Unit 3

Physics Unit Objectives: Dynamics
Dynamics I: Force Basics
Define a force and differentiate between contact forces and long-range forces.
List the four fundamental forces physicists have identified in nature and the environment in which each can be observed.
Recognize friction forces, applied forces, weight forces, etc. as manifestations of the one of the four fundamental forces.
Know the units of force: 1 N = 1 kg·m/s 2
Describe how the weight and the mass of an object are related.
Differentiate between the gravitational force weight and what is experienced as apparent weight.
Understand and apply the vector nature of forces to previous unit objectives.
Dynamics II: Newton’s Laws and Free Body Diagrams
Be able to explain Newton’s First and Second Laws and recognize their significance to problem solving.
Define and understand the concept of inertia.
Explain the meaning of “an object in equilibrium” (when F net
= 0).
Be able to draw and properly label free body diagrams for objects, according to the convention practiced in class: (e.g., F
A (M,B)
denotes the applied force of a man on a box.)
Be able to use free body diagrams to analyze whether an object is in equilibrium, and analyze the relative magnitude and direction of forces acting on an object.
Be able to use Newton’s Second Law to recognize which forces in a system are equal in magnitude, and analyze the magnitude and direction of the external forces on an object.
Solve 1-dimensional dynamics problems using newton’s laws and kinematics equations.
(elevator problems, helicopter problems, parachute problems, scale problems)
Dynamics III: 2-D Dynamics Problems and Third Law Pairs
Define the friction force and distinguish between static and kinetic friction.
Solves 2-dimensional dynamics problems using newton’s laws and kinematics equations.
(forces in four different directions)
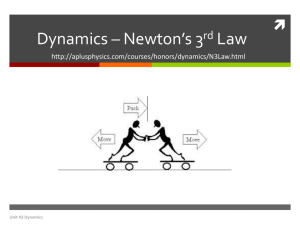
Dynamics IV: Newton’s Third Law
Explain the meaning of interaction pairs (third law pairs) of forces and how they are related by Newton’s third law.
Be able to label third law pairs in free body diagrams using x’s or dotted lines as practiced in class.
Be able to recognize when forces in a system are equal in magnitude according to
Newton’s Third Law.
Describe simple harmonic motion and explain how the acceleration due to gravity influences such motion.