Surveying I
advertisement

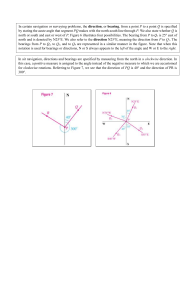
POKHARA UNIVERSITY Level: Bachelor Programme: BE Course: Surveying I Semester – Fall Year : 2005 Full Marks: 100 Time : 3hrs. Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Attempt all the questions. 1. a) What are the primary divisions of surveying? Explain the principles of surveying with suitable examples. 6 b) A field was surveyed with a 30m chain and its area was found to be 25.35 hectares. If it was found that the chain was 75 mm too long. Find the correct area of the field. 9 2. Explain various corrections applied in linear measurement. What correction in m must be applied per 100 m length of a line measured along a slope of i) 50 ii) 30. 15 3. a) What are the methods of designating the bearings? Explain briefly. 6 The following all the magnetic bearings of a closed travers ABCD, carried out in an area uncles the influence of local attraction. 9 4. Explain "two peg test" method of collimation adjustment. The following consecutive reading we taken with a dumpy level: 15 b) 3.864, 3.346, 2.932, 1.952, 0.854, 3.796, 2.639, 1.542,1.934, 0.864, 0.665. The level wad shifted after the fifth and the eighth readings. The first reading was taken an a bench mark of R.L. 150.250. Calculate the reduced levels of the change points, and the difference of level between the first and test points. 5. a) What are the field measurements necessary in theodolite traversing? Explain campass rule for balancing the traverse. 6 b) The following data refer to a closed traverse ABCDE. Find the length of the sodes DE and EA. Length in m Bearing 778.50 77030' 649.00 337030' 660.50 284048' ? 231006' ? 135040' 9 Line AB BC CD DE EA 6. a) b) Explain any one method of analytical resection. 6 Write the methods of plane table survey. 9 7. Write short notes on (any two): a) Triangulation and trilatution b) Reciprocal trigonometrical levelling c) Three point problem in P.T. survey 52