5. Advanced Technology a. society advances with technology b. Sumerians had many advances i ii II Sumerian City-States A. Advantages of cities & city-states 1. Cities: centers for 2. Cities ruled surrounding farmlands/villages (city-state) B. Sumerian city-states 1. Kish, Nippur, & Ur among others 2. Houses a. several rooms around a courtyard i 3. Ziggurat: City Center a. temple/center for city life i ii iii III Changes in Leadership A. Sumerian Religion 1. Polytheistic: many gods and goddesses a. 4 main gods created and ruled world i 2. Each city-state 3. Thousands of lesser gods 4. Gods looked and acted like people 5. Thought gods controlled weather, land etc… a. everyone made offerings to gods b. rituals often in ziggurat 6. After death souls went to land of no return B. Priests 1. Politicians and religious leaders 2. Priests claimed influence over gods 3. Lead city and ran public projects a. rich lives of Sumerians b. times of war c. new leaders took over priests’ job of ruling d. Sumer became a kingdom under 1 king 2375 B.C. e. priests job: Lesson 3: “Life in Sumer” pp.98-103 Key Terms & People: 1. bronze 2. pictograph 3. stylus 4. cuneiform 5. scribe I Sumerian Society: Social Classes A. Social groups/unequal classes that define power 1. King & priests at top of Sumerian upper classes a. Kings & priests had link to gods b. Others in upper class: 2. In-between classes had most people a. Class included 3. Lowest classes = slaves a. Slaves were: b. Slaves’ rights: 4. Women were in all social classes a. Upper class women could be priestesses b. Free women could: c. Main role - to raise children II. Sumerian Science & Technology A. Early Inventions 1. a. 2. a. 3. a. 4. a. b. B. Math developed to record crops & trade goods 1. a. b. 2. Used geometric shapes in building a. III. Sumerian’s Created 1st Written Language A. They needed to label goods and record trades B. Pictures stood for objects, then ideas, then sounds 1. Combined sounds to write more words 2. Sumerian writing = cuneiform – wedge-shaped writing a. Used stylus on clay tablets b. 600 different symbols c. Few people could read and write (very difficult) d. Scribes/professional record keepers studied for years 3. Written history from Sumer a. b. Chapter 4: Early Empires pp.108-123 Lesson 1: “Mesopotamian Empires” pp.112-116 Key Terms & People: 1. empire 2. emperor 3. Fertile Crescent 4. Hammurabi 5. code of law 6. justice I First Empires A. Akkadian Empire 1. Sargon of Akkad took control of Mesopotamia 2350 B.C. a. Fertile Crescent region 2. Empire spread Akkadian way of life a. 3. Empires change the way people live a. b. 4. Empire lasted 200 years a. empire fell apart i. ii. B. Babylonian Empire 1. Amorites invaded a. chose Babylon for their capital 2. Hammurabi: Amorite King ruled Babylonian Empire a. b. c. d. C. Hammurabi’s Code of Law 1. Hammurabi ruled a large empire a. needed a set of rules for all of his people 2. Code of Law a. i b. goal bring justice to people c. code gave rights & punishments i. women & children were given rights ii. punishments differed by social class D. Hammurabi’s Legacy 1. Code government provide a. b. c. Lesson 2: “Assyria Rules the Fertile Crescent” pp.118-123 Key Terms & People: 1. exile 2. tribute 3. Hanging Gardens of Babylon I Assyria Ruled After Babylonian Empire Fell A. Assyria in hilly northern Mesopotamia 1. Built up army to Assyria and a. b. c. 2. Assyrians: cruel and feared conquerors a. killed inhabitants sent people into exile b. burned Babylon c. enemies who surrendered i. no surrender d. enemy leaders other lands II Assyria Built an Empire A. Huge & well-organized empire 1. Native kings or governors ruled conquered lands a. conquered lands sent tribute to emperor i. tribute = iii. no tribute = b. Assyrians dealt with many revolts C. Assyrian Empire Fell 609 B.C. 1. III Chaldean/New Babylonian Empire A. Chaldeans took over most of the Assyrian Empire 1. Babylon became capital 2. Led by Nebuchadnezzar II a. Hebrews rebelled 598 B.C. b. seized Jerusalem, capital, and destroyed the Hebrew sacred temple c. Hebrews held captive in Babylon ~50 years 3. Nebuchadnezzar II rebuilt Babylon a. built Ishtar Gate, & Tower of Babel b. Hanging Gardens of Babylon i. one of 7 Wonders of the World B. Fall of the Empire 1. Weak rulers followed Nebuchadnezzar II 2. Internal conflict over religion 3. Conquered by Cyrus of Persia