Larsson's terms
advertisement

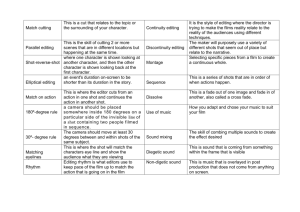
Updated 7 February 2004 Return to Section 2 Syllabus Home Page INTRODUCTION TO FILM: TERMS TO KNOW NOTE: THIS PAGE IS UNDERGOING REVISION The following are significant terms found in previous editions of Film Art. Most of these terms will be in boldface or italics. Some are defined in the online Glossary at the textbook website. All are defined within the text, although you may have to read the full paragraph to get the meaning. If you are unsure of any meanings, please ask me! Revised portions are in red text. Week 1: Chapter 1 Week 5: Chapter 4 Weeks 10 & 11: Chapter 8 Week 2, Chapter 2 Weeks 6 &7: Chapter 6 Weeks 12 & 13: Chapter 9 Weeks 3 & 4, Chapter 3 Weeks 8 & 9: Chapter 7 Week 14: Chapter 5 NOTE: There are no terms for Chapter 10, since that chapter deals with terms and concepts that have already been introduced. Read the pages listed for concepts related to the analysis of style in films (including the definition of different kinds of "style") and for the discussion of style in Citizen Kane. Week 1, Chapter 1: Film Production, Distribution, and Exhibition return to class schedule Read each column from top to bottom, left to right to correspond with discussion in Film Art frames ancillary markets critical flicker fusion film production apparent motion shots "letterboxed" and "full frame" videos preparation/preproduction phase projector camera standard shooting rate for sound film contact printer optical printer film base master shot assembly/postproduction phase editor dailies/rushes rough cut producer final cut screenwriter pitch session nonlinear systems sound editor automated dialogue replacement/ADR treatment emulsion gauge super 8 millimeter film shooting script negative cost production/shooting phase 16 mm. film director 35 mm. film 70 mm. film Imax system magnetic and optical sound tracks digital film sound production designer storyboard director's crew composer release prints dubbing/looping computer-generated imagery/CGI large-scale production exploitation production independent production cast small-scale production cinematographer production recordist/sound theatrical film exhibition mixer nontheatrical film exhibition special-effects unit differences between film and producer's crew video film distribution takes merchandizing slate documentary film fiction film compilation film animated film the film "author" return to top Week 3, Chapter 2: The Significance of Film Form return to class schedule Read each column from top to bottom, left to right to correspond with discussion in Film Art form formal expectations suspense surprise curiosity prior experience meaning referential meanings explicit meanings implicit meanings return to top interpretation themes symptomatic meanings ideology evaluation criteria coherence intensity of effect complexity originality functions motivation similarity and repetition motif parallelism difference and variation development segmentation scenes unity and disunity Week 4, Chapter 3: Narrative as a Formal System return to class schedule narrative story/plot/screen duration unrestricted/omniscient narration time temporal frequency restricted narration space story/plot/screen space hierarchy of knowledge story openings depth of story information explicit and inferred events in media res objective narration diegesis exposition point-of-view shot and sound perspective plot change in knowledge perceptual subjectivity nondiegetic material goal-oriented plot mental subjectivity cause and effect climax character/noncharcter narrator character traits open endings the classical Hollywood cinema temporal order narration closure temporal duration range of story information narrative form in Citizen Kane return to top Week 5, Chapter 4: Understanding Genre return to class schedule genre definitions genre conventions iconography genre history social functions of genre the Western the horror film the musical return to top Weeks 6 & 7, Chapter 6: The Shot: Mise-en-Scene return to class schedule mise-en-scene lighting quality colored lighting realism hard lighting movement and acting Georges Melies soft lighting "realistic"/"nonrealistic" acting setting lighting direction typecasting/typage selected settings frontal lighting acting and other film techniques constructed settings sidelighting (or crosslight) movement color in settings backlighting color differences miniatures and paintings underlighting balance of components props top lighting limited palette/monochromatic design motifs and parallels in settings lighting source depth cues costume and make-up key light planes of the image costume props fill light shallow-space composition costume coordinating with setting three-point lighting deep-space composition make-up background (or set) lighting mise-en-scene and time lighting high-key lighting mise-en-scene in Our Hospitality highlights and shadows low-key lighting return to top Weeks 8 & 9, Chapter 7: The Shot: Cinematography return to class schedule meaning of "cinematography" racking/pulling focus canted frame range of tonalities special effects camera height film stocks glass shot camera distance contrast superimposition extreme long shot "slow" film stock process/composite shots long shot "fast" film stock rear projection plan americain (or medium long shot) color film stocks front projection medium shot tinting, toning, and hand coloring mattes medium close-up exposure traveling mattes close-up filters digital compositing extreme close-up flashing framing functions of framing speed of motion frame dimensions and shape mobile framing/camera movement fast-motion effects aspect ratio pan shot slow-motion effects Academy ratio tilt shot time-lapse cinematography widescreen ratios tracking shot stretch printing hard matte crane shot perspective relations anamorphic process Steadicam lens focal length masks motion-control techniques short-focal-length (wideangle) lens iris hand-held camera middle-focal-length (normal) lens multiple-frame/split-screen imagery reframing long-focal length (telephoto) offscreen space lens following shot zoom lens angle of framing hand-held shots depth of field straight-on, high, and low angles mobile framing and time selective focus, deep focus camera level the long take return to top Weeks 10 & 11, Chapter 8: The Relation of Shot to Shot: Editing return to class schedule editing fade out/fade in dissolve wipe cut graphic relations in editing graphic match graphically discontinuous editing graphic conflict rhythmic relations in editing spatial relations in editing "Kuleshov effect" temporal relations in editing editing and order of events flashbacks, flashforwards elliptical editing overlapping editing reestablishing shot match on action cheat cut point-of-view cutting crossing the axis of action editing and frequency crosscutting repetition of an event temporal continuity continuity editing montage sequence 180 degree system graphic and rhythmic alternatives to continuity editing axis of action spatial and temporal discontinuity establishing shot jump cut shot/reverse shot non-diegetic insert Sergei Eisenstein and discontinuity editing eyeline match return to top Weeks 12 and 13, Chapter 9: Sound in the Cinema return to class schedule powers of sound in film rhythm in sound sound perspective loudness beat/tempo/accent sound and time pitch musical motif synchronous sound timbre coordination of rhythms in sound and image asynchronous (nonsynchronized) sound speech, music, noise "Mickey Mousing" simultaneous sound choosing and manipulating sounds disparity of rhythms in sound and image nonsimultaneous sound "dry" recording fidelity sound earlier than the image sound mixing diegetic sound, non-diegetic sound bridge sound dialogue overlap onscreen, offscreen diegetic sound selection, alteration, and combination internal, external diegetic sound sound and film form: music sound over sound later than the image return to top Week 14, Chapter 5: Documentary, Experimental, and Animated Films return to class schedule documentary compilation direct cinema/cinema verite relations of documentary and fiction categorical form rhetorical form arguments from source subject-centered arguments viewer-centered arguments experimental film abstract form associational form animated film drawn animation cels cut-outs three-dimensional animation clay, model, pixillation animation computer animation animation in Duck Amuck NOTE: There are no terms for Chapter 10, since that chapter deals with terms and concepts that have already been introduced. Read the pages listed for concepts related to the analysis of style in films (including the definition of different kinds of "style") and for the discussion of style in Citizen Kane. return to top