Macromolecule Booklet questions
advertisement

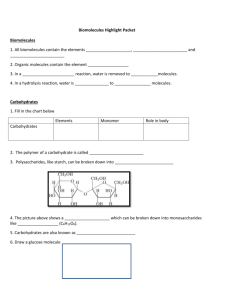
Questions about Macromolecules Proteins 1. What do proteins do? Provide three examples. 2. What are the monomers of proteins? 3. Draw the structure of the monomer. 4. What type of bond holds these monomers together? Ionic or covalent? 5. How does the structure determine the function of a protein? 6. What are enzymes? Why are they needed? 7. What are the basic elements in proteins? 8. In what types of foods are proteins usually found? Proteins 1. What do proteins do? Provide three examples. 2. What are the monomers of proteins? 3. Draw the structure of the monomer. 4. What type of bond holds these monomers together? Ionic or covalent? 5. How does the structure determine the function of a protein? 6. What are enzymes? Why are they needed? 7. What are the basic elements in proteins? 8. In what types of foods are proteins usually found? Proteins 1. What do proteins do? Provide three examples. 2. What are the monomers of proteins? 3. Draw the structure of the monomer. 4. What type of bond holds these monomers together? Ionic or covalent? 5. How does the structure determine the function of a protein? 6. What are enzymes? Why are they needed? 7. What are the basic elements in proteins? 8. In what types of foods are proteins usually found? Carbohydrates 1. What are carbohydrates? 2. What is the monomer? What are two examples? 3. Draw the structure of the monomer. 4. How do cells use carbohydrates? 5. When two monosaccharides link up, what forms? 6. What do the words monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides mean? 7. Give a name of a common disaccharide. 8. What is a condensation reaction? When does it occur? 9. What is starch? What is glycogen? What is cellulose? 10.What foods contain carbohydrates? Carbohydrates 1. What are carbohydrates? 2. What is the monomer? What are two examples? 3. Draw the structure of the monomer. 4. How do cells use carbohydrates? 5. When two monosaccharides link up, what forms? 6. What do the words monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides mean? 7. Give a name of a common disaccharide. 8. What is a condensation reaction? When does it occur? 9. What is starch? What is glycogen? What is cellulose? 10. What foods contain carbohydrates? Carbohydrates 1. What are carbohydrates? 2. What is the monomer? What are two examples? 3. Draw the structure of the monomer. 4. How do cells use carbohydrates? 5. When two monosaccharides link up, what forms? 6. What do the words monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides mean? 7. Give a name of a common disaccharide. 8. What is a condensation reaction? When does it occur? 9. What is starch? What is glycogen? What is cellulose? 10. What foods contain carbohydrates? Nucleic Acids 1. What are the monomers? 2. Draw the structure of a monomer. 3. What are the two types? 4. What do nucleic acids do for living organisms? 5. Draw each molecule. Nucleic Acids 1. What are the monomers? 2. Draw the structure of a monomer. 3. What are the two types? 4. What do nucleic acids do for living organisms? 5. Draw each molecule. Nucleic Acids 1. What are the monomers? 2. Draw the structure of a monomer. 3. What are the two types? 4. What do nucleic acids do for living organisms? 5. Draw each molecule. Lipids 1. What are lipids’ monomers? 2. What are the three main types? 3. What do our cells use lipids for? 4. What do our bodies use lipids for? 5. Draw a fat. Lipids 1. What are lipids’ monomers? 2. What are the three main types? 3. What do our cells use lipids for? 4. What do our bodies use lipids for? 5. Draw a fat. Lipids 1. What are lipids’ monomers? 2. What are the three main types? 3. What do our cells use lipids for? 4. What do our bodies use lipids for? 5. Draw a fat.