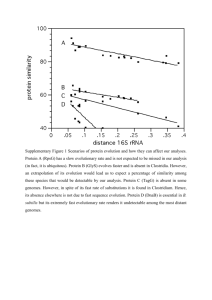
Externaldraft27Jul06
advertisement

Terminology of Developmental Abnormalities in Common Laboratory Mammals (Version 2) External Abnormalities – 27-Jul-2006 draft Region / Organ / Structure General Code Number Synonym or Related Term Generalized 10001 Anasarca Local Conjoined twins 10005 10002 Omphalosite Distended abdomen New Observation Edema Fetus Discolored New Pale New Hemorrhage Skin Head / Neck 10004 Absent 10003 Lesion Tag Acephalostomia New New 10008 Anencephaly 10010 Cranial meningocele 10016 Cranioschisis 10011 Exencephaly 10013 External aural fistula New Head Absent Domed 10009 10012 Non-preferred Definition Term An accumulation of interstitial fluid in subcutaneous connective tissue Localized accumulation of fluid Monozygotic twins with variable incomplete separation into two during cleavage or early stages of embryogenesis Abdomen appears larger than normal Skin discoloration Note Site and extent of fusion should be described May be due to presence of fluid in abdomen or enlarged organs See also “General - Pale fetus” Generalized or localized region of abnormal color (other than pale) Generalized absence of color when See also “General - Discolored compared to a normal specimen fetus” An accumulation of extravasated blood Petechia, Purpura, Ecchymosis, Hematoma Cutis aplasia Cutis lesion Acrania Acrania Acrania Acephaly Page 1 of 8 Localized region of no skin development Localized region of abnormal skin Small appendage of skin Absence of head but with the presence of mouth-like orifice in the neck region Absence of the cranial region of the head, with the brain absent or reduced Herniation of meninges through a defect in skull Fissure of the cranial region of the head with varying degrees of the brain exposed Brain protrudes outside the skull due to absence of all or part of the cranial vault An opening to a cyst produced by a persistent lateral cervical sinus or reduplicated 1st pharyngeal cleft usually located ventral to the ear. Absence of the head Cranial region of head appears more elevated and rounded than normal Erosion of brain tissue has not occurred as in Anencephaly May or may not be associated with hydrocephaly Terminology of Developmental Abnormalities in Common Laboratory Mammals (Version 2) External Abnormalities – 27-Jul-2006 draft Region / Organ / Structure Head / Neck – continued Ear Eye Observation Head Code Number Misshapen New Large Small 10015 10018 Iniencephaly 10014 Meningoencephalocele 10017 Meningohydroencepha locele Pinna Absent Fused New Pinna Cryptophthalmia Large Malpositioned Misshapen Small 10020 10021 10023 10022 10026 Macrotia Low set pinna Exophthalmos 10029 Eye bulge Microblepharia Palpebral coloboma Encephalomeni ngocele Anotia Synotia 10027 Malpositioned Open Absent 10030 10033 10025 Large Small 10028 10035 10031 10034 Non-preferred Definition Term Macrocephaly Leptocephaly, Microcephaly, Nanocephaly 10019 10024 Cyclopia Eye Synonym or Related Term Note Disproportionately large head Disproportionately small head Cephalocele, Craniocele, Encephalocele Exposure of occipital brain and upper spinal cord tissue; involves extreme retroflection of the head Herniation of brain and meninges through a cranial opening May or may not be covered by skin Herniation of brain, cerebral ventricle, and meninges through a defect in skull Absence of external ear Fusion or abnormal approximation of pinnae below the face Disproportionately large external ear Microtia Ear tab Cryptophthalm os Monophthalmia , Single eyeball, Synophthalmia Exophthalmia, Pop-eye Proptosis, Protruding eye Ablepharia Disproportionately small external ear Skin continuous over eye(s) without formation of eyelid(s) Single orbit; eyeball(s) can be absent, completely or incompletely fused May be associated with micro- or anophthalmia Snout may be absent or appear as a frontonasal appendage (proboscis) above the orbit Excessive protrusion of the eyeball Eyeball visible Abnormalities of eye prior to opening of the eyelid Short vertical dimension of eyelid A notch or fissure of the eyelid Page 2 of 8 Terminology of Developmental Abnormalities in Common Laboratory Mammals (Version 2) External Abnormalities – 27-Jul-2006 draft Face Absent whiskers Ankyloglossia New 10048 Cleft face Cleft lip Facial papillae Absent Fused Malpositioned Absent Cleft 10036 10051 New New New 10047 10056 Large 10057 Small 10058 Cleft New Large 10059 Maxilla (upper jaw) Small 10060 Mouth Absent Large Misshapen Small Atretic Fused Malpositioned Single Small 10050 10055 New 10062 10042 New 10039 10044 New Mandible (low jaw) Mandible (low jaw) Maxilla (upper jaw) Naris(es) Prosoposchisis Cheiloschisis Harelip Agnathia Gnathoschisis, Split mandible Mandibular Exognathia macrognathia, Protruding lower jaw, Prognathism Brachygnathia, Micromandible, Short lower jaw Gnathoschisis, Split maxilla Maxillary Exognathia macrognathia, Protruding upper jaw, Prognathism Maxillary micrognathia, Micromaxilla, Short upper jaw Astomia Macrostomia Wide mouth Microstomia Mononaris Page 3 of 8 Shortness or absence of the frenum of the tongue; tongue fused to the floor of the mouth Fissure of the face. Fissure of the upper lip Large or protruding lower jaw Terminology of Developmental Abnormalities in Common Laboratory Mammals (Version 2) External Abnormalities – 27-Jul-2006 draft Face – continued Palate Cleft 10052 Palate rugae High-arched Absent Misaligned 10053 New 10063 Misshapen 10064 Absent Short Malpositioned Misshapen Small Absent Large Misshapen Protruding Small Split Absent 10043 10038 10037 10040 10041 10045 10046 10054 New 10065 10061 New 20049 Proboscis Snout Tongue Tooth Asymmetric Bent Discolored Erupted Fused Large Malpositioned Not erupted Small Limb Hemimelia Limb Absent Palatoschisis, Uranoschisis One or more rugae absent Asymmetrically aligned palate rugae, Irregular palate rugae Bifurcated palate rugae, Discontinuous palate rugae, Short palate rugae Tubular projection replaces the snout Arhinia Aglossia Macroglossia May be protruding Microglossia Forked tongue Anodontia, Edentia New New New New New New New New New 10068 10066 Fissure of the palate Absence of one or more teeth Ectromelia Amelia, Ectromelia Page 4 of 8 Absence or shortening of the distal two May be further characterized, at segments of limb skeletal examination, as being fibular, radial, tibial, or ulnar Complete absence of one or more Fleshy tab may be present limbs Terminology of Developmental Abnormalities in Common Laboratory Mammals (Version 2) External Abnormalities – 27-Jul-2006 draft Limb continued Limb Bent 20067 Bowed limb, Curved limb Hyperextension 10069 Hyperflexion 10070 Flexed limb Large 10071 Macromelia, Long limb Malrotated 10072 Small 10073 Phocomelia Paw / Digit Digit(s) Digit(s) Claw The excessive extension or straightening of a limb or a joint. The excessive flexion or bending of a limb or a joint. Limb cannot be flexed Limb cannot be straightened. Limb turned toward the center (i.e., inward rotation) or the periphery (i.e., outward rotation) Micromelia, Nanomelia 10074 Acromelia Ectromelia Absent 10077 Adactyly Fused 10091 Large 10081 Malpositioned 10083 Ankylodactyly, Syndactyly, Webbed digits Dactylomegaly, Macrodactyly Clinodactyly, Camptodactyly Misshapen Pendulous Short 10085 New 10079 Supernumerary Absent Malpositioned Small 10088 10076 10082 10089 10080 Polydactyly Absent 10078 Fused 10092 Acheiria, Acheiropodia, Apodia Sympodia Ectrodactyly Paw Arthrogryposis Reduction or absence of proximal portion of limb, with the paws being attached to the trunk of the body Absence of all digits Partial or complete fusion of, or webbing between, digits Deflection of digit(s) from the central axis See Ecrtodactyly for absence of not all digits. Includes bony, cartilaginous, and/or soft tissue Includes fixed flexion deformity of digit(s). Confirmed by skeletal examination to exclude the possibility of artifact. Digit attached by a thread of tissue. Brachydactyly, Microdactyly Oligodactyly Absence of one or more, but not all, digit(s) Expected skeletal alterations include absence or shortening of phalanx(ges) Can be pendulous. Refers to distal-most tip, nail Refers to distal-most tip, nail Refers to distal-most tip, nail Expected skeletal alterations include absence of all phalanges in each affected digit Refers to hind paws in bipeds. Page 5 of 8 Terminology of Developmental Abnormalities in Common Laboratory Mammals (Version 2) External Abnormalities – 27-Jul-2006 draft Paw / Digit Paw – continued Malrotated 20084 Clubbed paw, Talipes Arthrogryposis Hyperextension 10086 Tail Trunk Tail Anus Anogenital distance (AGD) Hyperflexion 10087 Small Absent Bent Blunt-tipped Curled 10090 10093 10094 10095 20096 Discolored New Bifurcated 20097 Fleshy tab Hooked 10098 10099 Kinked Long Malpositioned Misshapen Narrow 10100 New 10101 New 10102 Short Thread-like 10103 10104 Absent 10105 Large Small Decreased New 10118 10107 Increased 10112 Flexed paw, Tarsal flexure, Carpal flexure Microcheiria Acaudia, Anury Angulated tail Paw turned toward the center (i.e., inward) or the periphery (i.e., outward) The excessive extension or Carpus or tarsus cannot be flexed. straightening of a paw. The excessive flexion or bending of a Carpus or tarsus cannot be paw. straightened. Shaped like an angle Rounded or flat at the end, not tapered Curved into nearly a full circle, or coiled Generalized or localized discoloration of tail Tail divided or split Curly tail Branched tail, Double-tipped tail, Forked tail Small tag of tissue at tip of tail. Approximately 180 degree bend or curve of the tail Localized undulation(s) of the tail Constricted tail Ring tail Brachyury Filamentous tail, Filiform tail Anal atresia, Aproctia, Imperforate anus, Nonpatent anus Should be specified as entire length or localized. Should be specified as entire length or localized. Absence or closure of the anal opening Shortened distance between anus and genital tubercle Increased distance between anus and genital tubercle Page 6 of 8 May be associated with absent/threadlike tail. Terminology of Developmental Abnormalities in Common Laboratory Mammals (Version 2) External Abnormalities – 27-Jul-2006 draft Trunk – continued Ectopia cordis 10108 Gastroschisis 10109 Genital tubercle Absent Large Misshapen Small Externalized heart Laparoschisis, Schistocelia Heart displaced outside thoracic cavity Fissure of abdominal wall, not involving the umbilicus, and usually accompanied by protrusion of viscera which may or may not be covered by a membranous sac Holorachischisis Hypospadias 10106 New New 10119 10110 10111 Kyphosis 10113 Humpback, Hunchback Lordosis 10114 Hollowback, Swayback, Saddleback Malpositioned umbilicus Narrow pelvic region New Omphalocele 20115 Prolapsed rectum New Scoliosis Short trunk 10116 10117 New Fissure of the entire spinal column Urethra opening on the underside of the penis or on the perineum Increased dorsal convexity in the curvature of the spinal column as viewed from the side Increased dorsal concavity in the curvature of the spinal column as viewed from the side Hindlimbs located more medially than normal A defect in the abdominal wall at the umbilicus, through which the intestines and other viscera protrude. These are usually covered by a thin, translucent sac composed of peritoneum and amnion. Protrusion of rectum through anus Exomphalos Lateral curvature of the spinal column Page 7 of 8 May be further defined as medial (gastroschisis) or lateral fissure (laparoschisis) Not readily apparent in fetuses or soon after birth The condition may present with ruptured sac. Not to be confused with umbilical hernia, where skin covers the defect. May be associated with large anus. May be associated with herniation of the large intestine. Terminology of Developmental Abnormalities in Common Laboratory Mammals (Version 2) External Abnormalities – 27-Jul-2006 draft Trunk – continued Spina bifida 10120 Spinal meningocele, Spinal, meningomyeloc ele, Spinal myelocele, Spinal myelomeningoc ele, Rachischisis Thoracocelosch isis Thoracogastroschisis 10121 Thoracoschisis 10122 Celosomy Thoracostenosis Umbilical hernia 10123 20124 Narrow thorax A family of defects in the closure of the May be covered with skin (spina spinal column bifida occulta); may involve protrusion of spinal cord and/or meninges Fissure of thoracic and abdominal walls with thoracic and abdominal viscera, or major parts thereof, exposed ventrally Fissure of thoracic wall Thoracic viscera may be herniated Narrowness of the thoracic region Protrusion of a segment of the Not to be confused with gastrointestinal tract and/or greater omphalocele, where no skin omentum, through a defect in the covers the defect. abdominal wall at the umbilicus, the herniated mass being covered with skin Page 8 of 8