Informative Speech

Informative Speech
Purpose: To inform the audience on your chosen topic. To give them information on a subject they may not be familiar with.
Organization:
I.
Introduction
A.
Attention Getter (see below)
B.
Statement of purpose – why you are giving this speech
C.
Statement of relevance – why should the audience care about this speech
D.
Preview the body of the speech
II.
Body
A.
3 main points about the topic
1.
Supporting materials – stories, facts, statistics, quotes, visual aids, etc
III.
Conclusion
A.
Brief summary of the body’s main points
B.
Restate the purpose of the speech
C.
Motivational Statement – leave you audience excited about your topic
Examples of Attention Getters
Identify with audience – “We are all in the same boat and have to give a speech.”
Statement of purpose – “The Titanic is a historically tragic event”
Startling statistic or fact – “More than 1,300 people died on the Titanic”
Story or Anecdote – a short story that leads to the main point of the speech
Comparison – compare your topic to something else that is familiar to your audience
Rhetorical Question – a question that does not expect an answer – “Can you believe the
Titanic was referred to as the unsinkable ship?”
Quotation – The Unsinkable Molly Brown once said, “April 15, 1912 is a day that will never leave my memory”
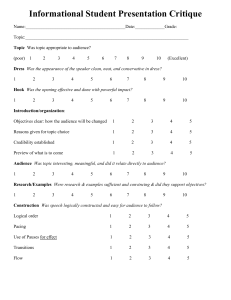
Explanation of Grading Rubric
Clear Voice – refers to the speaker’s ability to get their information across to the audience in an understandable way. Suggestions:
Reduce the number of technical words
Be specific in your explanations
Pronunciation – if you cannot pronounce a word, find another way to say it
Avoid verbal distractions – um, ahs, like, well, okay, etc.
Eye Contact – refers to the speaker’s ability to stay connected visually with the audience throughout the speech. Suggestions:
Scan the audience with your eyes
Avoid reading speech from note cards
Use notes as a resource, glancing occasionally
Posture – refers to the speaker’s ability to maintain a strong physical presence. Suggestions:
Stand up straight
Avoid disturbing gestures – podium dancing, hands in pockets, folded arms, inappropriate or excessive hand gestures, etc
Practice when to use hand gestures in your speech
Wear clothing that shows you respect yourself, your topic, and your audience
Time – refers to the speaker’s ability to deliver their speech in the required time
Visual Aids:
A visual aid is a visual representation that will add to the understanding of the topic. The visual aid shows support the speech and not dominate.
Examples – Posters, PowerPoint, Models, Webpage, Demonstration, Diorama, Shadow box, etc.
Note Cards
The note cards will contain a few words which act as signals so that the speaker remembers what to say next during the speech.
See additional handout
Hints:
Define a purpose for your speech
Be organized
Practice, Practice, Practice
Have organized note cards
Dress appropriately
Create a visual aid that will be effective to the purpose of the speech