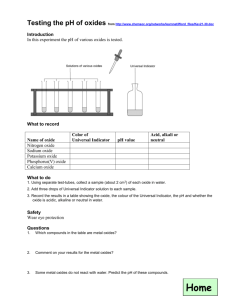
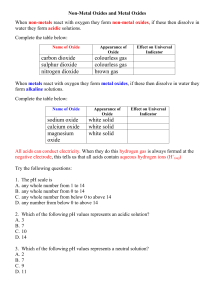
Students should be able to - Dover College Science
advertisement

A2 CHEMISTRY NOTES - Periodicity Trends in Period 3 Elements Element Na Mg Al Si P4 S8 Ar Structure Bonds Melting Points Boiling Points Atomic Radii Reactions of Sodium and Magnesium with water Sodium Sodium has a very exothermic reaction with cold water producing hydrogen gas and a colourless solution of sodium hydroxide 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) NaOH(aq) + H2(g) Magnesium Magnesium has a very slight reaction with cold water, but burns in steam. A clean coil of magnesium dropped into cold water eventually gets covered in small bubbles of ___________ gas which float it to the surface. Magnesium __________ is formed as a very thin layer on the magnesium and this tends to stop the reaction. Mg(s) + 2H2O(l) Mg(OH)2 (aq) + H2(g) Magnesium burns in steam with its typical _______ flame to produce white magnesium oxide and hydrogen. Mg(s) + H2O(g) MgO (aq) + H2(g) 1 A2 CHEMISTRY NOTES - Periodicity Reactions of Sodium to Sulphur with Oxygen Sodium Sodium burns in oxygen with an _________ flame to produce a white solid mixture of sodium oxide. 4Na(s) + O2(g) 2Na2O(s) Magnesium Magnesium burns in oxygen with an intense ______ flame to give white solid magnesium oxide. 2Mg(s) + O2(g) 2MgO(s) Aluminium Aluminium will burn in oxygen if it is powdered, otherwise the strong oxide layer on the aluminium tends to inhibit the reaction. If you sprinkle aluminium powder into a Bunsen flame, you get white sparkles. White aluminium _______ is formed. 4Al(s) + 3O2(g) 2Al2O3 (s) Silicon Silicon will burn in oxygen if heated strongly enough. Silicon dioxide is produced. Si(s) + O2(g) SiO2 (s) Phosphorus White phosphorus catches fire spontaneously in air, burning with a white flame and producing clouds of white smoke - a mixture of phosphorus(III) oxide and phosphorus(V) oxide. In an excess of oxygen, the product will be almost entirely phosphorus(V) oxide. P4(s) + 5O2(g) P4O10 (s) Sulphur Sulphur burns in air or oxygen on gentle heating with a pale ______ flame. It produces colourless sulphur dioxide gas. S(s) + O2(g) SO2 (g) Chlorine and argon Despite having several oxides, chlorine won't react directly with oxygen. Argon doesn't react either. 2 A2 CHEMISTRY NOTES - Periodicity The oxides of Sodium to Sulphur A quick summary of the trends The oxides we'll be looking at are: Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 P4O10 SO3 (Cl2O7) These oxides are known as the _________ oxides of the various elements, where the elements are in their highest ____________ states. In these oxides, all the outer electrons in the Period 3 element are being involved in the _________ - from just the ____ with sodium, to all ________ of chlorine's outer electrons. The structures The trend in structure is from the metallic oxides containing giant structures of _____ on the left of the period via a giant _________ oxide (silicon dioxide) in the middle to ___________ oxides on the right. Melting and boiling points The giant structures (the metal oxides and silicon dioxide) will have _____ melting and boiling points because a lot of ________ is needed to break the strong bonds (ionic or covalent). The oxides of phosphorus, sulphur and chlorine consist of individual _________ - some small and simple. The attractive forces between these molecules will be __ ___ _____ and _______-_______ interactions. These vary in size depending on the ____, ____ and _________ of the various molecules - but will always be much weaker than the ionic or covalent bonds you need to break in a giant structure. These oxides tend to be _______, liquids or low melting point solids. Electrical conductivity None of these oxides has any free or mobile _________. That means that none of them will conduct electricity when they are ______. The ionic oxides can, however, undergo electrolysis when they are molten. They can conduct electricity because of the movement of the ______ towards the electrodes and the discharge of the _____ when they get there. 3 A2 CHEMISTRY NOTES - Periodicity The metallic oxides The structures Sodium, magnesium and aluminium oxides consist of ______ structures containing metal ions and oxide _____. Magnesium oxide has a structure just like sodium chloride. There are strong attractions between the ____ in each of these oxides and these attractions need a lot of heat energy to break. These oxides therefore have high melting and boiling points. Electrical conductivity None of these conducts electricity in the solid state, but ________ is possible if they are molten. They conduct electricity because of the movement of the ______ present. Giant Covalent Oxide (Silicon dioxide) The structure There isn't enough electronegativity difference between the silicon and the oxygen to form an ionic bond. Silicon dioxide is a giant ________ structure. Crystalline silicon has the same structure as _________. Melting and boiling points Silicon dioxide has a high melting point, around _______°C. Very strong silicon-oxygen covalent bonds have to be broken throughout the structure before melting occurs. Silicon dioxide boils at _______°C. Electrical conductivity Silicon dioxide doesn't have any mobile electrons or ions - so it doesn't conduct ___________ either as a solid or a liquid. 4 A2 CHEMISTRY NOTES - Periodicity The molecular oxides Phosphorus, sulphur and chlorine all form oxides which consist of _________. Melting and boiling points of these oxides will be much _____ than those of the metal oxides or silicon dioxide. The intermolecular forces holding one molecule to its neighbours will be ___ ____ ________ forces or ________________ interactions. The strength of these will vary depending on the ______ of the molecules. None of these oxides conducts electricity either as solids or as liquids. None of them contains _____ or free _____________. Phosphorus(V) oxide Phosphorus(V) oxide (P4O10) has a large formula ______ and so the ___ ___ _______ bonds between molecules are relatively _______ This makes it is a solid at room temperature subliming at _____°C. . Sulphur oxides Sulphur has two common oxides, sulphur (__) oxide, SO2, and sulphur(__) oxide), SO3 but again we will only be looking at the highest oxide. Sulphur trioxide Pure sulphur trioxide is a white solid with a ____ melting and boiling point. It reacts very rapidly with water vapour in the air to form _________ acid. Gaseous sulphur trioxide consists of simple SO3 molecules in which all ____ of the sulphur's outer electrons are involved in the bonding. There are various forms of solid sulphur trioxide. The simplest one is a _______, S3O9, where _______ SO3 molecules are joined up and arranged in a ring. The ___ ____ _______ forces are weaker than those in P4O10 and so sulphur trioxde is a ________ at room temperature 5 A2 CHEMISTRY NOTES - Periodicity Property Formula Oxide Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 P4O10 SO2 Particles Bonding Structure Forces between particles Melting point Boiling point Electrical conductivity pH in water 6 SO3 A2 CHEMISTRY NOTES - Periodicity The trend in acid-base behaviour The trend in acid-base behaviour is shown in various reactions, but as a simple summary: The trend is from strongly _______ oxides on the left-hand side to strongly ________ ones on the right, via an ___________ oxide (aluminium oxide) in the middle. An _______ oxide is one which shows both ______ and _____ properties. Sodium oxide Sodium oxide is a simple strongly ______ oxide. It is basic because it contains the oxide ion, O2-, which is a very strong base with a high tendency to combine with _______ ions. Reaction with water Sodium oxide reacts exothermically with cold water to produce sodium ________ solution. Depending on its concentration, this will have a pH around ____. Na2O (s) + H2O(l) 2NaOH (l) Reaction with acids As a strong base, sodium oxide also reacts with acids. For example, it would react with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce sodium _________ solution. Na2O (s) + 2HCl(aq) 2NaCl (aq) + H2O(l) Magnesium oxide Magnesium oxide is again a simple _____ oxide, because it also contains oxide ions. However, it isn't as strongly basic as sodium oxide because the oxide ions aren't so free. It takes more energy to break the attractions between 2+ and 2-. Even allowing for other factors (like the energy released when the positive ions form attractions with water in the solution formed), the net effect of this is that reactions involving magnesium oxide will always be less ___________ than those of sodium oxide. Reaction with water Magnesium oxide doesn’t appear to react with water, however, if you test the pH of the liquid, you find that it is somewhere around pH 9 - showing that it is slightly ________. There must be some slight reaction with the water to produce hydroxide ions in solution. Some magnesium hydroxide is formed in the reaction, but this is almost insoluble - and so not many hydroxide ions actually get into solution. MgO(s) + H2O(l) Mg(OH)2(aq) Reaction with acids Magnesium oxide reacts with acids as you would expect any simple metal oxide to react. It would react with warm dilute hydrochloric acid to give magnesium _______ solution. MgO(s) + HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H2O(l) 7 A2 CHEMISTRY NOTES - Periodicity Aluminium oxide Aluminium oxide is ____________. It has reactions as both a _____ and an _____. Reaction with water Aluminium oxide doesn't react in a simple way with water in the sense that sodium oxide and magnesium oxide do, and doesn't dissolve in it. Although it still contains oxide ions, they are held too ____________ in the solid lattice to react with the water. Reaction with acids Aluminium oxide contains oxide ions and so reacts with _______ in the same way as sodium or magnesium oxides. That means, for example, that aluminium oxide will react with hot dilute hydrochloric acid to give aluminium _________ solution. l2O3(s) + 6HCl(aq) 2AlCl3(aq) + 3H2O(l) In this (and similar reactions with other acids), aluminium oxide is showing the ______ side of its amphoteric nature. Reaction with bases Aluminium oxide has also got an acidic side to its nature, and it shows this by reacting with bases such as sodium hydroxide solution. With hot, concentrated sodium hydroxide solution, aluminium oxide reacts to give a colourless solution of sodium tetrahydroxoaluminate. Al2O3 (s) + 2NaOH(aq) + 3H2O(l) 2NaAl(OH)4 (aq) Silicon dioxide (silicon(IV) oxide) By the time you get to silicon, electronegativity has increased so that there is no longer enough electronegativity difference between silicon and oxygen to form ______ bonds. Silicon dioxide has no basic properties - it doesn't contain oxide ions and it doesn't react with acids. Instead, it is very weakly acidic, reacting with strong bases. Reaction with water Silicon dioxide doesn't react with water, because of the difficulty of breaking up the giant covalent structure. Reaction with bases Silicon dioxide reacts with sodium hydroxide solution, but only if it is hot and concentrated. A colourless solution of sodium silicate is formed. SiO2(aq) + 2NaOH Na2SiO3(aq)+ H2O(l) 8 A2 CHEMISTRY NOTES - Periodicity Phosphorus(V) oxide Reaction with water Phosphorus(V) oxide reacts violently with water to give a solution containing a mixture of acids, the nature of which depends on the conditions. We usually just consider one of these, phosphoric(_) acid, H3PO4 - also known just as phosphoric acid. Reaction with bases Phosphoric(V) acid is also a weak acid with a pKa of 2.15. Acids of concentrations around 1 mol dm-3 will have a pH of about 1. It has __ OH groups, and each of these has an acidic hydrogen atom. If you were to react phosphorus(V) oxide directly with sodium hydroxide solution rather than making the acid first, you would end up with the same product. Sulphur trioxide Sulphur trioxide reacts violently with water to produce a fog of concentrated ____________ acid droplets. Pure un-ionised sulphuric acid has the structure shown. Sulphuric acid is a strong acid, and solutions will typically have pH's of around __. Sulphuric acid, of course, has all the reactions of a strong acid that you are familiar with. For example, the normal reaction with sodium hydroxide solution is to form sodium sulphate solution - in which both of the acidic hydrogens react with hydroxide ions. Sulphur trioxide itself will also react directly with bases to form sulphates. For example, it will react with calcium oxide to form calcium sulphate. This is just like the reaction with sulphur dioxide described above. 9 A2 CHEMISTRY NOTES - Periodicity Oxide Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 P4O10 SO2 SO3 Typical pH Structure Bonding Nature of Oxide 10