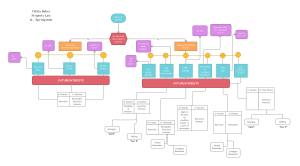
Property (Milot) Estate Chart
advertisement

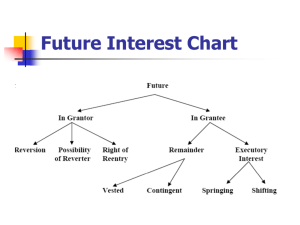
Fee Simple Absolute Present Interest Fee simple absolute Language Words of Purchase: Infinite and perpetual Example Future Interest Legal Effect O to A O to A and his heirs No future interest Absolute ownership Fee Simple Defeasible Present Interest Language Example Future Interest Legal Effect Fee Simple Subject to a Condition Subsequent Conditional: But, if, on the condition that, however, provided that O to A, but if A starts X, O has the right to reenter and take the property Right of Reentry Grantor has the right to take action to reclaim Fee simple determinable Temporal: so long as, during ,while, until, unless O to A, so long as A is a Possibility non-smoker, then the of Reverter property shall revert to O Fee Simple subject to an executory limitation Not distinguished based upon language. Either temporal or conditional Executory Interest Automatic reversion of title to grantor Automatic reversion to a Third Party Life Estates Present Interest Language Example Present Interest Future Interest Life Estate Temporal: for life, to live in, not to be sold during lifetime O to A for life, then to B Life Estate Per Autre Vie O to A for the life Third Party Temporality: "to A of B, then to C. for the life of B" Owner may use the property during lifetime, but may not waste, property right is alienable Grantor: Reversion Third Person: Remainder Same as life estate, except measured on life of third party Grantor: Reversion Third Person: Remainder Remainders Future interest Indefeasibly Vested Remainders Definition Not subject to a condition precedent; and owned by an ascertainable person Vested Class gift to a group of Remainder people identified by Subject to Open description not by name, in which other members Example O to A for life, then to B and his heirs. O to A for life, then to A's children, where A had at least one child. Legal Effect No contingency, if B dies it will still go to his estate. 1. Class closes: whenever nobody else can be born into may yet enter the class 2. Vested Remainder Subject to Divestment Occurs when the remainder is vested, but subject to a condition subsequent (condition may trigger after vested interest) Contingent Remainders Interest owner is either unascertained or subject to a condition precedent (condition must trigger in order to vest interest) Alternative Contingent Remainders Contingent remainders that will divest if the prior contingent remainder fails to develop class When any member of the class may demand distribution O to A for life, then to B and his heirs, but if B does not attain the age of 21, to C and his heirs. B has a vested remainder that will divest to C if A dies before B is 21. O to A for life, then to B's children. B is childless (unascertainable) O to A for life, then to B and his heirs if B survives A (condition precedent) If contingency not satisfied, reversion to grantor. O to A for life, then to B if B attains the age of 21, but if B does not attain the age of 21, to C. If B turns 21 he gets property and A gets nothing, if B dies before 21 he loses his interest and C gets property. If C dies and B is not 21, property reverts to O. Executory Interests Future Interest Definition Example O to A as long as used for X, but then reverts to B. Legal Interests Executory interest Future interest that provides reversion to a third party, instead of grantor Springing executory interest Cuts off a grantors interest O (to O, but) to A if A and springs to a third party graduates from law school. O has a defeasible fee subject to executory limitation, A has springing executory interest. Shifting Executory Interest Cuts off a grantee's interest and shifts it to a third party A has defeasible fee subject to executory limitation, B has an executory interest O to A and his heirs, but if B graduates from law school, to B and his heirs A has defeasible fee. B holds executory interest (automatic reversion)