Unit VI: The Gilded Age - The Rise of Industrial America (Closing of
advertisement

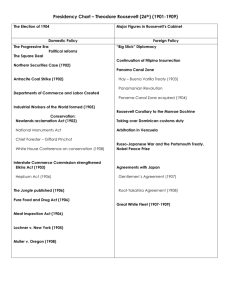
THE GILDED AGE APUSH - STEIKER Unit VI: The Gilded Age - The Rise of Industrial America (Closing of the West, The Gilded Age, Rise of Unions, Populism, Immigration, Urbanization, Progressivism) KEY QUESTIONS: How did the Homestead Act affect westward expansion? What role did cattle play in the West? How did the railroads affect the destiny the American Indian population? How did the tide of materialism foster the concept of “Social Darwinism’? How successful was the Dawes Act? How did Frederick Jackson Turner interpret the West in American History? How did new technology revolutionize American life? Did the captains of industry of the late 19th century violate the principles of the American economic system? What impact did Andrew Carnegie, John D. Rockefeller, Thomas A. Edison, & J.P. Morgan have on American business and American life? How did monopolies and trusts come to dominate American business? To what extent did the government support free enterprise? Explain the ideas of Henry George, Edward Bellamy, and Henry Lloyd. What conditions gave rise to Unions? How built the railroads and filled the factories? What conditions enabled the “bosses” and “machines” to organize voters? How did cities modernize at the turn of the century? Explain why political leaders in the late 19th century avoided taking stands on public issues in light of sectional, partisan, ethnic, and economic differences among the voters. Explain how and why the “Social Gospel” contrasted with tradition Protestantism and Catholicism. What conditions gave rise to the Populist Party? Why did the Populists advocate silver? What are the origins and philosophical basis of the Progressive Movement? What reforms were instituted at the city, state, and national levels? Was Roosevelt’s Square Deal effective? What were the reforms of the New Freedom? Did non-whites benefit from progressivism? VOCABULARY: INDUSTRIALIZATION AND THE RISE OF BIG BUSINESS corporation unlimited life unlimited capital limited liability pooling agreements trusts holding company mergers cartel monopoly horizontal integration vertical integration scientific management Subsidies protective tariffs immigration quotas Government Aid to Industry ROBBER BARONS RAILROADS significance of railroad on industrial development Erie Railway Wars Pacific Railway Acts 1862 and 1864 Transcontinental Railroad corruption of railroad companies Granger State Laws Munn v. Illinois (1877) Wabash Case (1886) Interstate Commerce Act (1887) Daniel Drew George Westinghouse Thomas Edison John D. Rockefeller Jay Gould J. P. Morgan Andrew Carnegie Cornelius Vanderbilt NEW INVENTIONS AND NEW INDUSTRIES Bessemer process Carnegie Steel Standard Oil American Telephone and Telegraph economies of scale new inventions (that help promote new industries): sewing machine, typewriter, light bulb, telephone, elevator, etc. new product delivery: Montgomery Ward; Sears and Roebuck; Department Stores NEW IDEOLOGIES laissez-faire Social Darwinism "Gospel of Wealth" philanthropy Myth of the "self-made man" Horatio Algier: “Rags to Riches” The American Dream pragmatism LABOR unions rank and file closed shop open shop collective bargaining strikes lockouts boycott black listing union busting Yellow dog contracts court injunctions UNIONS industrial unions craft unions National Labor Union (1870’s) Kinghts of Laborn(1860’s – 1890) - Uriah Stephens American Federation of Labor (1886 -) - Samuel Gompers Molly McGuires (1870’s) American Railway Union (1893-1895) - Eugene V. Debs The Industrial Workers of the World: The Wobblies (1905 – 1950) - William Haywood “Bread and Butter” unionism LABOR UNREST Pinkertons Railroad Strike of 1877 Haymarket Riot 1886 Molly McQuires Homestead Strike 1892 Lockout 1892 Pullman Strike 1894 Anthracite Coal Strike 1902 Mary Harris “Mother” Jones Triangle Shirtwaist Fire 1911 Immigration old immigration new immigration reasons for coming: political social and economic issued faced impact of immigrants on city development: ethnic communities, etc. melting pot theory salad bowl theory assimilation Americanization European Immigrants Chinese Immigrants ghettos quotas Chinese Exclusion Act Gentleman’s Agreement Urbanization urbanize living conditions in the city tenements slums suburbs suburban sprawl Effects of urbanization negative: political machines, unsanitary conditions and poor housing positive: community improvement, cultural opportunities, technological advancements Jacob Riis, How the Other Half Lives Settlement Houses: Jane Addams Tammany Hall Boss Tweed Gilded Age Culture Mark Twain essay on the Gilded Age John Dewy and progressive education development public education pragmatism Americanization Education: development of public school scientific advances architecture: bridges skyscrapers fancy homes mass culture: leisure time publishing yellow journalism music (ragtime; marching band; early jazz) Women’s Suffrage Temperance Populism Grange Movement: Farmer’s Alliances Granger Laws Populist Movement Omaha Platform: secret ballot; direct election of senators; initiative, referendum and recall, direct primary Gold vs. Silver and William Jennings Bryan Progressivism The Progressives: “Middle Class Reformers” Jane Addams, Lillian Wald, Margaret Sanger, Booker T. Washington, W.E.B. Dubois muckrakers: (Know who they are and their books or contributions) Thomas Nast: political cartoons Jacob Riis, How the Other Half Lives Ida B. Wells, A Red Record Frank Norris, The Octopus Ida Tarbell, The History of the Standar Oil Company Lincoln Steffens, Shame of the Cities Upton Sinclair, The Jungle Roosevelt’s Response to The Jungle Hull House Visiting Nurse Services POLITICS AND REFORM: City Reforms: City Commissioner Plan City Manager Plan State Reforms: Secret Ballot initiative referendum recall direct primary Federal Reforms: Newlands Reclamation Act (1902) Elkins Act (1903) Pure Food and Drug Act (1906/1911) Meat Inspection Act (1906) Hepburn Act (1906) Federal Reserve Act (1913) Clayton Antitrust Act (1914) Federal Trade Act (1914) Constitutional Amendments: 16th ; 17th; 18th; 19th Trustbusting: Sherman Anti-Trust Act 1890 Northern Trust Case 1904 Standard Oil Decision 1911 GOVERNMENT CORRUPTION Bosses of the Senate Credit Mobilier Ullysses S. Grant Roscoe Conkling James G. Blaine The Stalwarts The Half Breeds Bourbon Democrats Mugwumps mudslinging “waving the bloody shirt” PRESIDENT THEODORE ROOSEVELT Government Reform: Roosevelt’s New Nationalism Civil Service Reform Pendleton Act; Square Deal: Pure Food and Drug Act 1906 Meat Inspection Act 1906 Interstate Commerce Act Hepburn Act Sherman Anti-Trust Act Conservation Movement PRESIDENT WILLIAM HOWARD TAFT: Roosevelt’s Protégé or Backlash? 16th amendment: federal income tax 17th amendment: direct election of Senators Payne-Aldrich Tariff Act Dollar Diplomacy Bull Moose Party PRESIDENT WOODROW WILSON New Freedom: Federal Reserve Act 1913 Clayton Anti-Trust Act 1914 Federal Trade Act 1914 Adamson Act 1916