Sc9 - b 3.2 (teacher notes)
advertisement

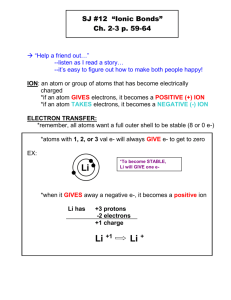
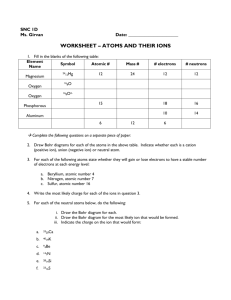
Learning outcomes: 1 I can describe the properties of ionic compounds. 2 I can name chemical formulas and write chemical formulas using only names. 3.2 Ionic compounds A metal (+ ion) and a non-metal (- ion) Ions are opposites and of course…opposites attract. They are all solids at room temperature When dissolved in water, conducts electricity. (this led to the invention of batteries) They have a distinct crystal shape. High melting point. When dissolved in water, it forms a solution of ions. Ex: Hydrogen Ion charge = 1+ ion Notation = H+ Oxygen Ion charge = 2 - ion Notation = O2- Table of Ion charge Element Copper Lead Aluminum Sodium Ion Charge Ion Notation + - A superscript ( + ) or a ( – ) are used to indicate the charge. Na and Cl Some ions can also form when certain atoms of elements combine. These ions are called polyatomic ions (poly meaning “many”). Polyatomic atoms are a group of atoms acting as one. Example: 1 carbon atom reacting with 3 oxygen atoms produces 1 carbonate group of atoms, which act as one. CO3 2- Then, when carbonate ions react with calcium atoms they produce calcium carbonate, or limestone. Ca CO3 2- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vscoYh6m46M Writing the formula of a compound using its name is a 5 step process. Sodium Chloride 1. Write the Symbols Na Cl 2. Write the charges (use the periodic table to find them) Na 1+ Cl 1- 3. Cross over the charges from top to bottom. Na 1+ Cl 1- Na1- Cl1+ 4. Eliminate the charges. Na1 Cl1 5. Simplify the numbers and eliminate the 1’s NaCl Table of formulas – I want to see the 5 steps Potassium Oxide Magnesium phosphoride Lithium floride Aluminum chloride Naming Ionic Compounds in a 5 step process Two rules: 1. The chemical name of the metal or positive ion goes first, followed by the name of the nonmetal or negative ion. 2. The name of the non-metal negative ion changes its ending to ide. NB: one exception – Where negative ions are polyatomic ions, the name remains unchanged. Some elements with more than one ion charge use a roman numeral in its chemical name to clearly show which ion is being used. Cu(II)SO4 (Copper II Sulfate) H2S LiH FeS CaCO3 Caricature analysis 1. What is the subject? 2. What conclusion can be made with this caricature? 3. What inference can be made with this caricature? Answer questions 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8 from page 149 Worksheet