Section 9.2 - TopCatMath
advertisement

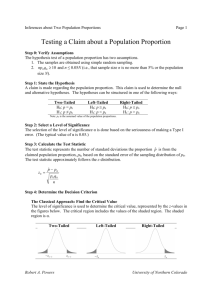
Math 160 - Cooley Intro to Statistics OCC Section 9.2 – Critical-Value Approach to Hypothesis Testing Test Statistic : The statistic used as a basis for deciding whether the null hypothesis should be rejected. Rejection region : The set of values for the test statistic that leads to rejection of the null hypothesis. Non-rejection region : The set of values for the test statistic that leads to non-rejection of the null hypothesis. Critical values : The values of the test statistic that separate the rejection and non-rejection regions. A critical value is considered part of the rejection region. Rejection Regions for all possible tests : Sign in Ha Rejection region Two-Tailed Test ≠ Both Sides Left-Tailed test < Left Side Right-Tailed Test > Right Side Obtaining Critical Values Suppose that a hypothesis test is to be performed at the significance level, . Then the critical value(s) must be chosen so that, if the null hypothesis is true, the probability is that the test statistic will fall in the rejection region. Some Important Values of z z 0.10 z 0.05 z 0.025 z 0.01 z 0.005 1.28 1.645 1.96 2.33 2.575 Exercises: The curve in the following graphs is the normal curve for the test statistic under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true. Determine the rejection region, the non-rejection region, the critical value(s), the significance level, and identify the hypothesis test as a left-tailed, a right-tailed, or a two tailed test. 1) 2) -1- Math 160 - Cooley Intro to Statistics OCC Section 9.2 – Critical-Value Approach to Hypothesis Testing Exercises: In the following exercises, determine the critical value(s) for a one-mean z-test. For each exercise, draw a graph that illustrates your answer. 3) A two-tailed test with 0.05 . 4) A left-tailed test with 0.05 . 5) A two-tailed test with 0.02 . 6) A right-tailed test with 0.02 . -2-