China: Sui, Tang, and Song Dynasties
advertisement

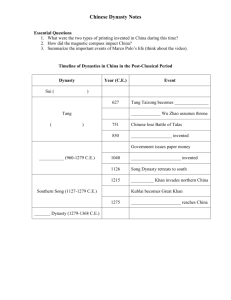
Post-Classical World: Medieval China’s Tang and Song Dynasties The Tang Dynasty, 618-907 AD After the fall of the Han Dynasty, China saw much chaos similar to what happened in Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire. Unlike Europe though, China was eventually reunited. The Tang Dynasty was the next Chinese Dynasty to unite China for an extended amount of time. Tang Culture The Tang dynasty is known as the "golden age" of Chinese culture. The capital of the Tang Dynasty, Chang-an, became incredibly wealthy and supported the flowering of Chinese culture. Due to the popularity of the Silk Road trade routes, Chang-an became a meeting place of many different cultures and religions: Christianity, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, and Islam all influenced Tang culture. Syrians, Jews, Arabs, Persians, Koreans, Tibetans, and Japanese all lived side by side with the Chinese of Chang-an. In 636, Christians from Syria were allowed to build a church and hold Christian services barely six hundred years after the founding of Christianity and less than three hundred years after Christianity had become the state religion of Rome. The foreigners not only brought in new religions, but new clothes, cuisine, literature, and music as well. The imperial court itself had several performing troupes of actors and musicians gathered from surrounding nations permanently performing at the court. Among their cultural achievements, the Tang craftsmen excelled in making porcelain and jade pottery, utensils and sculptures. Tang weavers advanced their silk-weaving, making clothes much softer and more extravagant than what Europeans were wearing in their scratchy wool. Porcelain and silk were in high demand, furthering increasing the trade between the world and China. Poetry became a popular subject for all these new readers. The poet Li Po (701-762) became quite popular. His poetry focused on simple language that allowed the reader to immediately understand his emotions. He loved to celebrate the beauty of life and nature and wanted to share that love. Questions: Tang Dynasty 1. Describe how foreign cultures were viewed in China during this time? 2. During the Tang Dynasty, what goods were in high demand on the Silk Road? AFTER YOU READ BOTH ARTICLES!!!!! (ONE ON THE BACK) RANK THE TOP FIVE IMPORTANT ACHIEVEMENTS FROM THE TANG AND SONG DYNASTIES IN ORDER AND EXPLAIN WHY!!!!!!!!! 1. 2. 3. 4 5. The Song Dynasty, 960-1279 AD Eventually, the Tang Dynasty fell under pressure from outside invasions and domestic rebellions. The Song Dynasty soon took control over China after the fall of the Tang. The Song Economy Under the Song Dynasty, China experienced an agricultural and commercial revolution. Chinese farmers saw their production and wealth increase dramatically. For hundreds of years Chinese dynasties had required peasants to do free manual labor for the government each year. This was how China built the Great Wall and roads. All the time they spent working for the government, was less time they worked on their fields. The Song Dynasty eliminated forced labor. Secondly, farmers were allowed to buy and sell land for the first time. You see, some people are just better at jobs than other people. By letting farmers buy and sell land, good farmers could buy land from bad farmers and produce more crops on that land. These two factors resulted in a phenomenal increase in agricultural production, and the wealth of the government and individual farmer increased significantly (though most farmers never became “wealthy.”) The most important economic innovation of the Song was the widespread use of money. China was the first country to use both paper and coin money. This helped China in 2 ways. First off, peasants used to have to pay their taxes in grain. The Song Dynasty now allowed farmers to pay their taxes in money. Since they no longer needed to grow grain, this freed up weak farmers to sell their farms and go get jobs they’d be better at in cities. Anytime you give people more freedom to choose their jobs, the economy will improve as they get jobs they’re better at. Secondly, before the widespread use of money, trade had to be done as bartering – people exchanged goods for other goods. If a farmer wanted to buy a goat, then he and the goat’s owner would have to come up with some sort of trade. “I’ll give you half a cow!” Obviously, that’s an awkward way to do things. So the use of money made trade MUCH easier, and the economy increased due to this! The booming economy led to the growth of cities. The city of Kaifeng eventually had a population of 250,000 households. The city of Hangchow had a population of 391,000 households. Compare that to Europe during the same period: Rome had an average population of about 35,000 households and London had a population of about 20,000 households. No civilization on earth was comparable to China during the Song Dynasty. Song Technology These Chinese cities were bursting at the seams with merchants and trade. What were some of the goods and inventions that other cultures wanted? Merchants along the Silk Road obviously made most of their money off the trade in porcelain and silks. During this time period, China also invented a process to make steel and began producing gunpowder weapons. The demand for goods and services was so great that China began an unprecedented acceleration of foreign trade. Chinese goods were traded as far away as Africa and the Middle East. China also created junks – the largest ocean-going vessels in the world at the time that carried Chinese goods over the Indian Ocean all the way to Africa. China also built numerous canals. Canals are man-made rivers that allowed shipping and transportation to new areas. The largest canal, the Grand Canal, was built to link the Yellow and Yangtze rivers and make it easier to ship rice from the north to the south, helping to prevent starvation and improving the economy. Even though they were prosperous, the Song Dynasty also fell like every other Chinese dynasty before it. This time, they were overrun by a dangerous people to their north: the Mongols. The Song Dynasty also saw the invention of the movable-type printing press. Originally, if someone wanted to make a copy of a book, they would have to write it all out by hand, which took a long time. Using movable-type however, craftsmen created blocks of letters like the type your future children will play with. When they wanted to make a book, they would arrange the letters into a copy of a page. While this took a long time, the printer could then roll ink over the blocks and then use the blocks to make hundreds and hundreds of copies. This allowed a VAST amount of books to be printed much more cheaply, causing literacy to be more widespread. Questions: Song Dynasty 1. Explain the TWO reforms made during the Song Dynasty that improved agricultural production from farmers. 2. Explain how the use of paper and coin money gave peasants more freedom. 3. Explain how the use of paper and coin money increased trade. 4. What were two technological inventions made in China during this time? 5. What function did “junks” have? 6. What was the purpose of the Grand Canal? 7. Why was the invention of movable type so important in Song china?