Autonomic Innervation to Head and Neck
advertisement

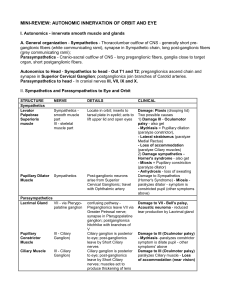
Eric Cheng Secret Study Sheet (shh…don’t tell Rod) Autonomic Innervation to Head and Neck General info on SYMPATHETICS: Preganglionic cell bodies in lateral horns of T1 to T4 ventral roots of T1 to T4 via white rami communicantes (WIN = white in, GOUT = gray out) sympathetic trunk (run upwards: thoracic cervical) 3 sympathetic cervical ganglia: ~synapse~ 1) inferior: level of 1st rib, often fused with T1 ganglion to form stellate ganglion postganglionic to gray rami of (C6), C7, and C8 2a) intermediate: lies close to vertebral a. (often called vertebral ganglion) 2b) middle: frequently absent, level of C6 postganglionic to gray rami of C5 and C6 to thyroid gland and larynx (hitchhikes along branches of thyroid aa) 3) superior: largest, anterior to transverse processes of C2 & C3, behind int. carotid a. postganglionic to gray rami of C1 to C4 supply blood vessels, pharynx (via pharyngeal plexus) postganglionics like to hitchhike with int/ext carotid aa, vertebral aa all three ganglia supply heart through cardiac plexus two cervical sympathetic trunks may be asymmetrical Distribution of Postganglionic Sympathetics: Cervical ganglia (esp. the superior) riding int. carotid a riding ext. carotid a. internal carotid nerve external carotid nerve thru carotid canal ride facial a. ride middle lateral branch medial branch submandibular meningeal a to cav sinus ganglion internal carotid plexus cavernous plexus otic ganglion submandibular sublingual tympanic plexus ciliary ganglion gland gland b.v. of parotid gland long ciliary n deep petrosal nerve dilator of pupil short ciliary n. n. of pterygoid canal vasomotor tone of ciliary blood vessels pterygopalatine ganglion Clinical Correlate: Horner’s Syndrome – lesion in cervical sympathetic pathways (pre or post-ganglionic) Symptoms: meiosis (constricted pupil), ptosis (droopy eyelid), anhydrosis (unilateral loss of sweating), & enophthalmos (recession of eyeball in socket) General info on PARASYMPATHETICS: Preganglionic cell bodies from nuclei of neurons in brain stem Postganglionic cell bodies from ganglia in the head Nucleus: Edinger Westphal (midbrain) Lacrimal Superior Salivatory (brain stem) Inferior Salivatory (medulla) Dorsal Motor Nucleus of the Vagus Nerve Nucleus Ambiguus Ganglion: Ciliary Pterygopalatine Submandibular Otic ganglia in cervical, thoracic, & abdominal Viscera Cardiac Plexus Cranial Nerve: Oculomotor (III) Facial (VII) Glossopharyngeal (IX) Vagus (X) Oculomotor Parasympathetics (III) Edinger-Westphal Nucleus (pregang cell bodies: midbrain) hitchhike with inferior branch of CN III Ciliary ganglion (suspended b/t nasociliary & inf. CN III; lateral to optic n.) ~synapse~ jump onto nasociliary n. (V1) short ciliary nerves (ride short ciliary aa) ciliaris muscle (accomodation of lens) & sphincter of pupil Facial Nerve Parasympathetics (VII) Superior Salivatory Nucleus (brain stem) Lacrimal Nucleus nervus intermedius / \ pass thru geniculate ganglion greater petrosal n. chorda tympani (joins deep petrosal: symp) pass thru petrotympanic fissure nerve of Pterygoid Canal (Vidian’s) hitchhike on lingual nerve (V3) submandibular ganglion ~synapse~ Pterygopalatine Ganglion ~synapse~ (medial to mandible; b/f lingual n. goes under Wharton’s duct) (just below maxillary of CN V) hitchhike on maxillary n. submandibular hop back on lingual n. jump to zygomaticotemporal n. gland lacrimal gland (in orbital cavity) sublingual gland & mucous glands of nasal & oral cavities Glossopharyngeal Parasympathetics (IX) Inferior Salivatory Nucleus (medulla oblongata) tympanic branch of CN IX (Jacobsen’s nerve) go to middle ear tympanic plexus lesser petrosal n. reenters cranial cavity via temporal bone, runs alongside V3 otic ganglion (medial to V3, suspended just below foramen ovale) ~synapse~ hitchhike on auriculotemporal nerve (V3) & then on branch of facial n. parotid gland note: otic ganglion also transmits (but not synapse) V3 motor fibers to supply two muscles: 1) tensor tympani, 2) tensor veli palatini Vagus Parasympathetics (X) Dorsal Motor Nucleus of the Vagus Nerve & Nucleus Ambiguus Sup/Inf Cardiac Nerves ganglia w/in viscera of neck, thorax, & abdomen Cardiac Plexus slow down heart rate no parasympathetic distribution to head or neck structures Summary of Autonomic Ganglia of the Head Ganglion Nerve Roots Ciliary para: oculomotor * short ciliary n ciliaris & pupillary sphincter sym: sup cerv ganglia int carotid n. long/short ciliary nn vasomotor tone for b.v. in eyeball sens: opthalmic n. nasociliary n. cornea, iris, ciliary body Pterygopalatine para: facial nervus intermedius greater petrosal n. nerve of pterygoid canal * V2 mucous glands in nasal/oral cavities & zygomaticotemporal n. lacrimal n. lacrimal gland sym: SCG ICN deep petrosal n. b.v. and glands in nasopharynx, nasal n. of pterygoid canal cavity, and palate sens: trigeminal ganglion V2 pterygopalatine nerves nasal cavity & palate (gen. sensation) Submandibular para: facial nervus intermedius chorda tympani lingual n * submandibular & sublingual glands sym: SCG ECN smooth muscle & b.v. in 2 glands sens: trigem ganglion V3 2 glands & their capsules Otic para: glossopharyngeal tympanic branch of IX tympanic plexus lesser petrosal n. * auriculotemporal n. VII branch parotid gland sym: SCG ECN b.v. of parotid gland sens: V3 auriculotemporal n. capsule of parotid gland motor: V3 motor fibers to tensor tympani & tensor palati * = synapse in ganglion SCG = superior cervical ganglion Target Distribution = pass thru ganglion but does NOT synapse ICN = internal carotid nerve ECN = external carotid nerve