Course number
advertisement
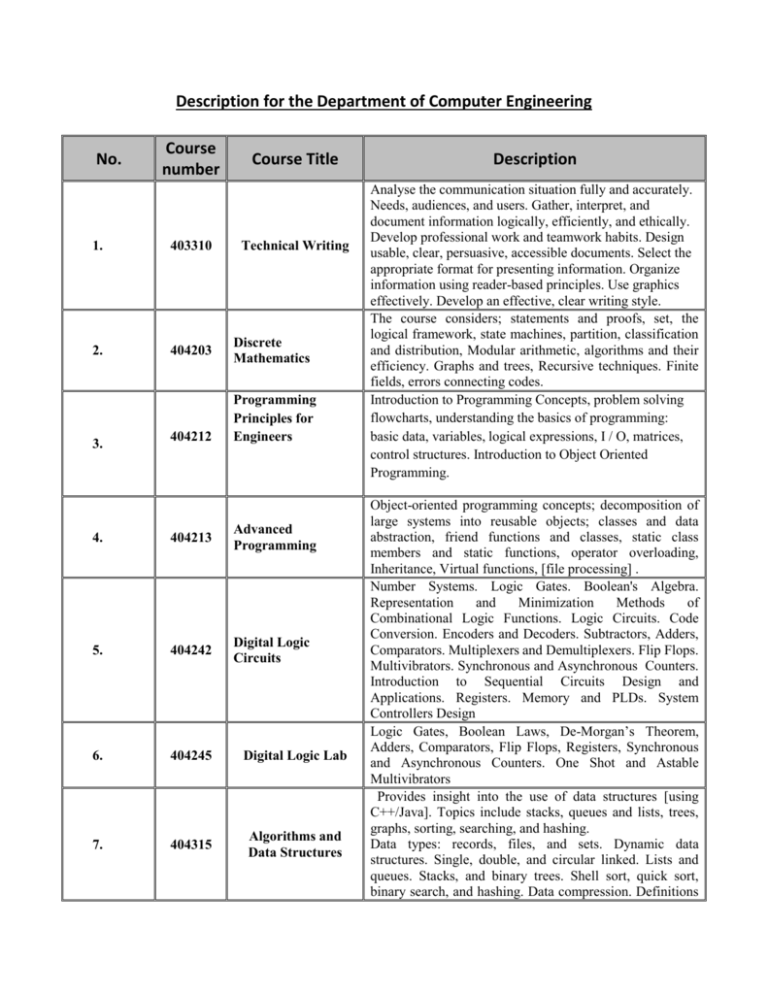
Description for the Department of Computer Engineering No. Course number 1. 403310 2. 202404 3. 404212 Course Title Technical Writing Discrete Mathematics Programming Principles for Engineers 4. 202404 Advanced Programming 5. 202424 Digital Logic Circuits 6. 202424 Digital Logic Lab 7. 404315 Algorithms and Data Structures Description Analyse the communication situation fully and accurately. Needs, audiences, and users. Gather, interpret, and document information logically, efficiently, and ethically. Develop professional work and teamwork habits. Design usable, clear, persuasive, accessible documents. Select the appropriate format for presenting information. Organize information using reader-based principles. Use graphics effectively. Develop an effective, clear writing style. The course considers; statements and proofs, set, the logical framework, state machines, partition, classification and distribution, Modular arithmetic, algorithms and their efficiency. Graphs and trees, Recursive techniques. Finite fields, errors connecting codes. Introduction to Programming Concepts, problem solving flowcharts, understanding the basics of programming: basic data, variables, logical expressions, I / O, matrices, control structures. Introduction to Object Oriented Programming. Object-oriented programming concepts; decomposition of large systems into reusable objects; classes and data abstraction, friend functions and classes, static class members and static functions, operator overloading, Inheritance, Virtual functions, [file processing] . Number Systems. Logic Gates. Boolean's Algebra. Representation and Minimization Methods of Combinational Logic Functions. Logic Circuits. Code Conversion. Encoders and Decoders. Subtractors, Adders, Comparators. Multiplexers and Demultiplexers. Flip Flops. Multivibrators. Synchronous and Asynchronous Counters. Introduction to Sequential Circuits Design and Applications. Registers. Memory and PLDs. System Controllers Design Logic Gates, Boolean Laws, De-Morgan’s Theorem, Adders, Comparators, Flip Flops, Registers, Synchronous and Asynchronous Counters. One Shot and Astable Multivibrators Provides insight into the use of data structures [using C++/Java]. Topics include stacks, queues and lists, trees, graphs, sorting, searching, and hashing. Data types: records, files, and sets. Dynamic data structures. Single, double, and circular linked. Lists and queues. Stacks, and binary trees. Shell sort, quick sort, binary search, and hashing. Data compression. Definitions 8. 9. 10. 204404 202424 202424 Programming Lab for Electrical Engineering Microprocessors and Assembly Languages Microprocessor Lab 11. 202444 Operating Systems 12. 202224 Advanced Logic Circuits Design 13. 202224 Advanced Logic Circuits Lab 14. 404547 Computer Organization and Parallel Processing Lab 15. 202240 Communications Engineering for of algorithms. Design & analysis of algorithms: Divide and conquer, Greedy algorithm. Dynamics programming. Backtracking. Branch and bound technique. NP-hard and NP-complete problems. Matlab: Introduction to Matlab, Matrix Operations, Strings, Systems of Linear Equations, Numerical methods, Graphics, Programming in Matlab, Toolboxes. Electrical and Electronics Circuits Simulations: Simulation of DC and AC Circuits, Frequency Response, Digital Circuits, Hybrid Circuits. Microprocessor Architecture and Organization, Timing, System Bus, External Memories Interfacing, Instruction Types and Formats, Addressing Modes, Programming Techniques, Timing Loops, Address Decoding, Signal Conditioning, Serial and Parallel Interface, Polled and Priority Interrupted Driven I/O Techniques, Real Time Systems. Arithmetic and Logic Operations, Bits Manipulation, Moving/Searching/Sorting data blocks, Time Loops Applications, Real Time System Applications. Operating system concepts; I/O programming; interrupt structure and processing; operating system interface (system calls); process management (scheduling and synchronization); memory management (partitioned, relocatable, paged, demand-paged, segmented, segmentedand-paged); file management; device management; sample operating system. Real time operating systems. Review of conventional logic design techniques; ASM design, introduction to Hardware Description Language (HDL), Design of behavioral models of combinational and sequential logic, synthesis of combinational and sequential logic, design and synthesis of data path and controllers. PLA, PLC, FPGA, and ASIC Introduction to standard cell design of VLSI digital circuits using hardware description language (HDL). Emphasis on how to write HDL modules that will map readily to hardware. Laboratory experiments using commercial grade computer-aided design (CAD) tools for HDL-based design, schematic-based logic entry, logic and HDL simulation, automatic placement and routing, timing analysis, and testing. [Note: once the FPGA boards are available, all the modules will be implemented]. Provide the student practical experiments to recognize various component of PC. The basic components of a PC are 1. Input Unit, 2. Output unit, 3. Memory unit,4. Control unit, 5. Arithmetic and logic unit. In both serial and parallel processing applications. Review of Fundamental Concepts: probability theory, random processes, autocorrelation and power spectrum Computers 16. 202404 Visual Programming 17. 202440 Database Systems 18. 202444 Data Communications 19. 202444 Computer Networks density, Fourier analysis of signals and systems. Analog versus Digital, Digital Communication System (DCS), Discrete Memory-less Channel (DNC), Information Theory, Source Coding, Huffman Coding, Channel Capacity, Channel Coding theorem. Band-pass Modulations and their Computer Simulations (like MATLAB simulator): BPSK, QPSK, M-ary PSK, OFDM, CCK. Soft and Hard Decisions, Error Control Coding, Viterbi Decoding, Trellis Coded modulation (TCM). Using Computer Programs like MATLAB to Simulate Digital Communications System for several modulation techniques. Advanced tools for the programming of object oriented visual applications; principles and main features of a few popular visual programming tools including GUI, API, and event handling. A set of laboratory experiments will provide hands-on experience in related topics. Access methods and file systems to facilitate data access. Hierarchical, network, relational, and object-oriented data models. Query languages for models. Embedding query languages in programming languages. Database services including protection, integrity control, and alternative views of data. High-level interfaces including application generators, browsers, and report writers. Introduction to transaction processing. Database system implementation to be done as term project. Introduction to Data Communications, Analog and Digital Signals, Data Encoding: D/D, D/A, A/A and A/D, Parallel and Serial Transmissions, Interfaces, Simplex, Duplex, Modems, and Modulation Methods. Communication Media: Types and Standards, Multiplexing, Access Techniques: TDMA, FDMA, CDMA, Spread Spectrum, Direct Sequence and Frequency Hopping. Introduction to TCP/IP, Local Area Networks (LAN), Wide Area Networks (WAN) and Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN). Network architectures; OSI model; communication protocols; network topologies; local area networks; internetworking devices; high-speed bridged networks; wide area networks; introduction to Internet and TCP/IP, introduction to ISDN, DSL, and ATM networks. Highspeed local networks; metropolitan area networks; bridges; routers; gateways; TCP/IP; application services; IP addressing; IP forwarding, encapsulation, and fragmentation; Address Resolution (ARP& RARP); IP next generation (IPvx); [Inter Control Message Protocol (ICMP)]. 404536 20. Networks Protocols Open standard for networks with seven classes, information link layer protocols, network layer protocols, transport layer protocols, the session layer protocols, the presentation layer protocols, application layer protocols. This is through a review of the following: OSI, IEEE802, HDLC, X.25, IP, ICMP, ARP, TCP, UDP, HTTP, FTP, SMTP, ISDN, ADSL, ATM, DNS, VOIP, QoS, PPP, SSL, Telnet, Routing Protocols, Congestion Control Protocols, Wireless Network Protocols. 21. 202444 Computer Networks Lab 22. 202420 Computer Organization and Design 23. 202422 Embedded Systems 24. 202424 Parallel Processors The lab teaches the fundamentals of computer networks. Topics include but not limited to: how to achieve reliable/secure communications, how to find a good path through a network, how to share network resources among competing entities, how to find an object in the network, and how to build network applications. The lab offers an integrated educational process in the field of computer networks, emphasizing the issue of networks, their design, protocols & layering, administration and management. Evolution Eras. Computer Generations and Classifications. Architecture Examples. Fast Adders. Multiplication and Division Algorithms. Fixed and Floating Point Arithmetic. Synchronous, Delay Elements, Microprogrammed and Nanoprogrammed Based Control Units. Microinstruction Types. RISC Machines. Memory Types and Organization. Input/Output Systems. Introduction to Parallel and Pipelined Processors. Term project. Design of computing systems that are embedded in a larger system such as communication and control systems; design aspects of embedded systems; architectures, microcontrollers, data formats, memory hierarchy, I/O, timers and exceptions, interfacing, and data acquisition; embedded operating systems and device drivers Introduction to parallel processing; system bandwidth, parallelism in uni-processor system, parallel computer architecture and classifications (SISD, SIMD, MISD, MIMD), memory and I/O subsystems for parallel processors (multi-port, interleaved memory, data organization). Principle of pipelining and vectorization. Pipeline and vector computer. Switching and interconnection circuits. Synchronization: global operations, mutual exclusion, and events. Array processor (SIMD). Multiprocessor architecture. Parallel programming models, communication primitives, Task scheduling, Multitasking and multithreading. Network design: topology, packaging, k-ary n-cubes, performance under contention. 25. 202404 Project (1) Graduation Project 26. 202402 Project (2) 27. 404500 Engineering Training Continuation of the Graduation Project(1). The training engineering by (320) hours of actual, and begins after performing the student successfully close (90) credit hours, and the training is at once connected, and can if necessary, divide it in two shifts to be not less than the period from one (120) hours of work 28. 29. 30. 204444 204444 204444 Engineering Mathematics and Analysis (1) Engineering Mathematics and Analysis (2) Engineering Mathematics and Analysis (3) Basic concepts of n- dimension vectors, Real vector space and subspaces, Linear independency, Algebra of linear transformation, Matrices Notations, Arithmetic Operations on matrices, Calculation with partitioned matrices, Scalarvalued functions on matrices, Raw Equivalence and linear systems, Matrix inverses using elementary row operation, The nature of solving linear algebraic equations, Eigenvalue and Eigenvector problem, Cayley-Hamilton theorem, Companion matrices, computational techniques, Introduction to statistics; arithmetic and geometric means – medium - variance – correlation and auto-correlation – Linear regression - experiment tests. DE in engineering problems an introduction of modeling, DE classification, First-order ordinary DE; variable separable- exact and reducible to exact- linear, reduction of order techniques, Second-order DE of constant coefficients, higher-order DE; the Wornskain- method of undetermined coefficients- variation of parameters, System of linear DE; fundamental matrix- constant coefficient case, matrix exponential, Variable coefficient and solution in series form, Special 2nd-order homogenous DE, Bessel’s equation and equations reduced to Bessel’s, Partial DE; the first and second-order homogenous- the general formLaplace, wave and heat equations- general concept of solution – application in wave propagation of electromagnetic wave. Time-domain and frequency-domain concepts, Fourier series and concepts of signal analysis, Fourier transform; definition - FT of finite and infinite energy functions - FT properties – AM modulation representation using FT introduction to discrete FT, Laplace transformation; definition – transformation of elementary functions – Laplace inverse – theorems and their use in obtaining LT and inverse LT of complicated functions - solution of DE using LT – the concept of transfer function, The ztransform; concepts of discrete functions – sampling theorem – relation between LT and z-transform, ztransform of elementary functions and discrete transfer function, Introduction to partial z-transform 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 204444 Engineering Mathematics and Analysis (4) 204400 Electrical Circuits (1) 204404 Electrical Circuits (2) 402219 204444 Electrical circuits lab Electronics (1) Review of vectors in space and basic computation, Triple scalar product and its application, Vector functions definition, Coordinate systems, Ordinary and partial differentiation of vectors; rules – computation and applications, Gradient, divergence, and curl operations and their interpreting in engineering. Integration of vector function; rules – computation and applications – line, surface and volume integrals – Green, Gauss and Stock theorems, Review of complex numbers and algebraic computation, Complex variable functions, Complex planes, Analyticity of complex function; transformation between different representation - continuity – limit – differentiation and integration concepts, Computation of elementary function of complex number, series in complex variable, residual theorem and its application for integration computation Volt-Amper Characteristics for Circuits Elements; Independent and Dependent Sources; Kickoff's Laws and Circuits Equations. Source Transformation; Thevenin’s and Norton’s Theorems; Superposition. Transient Response of RC, RL and RLC Circuits. AC circuits, impedance concept, AC Steady State analysis. Instantaneous and Average Power, Polyphase Circuits, Complex Frequency, Frequency Response, Resonance, Magnetically Coupled Circuits, Two port Networks, use of Laplace transform techniques to analyze linear circuits. Introduction to Filter Synthesis. DC circuits. Kirchhoff's voltage law and Kirchhoff's law of the stream. Theories of networks. The concept of resistance and inductance. Capacity and resonance The p-n junction. Diodes and applications. Special diodes. Bipolar Junction Transistors. Characteristics, Biasing, and Circuits. Field-Effect Transistors (JFETs and MOSFETs). Modes, Characteristics, Biasing and Circuits. Introduction to Operational amplifiers. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 204402 Numerical Methods 204404 Probability & Random Signals 204444 Systems & Signals Processing 204440 Electromagnetic (1) 204444 Electronics (2) 204442 Digital Electronics 204444 Electronics Lab 204440 Digital Electronics Lab 204420 Digital Communication Preliminaries, Solution of Nonlinear Equations, Solution of Systems of Linear Equations, Interpolation and Polynomials Approximation, Curve Fitting: Least Square Method, Numerical Differentiation, Numerical Integration, Solution of Ordinary and Partial Differential Equations Sampling, average and variance, discrete and continuous distribution, types of various distributions. An introductory treatment of probability theory including distribution and density functions, moments and random variables. Applications of normal and exponential distributions. Estimation of means, variance. Correlation and special density functions. Random processes and response of linear systems to random inputs. Types of Signals and Systems, Energy and Power Signals. Fourier Series and Transform. Time and Frequency Power Bandwidth Relation. Linear System Signals. Convolution and Impulse Response. Time and Spectrum Density Relation. Fast Fourier Transform. Separated Linear Systems. Z-Transform Review of Vector Operations and Coordinate Systems. Coulomb's Law and Electric Field Intensity. Electric Flux Density. Gauss's Law and Divergence. Boundary Conditions. Steady Electric Current. Magnetic Field Density. Stock's Theory. Magnetic Vector Potential. Inductance. Static Magnetic Fields of Ferromagnetic Materials and Magnetic Circuits. Introduction to Time Varying Fields. Small-Signal amplifiers and applications. Multistage amplifiers. Power amplifiers and applications. Frequency Response of amplifiers. Feedback Amplifiers. Operational Amplifiers applications. Transistors as Switches. Switches and Speed Circuits of RTL, TTL, DTL, MOS Logic Gates. Analog Switching Circuits. Comparators and Schmitt Triggers. A/D and D/A Converters. Sample and Hold Circuits. Multivibrators. Timing Circuits. Diode Characteristics and Applications. Transistor Characteristics and its use as an Amplifier. Amplifiers Frequency Response. Differential Amplifiers. Operational Amplifiers and their Applications. The Transistor as a Switch. RTL, DTL, TTL and CMOS Logic Gate Characteristics. Multivibrators. Comparators and Schmitt Triggers. A/D and D/A Converters. IC Timers. Sample and Hold Circuits. Interfacing TTL and CMOS IC Gates Digital waveform generators, waveform analysis; pulse amplitude modulators and demodulators; sample and hold circuits; Delta modulation; PCM; ASK, FSK, PSK, DPSK Lab. 45. 202400 Digital Image Processing 46. 202400 Software Engineering 47. 202424 Modeling and Simulation 48. 202424 Digital Control Systems 49. 202220 Microcomputer Engineering 202440 Introduction to 50. systems. Image perception; image sampling and quantization; image transforms; image representation, geometrical operations, enhancement, filtering, restoration, and segmentation; edge detection; region extraction; fundamental issues and techniques of computer vision ; image reconstruction from projections; pattern recognition; image analysis and computer vision; and image compression. software characteristics, history, components, applications. software project management, software project life cycle, scheduling, quality measuring factors, planning & estimation. software analysis, object oriented analysis and data modeling, formal methods in software analysis. software design; procedural methods, data flow oriented method, and design optimization. software ensuring, maintaining, integrity; quality assurance, quality metrics, reliability and testing. The course is concerned with the efficient representation and manipulation of logic functions in the computer and how this is applied to the analysis and synthesis of both combinational and sequential logic. Computer algorithms, techniques, and theory used in the simulation of electrical circuits and systems. Techniques for the verification of correct behavior of complex electronic circuits and systems including detailed simulation of integrated circuits at the transistor level in the time and frequency domain, discreteevent logic simulation, cycle-based logic simulation, RTL and behavioral simulation, equivalence checking, timing analysis, power estimation. Introduction to Digital Control Systems and their Characteristics. Representation of Control Systems using Z-Transform. Frequency Response. Stability. Quality and Performance of Digital Controllers. Design of Digital Controllers and their Applications. Term project Microcomputer System Connection, Interface Methods, Serial and Parallel Interface, Interrupt Service and Priority Management, Direct Memory Access Techniques, Screen Printer, and Disk Interfaces, Analog Interfacing and Industrial Control Applications, Microcomputer Development and Testing Systems. Fundamental of Control Structures, Data Structuring, Sorting, Searching and Management of Data. Parameters Passing, Sub programming, Static and Dynamic Structured Data Types, Sets, Linked Lists and Pointers, Windows and Graphic Programming. Term project. AI Principles, Fields of AI, AI Applications, Knowledge Artificial Intelligence 51. 202444 Introduction to Robotics 52. 202400 Selected Topics in Computer Eng. 53. 204242 Digital Signal Processing 54. 402530 Error Control & Coding 55. 204444 Introduction to Wireless Networks 56. 204444 Introduction to VLSI Design 57. 58. 204244 204240 Power Electronics Electric drive systems Representation Methods, Knowledge Based Systems, Rule Based Systems, Chaining Types, Search Strategies, AI Applications Programming. Introduction to Expert Systems. Term project. Introduction to the science and engineering of robotic devices. Kinematics, dynamics, control, and programming of manipulators. Introduction of sensors, machine vision, actuators, end effectors, and system integration for automation. Basic concepts in the organization and operation of computer-controlled manipulators. Term project. Statement of the council of the Electrical Engineering Department. Discrete Time Signals and Systems. Discrete and Fast Fourier Transform (review). Z-Transform and its Applications to Discrete Signals. Elements of Digital Signal Processing Systems. Digital Filters (recursive and non recursive): Analysis and Design. Fundamental topics of information theory, source and error control coding, concepts of code-space, linear (n,K) block codes, error detection and correction concepts, parity check matrices and syndromes. Hamming codes, cyclic codes, error trapping decoding, BCH codes, burst-error-correcting codes, interleaving and product codes, convolutional codes, and Viterbi algorithm. Term project Introduction of the fundamentals of wireless communication. Modeling of the wireless multipath fading channel and its basic physical parameters. Coherent and noncoherent reception. Diversity techniques over time, frequency, and space. Spread spectrum communication. Multiple access and interference management in wireless networks. Frequency re-use, sectorization. Multiple access techniques: TDMA, CDMA, OFDM. Capacity of wireless channels. Examples from existing wireless standards. Term project VLSI Circuits Development. Design Concepts. IC Development and Design. Physical Design Tools. Review of Solid-State Device Concepts. Device Structures. Device Modelling and Circuits Simulation. MOS Circuit Design. VLSI Test Methods. VLSI Circuit Processing Developments. Term project. Power Semiconductor Diodes. Diode Circuits and Rectifiers. Thyristor Rectifiers. AC Voltage Controllers. DC Choppers. PWM Inverters. Power Converters, Introduction to drives, DC drives, AC drives, Induction motors, DC motors, Stepper motors, Control: Closed and open loop systems, Induction motor drives, Feedback control of AC and DC machines.






