Preparation and Transduction of MFGnlsLacZ
advertisement

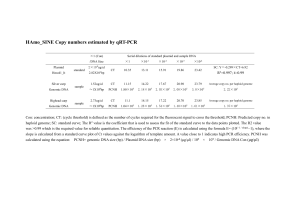
Supplemental Materials and Methods Reagents All chemicals were from Sigma-Aldrich Chemicals (USA), unless otherwise stated. HIL-6 (HIL-6) was produced as previously described (1). Histological and Immunohistochemical Analysis Livers samples were fixed in 4% buffered formaldehyde, followed by 80% ethanol and embedded in paraffin blocks. P-STAT3 immunohistochemical staining was performed as described (2). BrdU incorporation was analyzed using Mouse monoclonal anti-BrdU antibody (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) diluted 1:50, followed by anti-Mouse HRP polymer (Dako) and developed with AEC. PCNA was stained using Mouse monoclonal anti-PCNA (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) diluted 1:200, followed by anti-Mouse HRP polymer (Dako) and developed with AEC. Ki-67 was stained using Rat anti-Mouse Ki-67 antigen (clone TEC-3, Dako), diluted 1:25, followed by Biotinylated Rabbit Anti-Rat (Dako) 1:50, and anti-Rabbit HRP polymer (Dako) and developed with AEC. LacZ immunohistochemical staining on paraffin embedded sections was performed using Rabbit anti-β-gal (Abcam Cambridge, UK) diluted 1:400, followed by anti-Rabbit HRP polymer (Dako) and developed with AEC. In situ staining for β-galactosidase activity was performed on frozen liver sections. Liver samples were removed and fixed in 2% formaldehyde for 30 min at 4°C. Samples were then washed with PBS and put in 0.5M sucrose in 1X PBS overnight at 4°C. Tissues were embedded in Tissue-Tek OCT Compound (Ted Pella Inc., Redding, CA) and frozen at -80°C. 12 micrometer tissue sections were cut using a cryostat and placed on super frost plus slides (Menzel-Gläser, Braunschweig, Germany). Frozen sections were stained by incubation for 1 hour at 37°C with staining solution containing 0.1M sodium phosphate buffer PH 8.3-8.5, 2 mM MgCl2, 0.1% sodium deoxycholate, 0.2% Triton-X, 5mM potasssium ferricyanide, 5mM potassium ferrocyanide and 1mg/ml X-gal (4-chloro-5-bromo-3-indolyl β-Dgalactopyranoside) and counter-stained with Nuclear Fast Red (Sigma). Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) staining was performed using a Sigma Periodic Acid-Schiff kit following the manufacturer's instructions. Western blot analysis Protein extracts were prepared from tissue samples (~100mg) by homogenization and subjected to Western blot analysis probed with antibodies to p-STAT3, STAT3, SMAD2/3, ERK2 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA), p-ERK1/2 (antidiphosphorylated ERK1/2, Clone MAPK-YT, Sigma), pSMAD2 (Ser465/467) (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA), p-AKT (Ser473) and AKT (Cell Signaling), or -actin (Sigma), as indicated, was performed as previously described (2). Blots were stripped and re-probed for β-actin as a loading control. Quantitation of Western blot bands was performed using TINA® 2.10g Imaging software. Calculation of relative fold change in p-AKT levels was performed by dividing the OD value of p-AKT (ODp-AKT) of each sample by the OD value of -actin (OD-actin) and then normalized to the average ODp-AKT/OD-actin values of two Control Plasmid sample that were common to all gels. Preparation and Transduction of MFGnlsLacZ Ecotropic retroviral vector, MFGnlsLacZ (3), was concentrated by low speed centrifugation (6000 x g) at 4° C for 16 h (4) from 1 L conditioned media from TM01 cells (3) (kindly provided by F-L Cosset, CNRS, Lyon, France) and gently resuspended in 10 ml PBS containing 10 mg/ml lactose. For in vivo transduction experiments (Supplemental Fig. 1D), mice were administered 3 doses of MFGnlsLacZ (1x108 TU) in 1ml saline by high pressure intravenous injection on three consecutive days beginning 24 hours following plasmid DNA transfection. Retroviral transduction was evaluated 2 days following the last MFGnlsLacZ injection. Plasmid DNA Constructs Details of plasmid DNA construction and preparation are in the Supplementary Methods. Construction of expression plasmids phAAT-IL6 and phAAT-HIL6 were described previously (2). phAAT-HGF was constructed by ligation of an XbaI – SalI DNA fragment encoding human HGF cDNA (a kind gift from Ilan Tzarfati, Univ. Tel Aviv, Tel Aviv, Israel) into the SmaI-NotI sites of pCI (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The CMV promoter was removed by digestion with BglII and HindIII, filled in at the HindIII site and replaced with a BglII – NotI (filled) DNA fragment containing the human α1-antitrypsin promoter (kindly provided by Dr. Katherine Ponder, University of Washington, St. Louis, MO, USA). pBS-sgp130Fc was constructed by ligation of a NotI (filled) – SalI restriction fragment encoding the murine sgp130-Fc cDNA (S.R.-J.) into the SalI and EcoRV digested pBS-HCRHPI-A (5) (a kind gift from Carol H. Miao, University of Washington, Seattle, WA). For in vivo administration by high-pressure tail vein injection, plasmid DNAs were purified using Enodotoxin-Free plasmid Maxi kits (NucleoBond® from MACHEREY-NAGEL, Düren, Germany or Qiagen Sciences, Maryland, USA). All plasmid DNA solutions for injection were prepared in endotoxin tested normal saline and normalized with control plasmid DNAs to 20 μg DNA in a final volume of 1.8 ml. RNA extraction and RT-PCR RNA samples were prepared from approximately 100 mg snap-frozen tissue and subjected to RT-PCR as previously described (2). The primer sequences used were as follows: SOCS3 (sense) 5’-TCAGTACCAGCGGAATCTTC and (anti-sense) 5’TACTGATCCAGGAATCTCCCGA; GAGGTCTCCAGCCAGAAGTG SOCS1 and (sense) (anti-sense) 5'5'- CTTAACCCGGTACTCCGTGA. ELISA Analyses Murine IL6 and sIL6R, and human HGF levels were determined using a mouse IL6, a mouse sIL6R and human HGF DuoSet ELISA kits, respectively (R&D) according to the manufacturer’s instructions on serum samples that were collected and frozen at -20° C until analysis. Hyper-IL6 levels were analyzed using a human IL6 DuoSet ELISA kit (R&D). Serum msgp130Fc levels were determined using goat anti-Human IgG-Fc antibody (Bethyl Laboratories, Montgomery, TX, USA) diluted 1:2000 as a capture antibody, and biotinylated goat anti-Mouse gp130 (R&D) (0.2µg/ml) as a detection antibody and measured against a purified recombinant sgp130Fc protein standard. Transcription factor assay (non-radioactive EMSA) Nuclear protein extracts were prepared from liver samples using a Nuclear Extraction kit (Millipore, Billerica, MA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. DNA binding activity for STAT3 and AP-1 was evaluated in 25μg of nuclear proteins extract using Transcription Factor Assay kits (Millipore) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Statistical Analysis Comparisons were subjected to either the Student t-Test, or Tukey One-way ANOVA analysis, with P0.05 considered statistically significant was performed using GraphPad InStat version 3.00 (GraphPad Software, San Diego California USA). References for Supplemental Methods 1. Fischer M, Goldschmitt J, Peschel C, Brakenhoff JP, Kallen KJ, Wollmer A, et al. I. A bioactive designer cytokine for human hematopoietic progenitor cell expansion. Nat Biotechnol 1997 Feb;15(2):142-145. 2. Nechemia-Arbely Y, Barkan D, Pizov G, Shriki A, Rose-John S, Galun E, et al. IL-6/IL-6R Axis Plays a Critical Role in Acute Kidney Injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 2008 Mar 12. 3. Cosset FL, Takeuchi Y, Battini JL, Weiss RA, Collins MK. High-titer packaging cells producing recombinant retroviruses resistant to human serum. J Virol 1995 Dec;69(12):7430-7436. 4. Prachar J, Hlubinova K, Kovarik A, Feldsamova A, Simkovic D. Concentration of retroviruses by low-speed centrifugation. Neoplasma 1988;35(6):651-655. 5. Miao CH, Ye X, Thompson AR. High-level factor VIII gene expression in vivo achieved by nonviral liver-specific gene therapy vectors. Hum Gene Ther 2003 Sep 20;14(14):1297-1305.