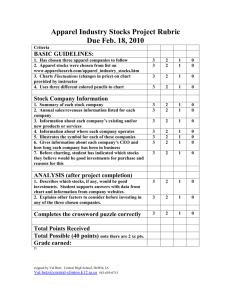
Stock Market

HIST 102: Economics Unit: Stock Market Notes
Copy down what you see below on paper- feel free to copy these with flow charts or any other method.
Anything that is written in yellow is commentary- you do not need to copy it down, just read it to help you understand.
I.
Stock Corporate Structure a.
Three Types of Business Organizations i.
Proprietorship-single owner: keep all profits: no stock ii.
Partnership: two owners: split profits: no stock iii.
Corporation: stock holders own company b.
The corporate organizational structure
Chairman-
Board of Directors
Stockholders c.
Two types of stocks and stock holders
CEO or President i.
Common: most stocks: they are riskier than preferred. These stocks are paid
II.
dead last and their dividend varies ii.
Preferred: (Pf) after corporation symbol. These stocks are paid before common stock. They have a fixed dividend rate and are more stable.
Making money from stocks a.
Two Basic Ways i.
Buying and holding on to them: accumulate dividends (a share of the profits) ii.
Buy and Sell: Buy stocks at low cost and sell when they increase to max value
- over 20 to 30 years you will make money by letting it sit b.
Why corporations go “public” and sell stock confidence that the market will be good for the foreseeable future. c.
How you buy stock i.
To expand or start a company and get capital (money) its been tough to get people to invest money because people don’t have the i.
1 st : you open an account with a stock broker
Citi Group; TD Waterhouse; SmithBarney (professionals) or yourself- (eTrade)
III.
ii.
2 nd : he/she orders you stock directly to the NYSE floor either through a floor broker or through a specialist (via phone or computer)
1.
Prices go up if demand increases: buy them
2.
Prices go down if demand decreases: sell them iii.
3 rd : once the trade is made : it goes on the ticker tape : IBM 50 and the whole world knows your purchase. TT: an ongoing record of buys and sells: today this is the ticker on the bottom the TV- this is what you see on the bottom of the page on cnn/msnbc, etc. d.
Stock’s advantage is its liquidity: the ability it can be turned into cash: it is wise that your portfolio (your list of stocks) are diversified meaning: if your stock purchases are all mixed up in computer, technical, cars, steel, you will not lose them all if a panic occurs)
The safest way to buy is through mutual funds: (less risk, less reward)
Thousands of people give $ to a fund manager and the money is invested in many different stocks. These companies research companies and invest money in companies that they have deals with. They don’t put all of your eggs in one basket- incase the market tanks, you will lose some but not all e.
Hedge Fund: A group of investors pool their money together and buy stocks in bulk:
They go after low risk low reward (75%) and high risk high reward (25%) f.
Two kinds of markets i.
A Market where prices are going up is a Bull market ii.
A Market where prices are going down is a Bear market iii.
Making money on a Bull market: sell when high and buy when low: buy with money that you don’t have: it is borrowed from the broker and paid back when the stock is sold. iv.
Making money on a down market: selling short
Buy the stock: sell when the price is high, wait until the price goes down and buy it when the price is down.
Stock Markets and the Indexes to measure whether these markets go up or down a.
Markets: 3: _Dow Jones__ ___NASDAQ__ ___Standard &Poors 500___ b.
Index: i.
Most popular is the blue chip index (sound companies who can weather a downturn in the economy (google/apple/walmart) ) It comes from a poker term where blue has more worth than white.:
1.
Dow Jones: This is the narrowest measure because it measures only 30
industrial corporations in America.
Industrial
Alcoa (steel) Microsoft
Walmart Home Depot
Transportation
Boeing/GM/Ford
Utilities
Exxon/Verizon/GE
2.
A wider sampling of the market is the S&P 500. It measures 500 stocks
3.
The broadcast (widest) measure is the NYSE Composite: all stocks
4.
AMEX composite: all 700 listings
5.
NASDAQ Composite: All NASDAQ listings- It has no real location, like the
New York Stock Exchange. It all takes place on computers and is the home of penny stocks- you can buy almost all stocks for less than $5.
IV.
Other terms: stock splits /SEC/ Buying On Margin a.
Stock Splits: Doubles your stock in companies: Price is cut in half but your number of stocks held doubles b.
SEC: Securities and Exchange Commission: The Stock Market Police! i.
Reform of FDR and 1920’s de-regulation ii.
Sets Margin Rates iii.
Screen companies: it makes sure that they are good and sound to sell stock iv.
Pooling police v.
Inside information: Information to one person where they have the edge to buy or sell before the general public has the idea to do so. c.
Economic Indicators i.
Biggest: Interest Rates
1.
As IR increase, potential buyers decrease. Profits will tend to decrease. ii.
Other
1.
Economic Indicators (per month/per quarter) Auto sales and Housing starts: Think multiplier Effect 1920’s – Autos- 2011- Black Friday sales were largest in history- expect economy to rally and people to spend money in next few weeks- good news.
2.
Unemployment decreases: 2000- 4% Today 9%
3.
CPI: Inflation rate
4.
Stock Indexes: Dow increases people buy. It signals higher productivity-
If it goes up over a few weeks, expect it to rally.
5.
Buyouts and Mergers: If x buys y: x is good to have
6.
CONFIDENCE
NOW CHECK OUT GOOGLE FINANCE AND START TO RESEARCH SOME STOCKS