Practice Test: Kinetic Theory of Matter
advertisement
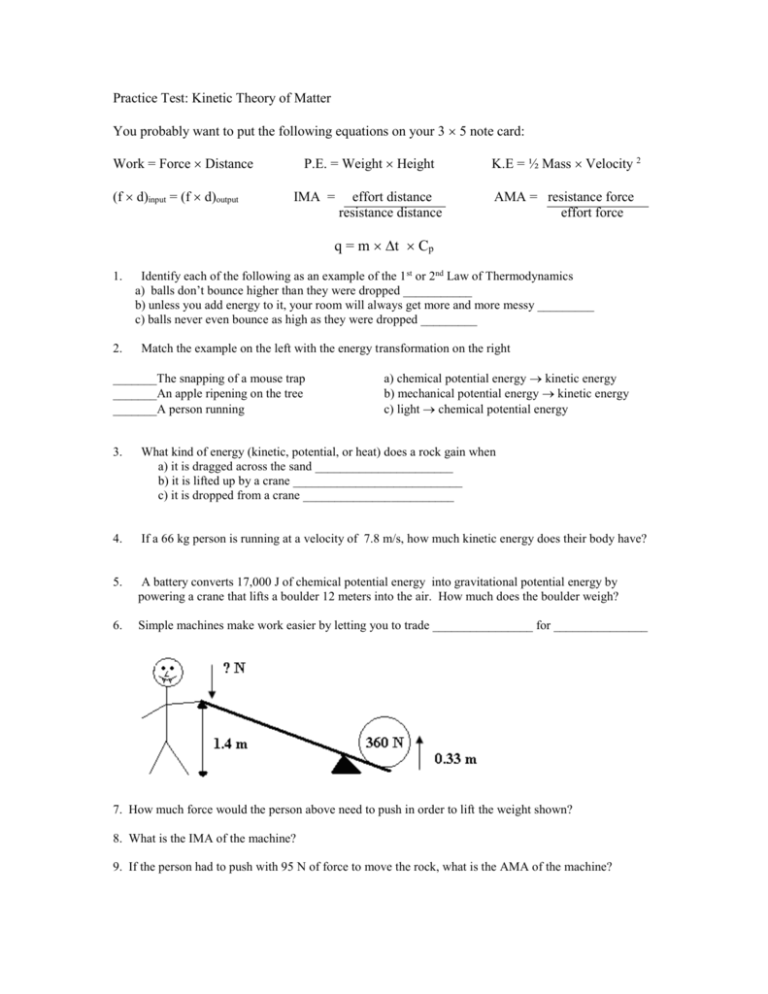
Practice Test: Kinetic Theory of Matter You probably want to put the following equations on your 3 5 note card: Work = Force Distance (f d)input = (f d)output P.E. = Weight Height IMA = effort distance resistance distance K.E = ½ Mass Velocity 2 AMA = resistance force effort force q = m t Cp 1. 2. Identify each of the following as an example of the 1 st or 2nd Law of Thermodynamics a) balls don’t bounce higher than they were dropped ___________ b) unless you add energy to it, your room will always get more and more messy _________ c) balls never even bounce as high as they were dropped _________ Match the example on the left with the energy transformation on the right _______The snapping of a mouse trap _______An apple ripening on the tree _______A person running a) chemical potential energy kinetic energy b) mechanical potential energy kinetic energy c) light chemical potential energy 3. What kind of energy (kinetic, potential, or heat) does a rock gain when a) it is dragged across the sand ______________________ b) it is lifted up by a crane ___________________________ c) it is dropped from a crane ________________________ 4. If a 66 kg person is running at a velocity of 7.8 m/s, how much kinetic energy does their body have? 5. A battery converts 17,000 J of chemical potential energy into gravitational potential energy by powering a crane that lifts a boulder 12 meters into the air. How much does the boulder weigh? 6. Simple machines make work easier by letting you to trade ________________ for _______________ 7. How much force would the person above need to push in order to lift the weight shown? 8. What is the IMA of the machine? 9. If the person had to push with 95 N of force to move the rock, what is the AMA of the machine? 10. A pulley system with an IMA of 4.0, and you pulled 22 meters of rope through it, how far would it lift a box? 11. If the person in the diagram above was using 26 N of force to pull the crate of the ramp, and the crate weighed 120 N, what is the length of the ramp surface? For 12 – 16 choose your answers from the following list: temperature, heat, internal energy, calorie, specific heat capacity, heat of fusion 12. The energy that flows between objects because of temperature differences _______________ 13. The energy needed to raise 1 g of any substance by 1C _____________________ 14. The energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1C _____________________ 15. The total potential and kinetic energy of the atomic particles in a substance _______________ 16. The average kinetic energy of the atomic particles in a substance _______________________ The graph above shows the change in temperature as a 44g sample of Substance X is heated, use it to answer questions 17 - 24 17. Is “Substance X” a solid, liquid, or gas at 50 oC? ______________ 18. What is the boiling point of “Substance X”? __________________ 19. How many calories of energy did the melting process for this sample require? 20. At what temperature does this substance melt? _____________ What kind of energy (kinetic or potential) were the atoms in this sample gaining 21. Between point B and point C? 22. Between point C and point D? 23. Does this substance absorb or release energy as it melts? 24. What is the heat of vaporization of “Substance X”? ____________ 25. The heat of fusion for Sulfur is 12.7 cal/g. What does this tell you about Sulfur? 26. A 100g piece of lead releases 60 calories of energy when it is placed in an ice bath and cools from 20oC to 0 oC. What it the specific heat of lead? 27. A typical living room has about 132,000g of air in it. The specific heat capacity of air is 0.237 cal/g oC. How much energy is needed to raise the temperature of the room from 15 oC to 20 oC? 28. Two identical pans are placed on identical burners. One pan contains 100g of oil, and the other contains 100g of water. After both pans are heated for 5 minutes, the oil ends up at a temperature of 234 oC, but the water is only 47 oC. Why is this? 29. What chemical do most scientists think is responsible for global warming? 30. What human activity puts this chemical into the atmosphere? 31. Explain why fossil fuels can be considered a form of solar energy. 32. Identify a source of energy that isn’t a fossil fuel, and give at least one benefit and one drawback to using it as a major supply of energy in our society. 33. Explain how a planet and the sun can be in thermal equilibrium. Then describe how the system could be moved out of equilibrium. Answers: 1. a) 1st b) 2nd c) 2nd 2. B C A 3. a) heat b) potential c) kinetic 4. 2000 J 5. 1,400 N 6. force for distance 7. 85 N 8. 4.2 9. 3.8 10. 5.5 m 11. 10 m 12. heat 13. specific heat capacity 14. calorie 15. internal energy 16. temperature 17. solid 18. 80 oC 19. 50 calories 20. 60 oC 21. kinetic 22. potential 23. absorb 24. 6.8 calories/g (300 cal 44g) 25. it takes 12.7 calories of heat energy to get one gram of it to melt 26. .03 cal/g oC 27. 156,000 calories 28. water has a higher Cp, so it is harder to warm up 29. CO2 30. burning anything, especially fossil fuels 31. the plants from which fossil fuels were made got their energy from sunlight 32. (answers will vary) 33. in equilibrium, the amount of energy reaching the planet in the form of visible light equals the amount of energy leaving the planet in the form of infra red light. If the star gave off more energy, the system would be moved out of equilibrium, and the planet would get hotter