AT351Lab9
advertisement

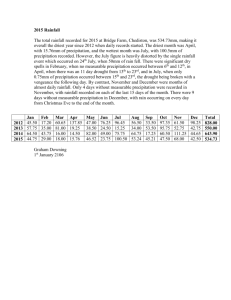
ATS 351, Spring 2010 Lab #9 Weather Radar - 55 points 1. (5 points) If a radar has a maximum unambiguous range of 300km, what is its PRF? (The speed of light, c, is equal to 3x108 m/s) 2. (5 points) Explain the presence of a bright band. 3. (5 points) What are the differences between the Clear Air Mode and the Precipitation Mode (including which features can be identified easier depending on the mode)? 4. (5 points) Using the PPI radar reflectivity image below, answer the following questions: a. Which letter indicates the location of the radar? b. Which letter indicates the region of ground clutter? c. Which letter indicates the region of highest reflectivity values? d. Which letter (A or B) indicates a region of lower rainfall rates? e. What type of precipitation system is this (supercell, snow, bow echo)? B A C D 5. (4 points) On the reflectivity and velocity images below, indicate with an arrow (on both) the most probable location of the tornado? Fort Collin's Flood Case Study On July 28th, 1997 a major precipitation event occurred along the foothills in Fort Collins. Over 14 inches of rain fell in a concentrated area in Fort Collins during a 5-hour period. This heavy rainfall caused the Spring Creek to spill over its banks, which resulted in massive flooding. Much of the CSU campus was under several feet of water. This part of the lab will help you understand how the precipitation was initiated, and how to interpret the radar images associated with the rainfall itself. Part 1: Precipitation Initiation 6. (2 points) On the afternoon of July 28, the prevailing winds along the Front Range were from the East. As the warm air mass from off the plains came in contact with the topography of the foothills, it was forced to rise. Referring to the attached atmospheric sounding, an air parcel being lifted from the surface would initially be: a. unsaturated b. saturated 7. (2 points) As the air was forced to rise up the topography, it initially cooled at: a. ~6.5 oC/km, the moist adiabatic lapse rate b. ~10 oC/km, the dry adiabatic lapse rate c. the environmental lapse rate d. the air did not cool as it rose 8. (3 points) Refer to Image 1. Starting from the surface dew point temperature, follow the purple constant mixing ratio lines up and draw a line. Starting from the surface temperature, follow the green dry adiabatic lines up and draw a line, until this line intersects the dew point line you just drew. This is the Lifting Condensation Level (LCL), where the air parcel has expanded and cooled to the point of saturation. At approximately what level is the LCL located? 9. (3 points) The parcel path follows the moist adiabat (the curving blue line) up once it becomes saturated at the LCL. The Level of Free Convection (LFC) is located where the parcel path intersects the environmental temperature profile. At approximately what level is the LFC located? 10. (2 points) The mountains of the Front Range rise up to about 600 mb in the atmosphere. Knowing this, what was the mechanism that initiated the convection in Fort Collins on July 28 th? a. Buoyant air rising to the LFC b. Air being forced to rise along the topography of the Front Range to the LFC c. Saturated air sinking to the surface Part 2: Weather Radar Refer to Images 2,3 Image 2 is a time series of Radar Reflectivity during the heaviest rainfall of the storm on July 28, 1997 in 15 minute increments. Please read the caption under the image to understand the underlying grid system. 11. (3 points) At what time period was the strongest reflectivity covering the largest area in Fort Collins, and what was the measured reflectivity for this time period (in the correct units)? 12. (2 points) Following the contours of strongest reflectivity, would you say this storm was: a. stationary b. moving to the northwest c. moving to the southwest d. moving due north Image 3 is a contour map of total rainfall amounts for the lifetime of the storm. Recall our radar images are only a subset of the total storm, however, they represent the heaviest rainfall of the storm. 13. (4 points) Compare the reflectivity from image 2 to the precipitation totals from image 3. We can see that strong reflectivity corresponds to the area of heaviest rainfall accumulation. Explain why this is the case. Part 3: Application (10 Points) 14. In your own words, describe the mechanisms that caused the Spring Creek to flood its banks during this rainfall event. For full credit, tell me about atmospheric stability, atmospheric moisture, storm movement, and rainfall rates. Image 1 The Denver Atmospheric Sounding for 6 AM on July 28, 1997 Image 2 Image 3