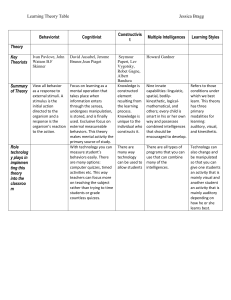
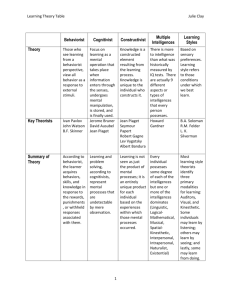
edebé
advertisement

Social Science 5 EP CLASSROOM PROGRAMMING Programming for the educational lessons edebé Legal Deposit B-17162-2014 Lesson 1. The Earth and the Universe 1. Objectives in terms of skills and in relation with the multiple intelligences 1. Know the origin and the structure of the universe and the solar system, in order to better understand the world in which we live. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist) 2. Locate the Earth as a planet of the solar system and identify its basic characteristics, its structure and the movements that it makes, in order to understand that it is the only planet with life on it, as well as the day-night sequence and the seasons. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist) 3. Understand and grasp the concepts of the meridian and parallel lines as imaginary ones that form a coordinate system in order to locate any point of the globe. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Logic and mathematics. Naturalist. Visual and spatial) 4. Identify different types of maps according to the information that they represent. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist) 5. Analyse the importance of physical activity and a healthy posture in order to have a healthy life, and adopt healthy habits for the locomotor system. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Logic and mathematics. Naturalist. Visual and spatial) 6. Participate in group activities, demonstrating a cooperative attitude and responsible participation, accepting both the differences in ideas and the contributions made in a respectful and tolerant manner. (Social science and civics. Sense of initiative and entrepreneurial spirit. To learn how to learn / Interpersonal. Intrapersonal) 2. List of contents / Evaluation criteria / Learning standards Contents • Observing and commenting on images. P Evaluation criteria • Explain how and in what form the universe and its main components came about. • Appreciating the opinion of others. V • Knowledge of the components of the universe: planets, galaxies, stars, satellites, asteroids, comets and meteorites. P • The solar system. C • Classification of the planets according to their position with respect to the Sun. C • Knowledge of the movement of rotation of revolution of the Earth around the Sun and its purpose. C • Interpretation of natural phenomena: day, night and the seasons. P • The Moon. Movement and phases. C • Eclipses: concept and types. C • Interpretation of solar eclipses. P • Knowledge and identification of the Earth's layers. C • Describe the main characteristics of the solar system, identifying the different types of stars and their characteristics. • Explain the movements of the Earth and its consequences. • Explain the different representations of the Earth and interpret both the cartographic language and the icons and symbols used in order to better understand the reality. • Carry out different exercises and presentations individually or in groups, involving the search for, collection and organisation of texts on the topic of geography. Learning standards • Defines terms related with the universe and the solar system, like: asteroid, comet, eclipse, galaxy, meteorite, orbit, planet, rotation, satellite, revolution, the Milky Way, star. • Explains the characteristics of the Sun and locates the planets according to their proximity to this star. • Defines the revolution movement of the Earth, the rotation axis and the geographic poles and associates them with the seasons of the year and their combined effect. • Explains day and night as the result of the Earth's rotation and as units to measure time. • Defines the revolution of the Moon and identifies and names the phases of the Moon. • Describes the most commonly found symbols on maps and explains the meaning of the different elements. • Carries out different exercises and presentations individually or in groups, involving the search for, collection and organisation of texts on the topic of geography. INTERDISCIPLINARY TEACHING • Culture of peace: respect for the diversity of opinions. Consideration of the importance of following sustainable habits: the use of biodegradable products. – – – – – – – – – – – – – LEARNING ACTIVITIES Reflect on the importance of using biodegradable products in relation with the environment. Study the universe: where it comes from, structure and characteristics. Observe the differences between a satellite and an asteroid. Distinguish which celestial bodies emit light. Reflect on the name of our galaxy, the Milky Way. Study the rotation and revolution movements of the Earth. Learn that the seasons exist as a result of the Earth's revolution. Identify that, as a result of the Earth's rotation, there are different time zones. Know what a leap year is. Study the Moon: characteristics, phases and eclipses. Understand how the Moon affects the tides. Reflect on the position of the Sun, the Earth and the Moon where there is a new moon. Study the four spheres of the Earth and the characteristics of each one. OTHER ACTIVITIES INITIAL EVALUATION MOTIVATION SKILLS AND MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES SUPPLEMENTARY ACTIVITIES Class group – Brainstorm the key contents of the lesson to focus the attention and enable the activation of necessary prior knowledge (in this case, to reflect on the planet Earth). – Explain to the students that in this lesson they will study the universe, they will learn about the differences between a satellite and an asteroid, they will learn the characteristics of the Moon and how it affects the tides as well as reflecting on the position of the Sun, the Earth and the Moon. THE CHALLENGE: Create your own thematic map! In pairs, the students will draw a map of their local area, which will contain the points of interest in the area. To do so, they will look for information about the places that they want to indicate on the map, making use of the Google Maps application. Finally, they will be able to upload the map online and share it with family and friends. – I am the Earth: encourage the students in their learning of the lesson by means of singing a song about looking after planet Earth. – Outer Space: know in depth about the solar system. Watch a video with the students and write down the information obtained. Then, watch the video Our Solar System and explain the most important aspects. – Earth’s rotation: watch the video about the Earth's rotation. The students will have to take a torch to class and carry out the same activity as appear in the video. Show them the globe and turn out the lights. The teacher will use a torch to show the students the difference between day and night, and they should answer the questions asked by the teacher about what will happen if there were no day. – Moon craters: encourage the students in their learning of the lesson by means of plastic art. Organised into groups and provided with the necessary materials, the students should make a paste by mixing white glue, shaving cream and white tempera. They will cover the tables with paper and spread the paste over it, leaving some parts coarser, and they will be left to dry overnight. The students will cut out the Moon in the phase that they like and will stick it to a black piece of cardboard. The remaining space can be decorated as they like. – The spheres of the Earth: encourage the students in their learning of the content by means of group work and research. They will split into four groups, depending on the sphere they have chosen (atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, geosphere). Each group will carry out an investigation about the corresponding sphere and they should then present their findings to the rest of the class. The work they carry out will be stuck up in the classroom as an exhibition. ATTENDING DIVERSITY CURRICULAR ADAPTATION: Photocopiable reinforcement files: – Complete sentences with the terms provided. – Look for words in the word search. Photocopiable consolidation files: – Make a drawing of the solar system. – Indicate if the sentences are true or false and correct the false ones. EVALUATION OF THE LESSON OF SKILLS/MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES Evaluation resources (materials for teachers) Programming and teaching instructions – Photocopiable evaluation file: • Complete the text with the corresponding Guides for continuous evaluation terms. • Draw a thematic map with its elements – Skills work / Multiple intelligences. and create a key. – Evaluation of skills / Multiple intelligences. Individual record. – Portfolio contents. – Evaluation report. ACTIVITIES PROMOTING READING AND DEVELOPMENT OF ORAL/WRITTEN EXPRESSION Reading Employing strategies for reading skills. - Silent reading (self-regulation of comprehension). - Reading aloud. Reading texts comprehensively. Reading other written texts, digitalised texts, interactive activities… to obtain information, learn, have fun and communicate. Reading parts of a text. Oral/written expression Oral activities for breaking the ice to create an appropriate atmosphere and introduce the topic. Expressing what is learnt orally/in writing appropriately by using precise vocabulary. Responding to questions linked to the contents of the lesson in writing. Listening to sounds corresponding to objects and actions and identifying them. Looking at images and commenting on them. Using open questions, information search tasks, games… Singing songs. ICT ACTIVITIES Online resources (www.edebe.com) – Interactive Digital Book. Web links Information about the Big Bang (http://links.edebe.com/6jtc). Observation of the universe using a virtual telescope (http://links.edebe.com/6jtc). Video about the Solar System (http://links.edebe.com/3urap). Video called Our Solar System (http://links.edebe.com/xxyigr). Video of the song I am the Earth (http://links.edebe.com/hn48uq). MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS FOR A POSITIVE EVALUATION – – – – Knows and defines the components of the universe. Describes the movements of the Earth and the Moon. Defines what an eclipse is. Differentiates between the different phases of the Moon. GRADING CRITERIA – – – – – Definition of the terms related with the universe and the solar system, like: asteroid, comet, eclipse, galaxy, meteorite, orbit, planet, rotation, satellite, revolution, the Milky Way, star. Explanation of the characteristics of the Sun and locating the planets according to their proximity to this star. Definition of the revolution movement of the Earth, the rotation axis and the geographic poles and to associate them with the seasons of the year and their combined effect. Explanation of day and night as a result of the Earth's rotation and as units to measure time. Definition of the revolution of the Moon and identification of the phases of the Moon. METHODOLOGY MATERIALS AND RESOURCES – – – Student’s book Social Science 5, edebé Flashcards Posters Online resources – Interactive Digital Book – Listening exercises – Flashcards – Art and Science Other resources – Activity book Social Science 5, edebé – Digital whiteboard – Educational resources – Perishable materials SPACES – TIMES – – Classroom; other spaces. Approximate time: three weeks. METHODOLOGICAL STRATEGIES The proposed methodology promotes the structure of significant learning based on the sequence: • Suitability of the presentation of the content to the linguistic competency of the students in the English language. • Initial motivation and evocation of prior knowledge. • Progressive and careful inclusion of contents by means of examples taken from everyday and contextualised situations to enable the transfer, generalisation and expansion of learning, and which connect with the skills identified. • Application of what is learnt to different activities: Applying, reasoning, working with skills and multiple intelligences, projects, cooperative group, interactive activities, reinforcement and in greater depth activities..., sequenced by levels of difficulty, and which facilitate the skills and the different cognitive styles of the students. • Different kinds of digital resources, using the digital whiteboard and the computer. These resources include activities integrated into the learning sequence, interactive activities and carefully selected Internet links. Lesson 1 STRUCTURE: – The lesson work begins with an image related to the content of the lesson and includes work eliciting prior knowledge (Look and think). – The content to be worked on is presented. – The content is developed sequentially, which is based on the image, which relates to essential realities for understanding what is being explained. – Each sequence includes a range of oral and written learning activities, for working on the content (Facts, Notebook Activities, Talk about it, Online). – Investigate is a proposal located at the end of every second lesson. This is an experimental activity linked to the content in question, which alludes to the main stages of scientific method. – An integrated task or The challenge is presented with activities for working and evaluating skills and multiple intelligences. Contextualised activities are proposed, referring to real and everyday situations for the student/s, in which they must show initiative and apply what they have learnt. During these activities different abilities and learning styles are taken into account (reading, reasoning, movement, dramatization, artistic representation...). – Final activities, both theory-based (Mental maps, Glossary) and practical (Key concepts, Test your knowledge, Pastimes) in which the student can revise the content studied. EVALUATION PROCEDURES AND TOOLS WRITTEN – – Wide-ranging student tasks carried out in the daily activities of the class. Wide-ranging student evaluation activities (book, photocopiable files...). Group work. ICT activities: interactive, Internet links. Individual dossier. ORAL – – – – Individual and collective questions. Dialogue. Oral presentation. Oral individual test. OTHERS Programming and teaching instructions Guides for continuous evaluation – Skills work / Multiple intelligences. – Evaluation of skills / Multiple intelligences. Individual record. – Portfolio contents. Valuation of the approach and processes employed Observation and valuation of the degree to which each – Evaluation report. as well as the result obtained. student participates and the quality of their involvement. – – – EVALUATION OF THE TEACHING ADAPTATION OF THE PLANNING There is consistency between what is programmed and the actual classes. There is a balanced distribution over time. The classes are adapted to the characteristics of the group. Significant learning objectives have been taken into account. Use of suitable Interdisciplinarity is considered (during activities, handling contents, etc.). methodology The methodology promotes motivation and develops the skills of students. Degree of monitoring of students. Regulation of the Suitability of resources used in class to the learning. teaching in practice The promotion criteria are agreed between the teachers. The criteria for positive evaluations are linked to the objectives and contents. The evaluation tools enable the registration of numerous learning Evaluation of what is learnt and the resulting variables. information supplied to The grading criteria are suited to the typology of planned activities. students and families The evaluation criteria and the grading criteria are made available: To the students. To the families. Measures are taken in advance to become familiar with learning difficulties. Employment of A response is made to different learning speeds and skills. measures for attending There are sufficient measures and resources available. diversity Application of special measures recommended by the teaching staff in response to psycho-pedagogical reports. Class preparation and educational materials ACADEMIC RESULTS SUGGESTIONS FOR IMPROVEMENTS PROGRAMMING SUPPORTING SEN – – – – – – … Individualised attention in the classroom for the execution of the proposed activities. Adaptation of the activities of the programme. Individualised attention inside and outside the classroom for the execution of adapted activities. Significant curricular adaptation due to SEN. Curricular adaptation for high intellectual capacity. Adaptations made to the curricular material for late inclusion in the Education System. 1 … ... 2 … … 3 … … Students 4 5 6 … … … … … … 7 … … 8 … … … Lesson 2. Mapping the Earth 1. Objectives in terms of skills and in relation with the multiple intelligences 1. Know the origin and the structure of the universe and the solar system, in order to better understand the world in which we live. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist) 2. Locate the Earth as a planet of the solar system and identify its basic characteristics, its structure and the movements that it makes, in order to understand that it is the only planet with life on it, as well as the day-night sequence and the seasons. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist) 3. Understand and grasp the concepts of the meridian and parallel lines as imaginary ones that form a coordinate system in order to locate any point of the globe. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Logic and mathematics. Naturalist. Visual and spatial) 4. Identify different types of maps according to the information that they represent. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist) 5. Analyse the importance of physical activity and a healthy posture in order to have a healthy life, and adopt healthy habits for the locomotor system. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Logic and mathematics. Naturalist. Visual and spatial) 6. Participate in group activities, demonstrating a cooperative attitude and responsible participation, accepting both the differences in ideas and the contributions made in a respectful and tolerant manner. (Social science and civics. Sense of initiative and entrepreneurial spirit. To learn how to learn / Interpersonal. Intrapersonal) 2. List of contents / Evaluation criteria / Learning standards Contents • Observing and commenting on images. P Evaluation criteria • Explain how and in what form the universe and its main components came about. • Appreciating the opinion of others. V • Parallel lines. C • Meridian lines. C • Coordinates. C • Locating coordinates on a map. P • The globe, maps and street maps. C • Scales, keys and orientation. C • Types of maps. P • Reading maps. P • Use of new technology applied to maps. C • Knowledge of the consequences of human actions on the poor use of water. V • Introduction to the scientific method: hypothesis, • Describe the main characteristics of the solar system, identifying the different types of stars and their characteristics. • Explain the movements of the Earth and its consequences. • Explain the different representations of the Earth and interpret both the cartographic language and the icons and symbols used in order to better understand the reality. • Carry out different exercises and presentations individually or in groups, involving the search for, collection and organisation of texts on the topic of geography. Learning standards • Defines terms related with the universe and the solar system, like: asteroid, comet, eclipse, galaxy, meteorite, orbit, planet, rotation, satellite, revolution, the Milky Way, star. • Explains the characteristics of the Sun and locates the planets according to their proximity to this star. • Defines the revolution movement of the Earth, the rotation axis and the geographic poles and associates them with the seasons of the year and their combined effect. • Explains day and night as the result of the Earth's rotation and as units to measure time. • Defines the revolution of the Moon and identifies and names the phases of the Moon. • Describes the most commonly found symbols on maps and explains the meaning of the different elements. • Carries out different exercises and presentations individually or in groups, involving the search for, collection and organisation of texts on the topic of geography. experimentation, analysis of the results and conclusion. P • Communication and information technology in order to obtain information. P INTERDISCIPLINARY TEACHING • Culture of peace: respect for the diversity of opinions. • Our heritage: reflection on the need to look after the environment and not to pollute water. – – – – – – – – – – – LEARNING ACTIVITIES Study the planet Earth: its form and composition. Identify what the parallel and meridian lines are and what they are used for. Learn how to use a coordinates map and find certain points on the map. Study what a map is and its types and know its advantages and inconveniences. Know what a globe is and observe its advantages and inconveniences. Learn what a thematic map consists of and know about the different types: weather map, road map, economic map... Identify what type of map is used to represent the River Ebro, the elevation of a hill, the capital of Andalusia, the population of Europe, the streets of Valladolid, the towns of Catalonia and the weather. Learn how to read a map: the scale, the key and the orientation. Distinguish what maps and sketches are reflect on their use. Understand the importance of technology in the creation of maps: satellite maps and the GPS system. Reflect on the negative impact of pouring waste down the drain, the toilet or the shower (water pollution). OTHER ACTIVITIES INITIAL EVALUATION MOTIVATION SKILLS AND MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES SUPPLEMENTARY ACTIVITIES Class group – Brainstorm the key contents of the lesson to focus the attention and enable the activation of necessary prior knowledge (in this case, to reflect on the land surface and the different methods for measuring and studying it). – Explain to the students that in this lesson they will learn about what planet Earth is made up of, what the parallel and meridian lines are, how to use a coordinates map, the different types of maps and how to read them, as well as the importance of technology in the creation of maps. THE CHALLENGE: Create your own thematic map! In pairs, the students will draw a map of their local area, which will contain the points of interest in the area. To do so, they will look for information about the places that they want to indicate on the map, making use of the Google Maps application. Finally, they will be able to upload the map online and share it with family and friends. – Longitude and Latitude Song: encourage the students in their learning of the lesson content by means of a song. – Parallel and meridians: watch the video of the proposed link and write, together, a summary that summarises the information. – Types of maps: know about the different types of maps. After completing interactive maps on the proposed link, the students will have to draw two types of maps in pairs and then present them to the class. – Poster: after showing the lesson poster, the students will have to look closely at a map and trace a route, indicating which roads or paths they have chosen and the geographic accidents that cross them. Each group will present their route to the class. – Look after our water: be aware of the importance of the responsible use of water. The students, in pairs, will have to look for information about the poor use of water on our planet, as well as contributing ideas in order to prevent the consequences deriving from such poor consumption. ATTENDING DIVERSITY CURRICULAR ADAPTATION: Photocopiable reinforcement files: – – – – Write what parallel and meridian lines are and what they are used for. Explain the meaning of coordinates. Describe the meaning of water pollution and name four things that can be done at home to avoid this problem. Explain if they recycle at home and what they do to recycle. Photocopiable consolidation files: – Invent a name and draw a thematic map, showing its main characteristics. – Draw their bedroom. EVALUATION OF THE LESSON Evaluation resources (materials for teachers) – Photocopiable evaluation file: • To complete the text with the corresponding terms. • To draw a thematic map with its elements and to create a key. OF SKILLS/MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES Programming and teaching instructions Guides for continuous evaluation – Skills work / Multiple intelligences. – Evaluation of skills / Multiple intelligences. Individual record. – Portfolio contents. – Evaluation report. ACTIVITIES PROMOTING READING AND DEVELOPMENT OF ORAL/WRITTEN EXPRESSION Reading Employing strategies for reading skills. - Silent reading (self-regulation of comprehension). - Reading aloud. Reading texts comprehensively. Reading other written texts, digitalised texts, interactive activities… to obtain information, learn, have fun and communicate. Reading parts of a text. Oral/written expression Oral activities for breaking the ice to create an appropriate atmosphere and introduce the topic. Expressing what is learnt orally/in writing appropriately by using precise vocabulary. Responding to questions linked to the contents of the lesson in writing. Listening to sounds corresponding to objects and actions and identifying them. Looking at images and commenting on them. Using open questions, information search tasks, games… Singing songs. ICT ACTIVITIES Online resources (www.edebe.com) – Interactive Digital Book. Web links Looking for coordinates (http://links.edebe.com/7zd6). Observation and differentiation of the different types of maps (http://links.edebe.com/6mndbh). Video called Earth, Parallels and Meridians (http://links.edebe.com/xkvi2a). Interactive map (http://links.edebe.com/x56) MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS FOR A POSITIVE EVALUATION – – – – – Defines the concept of longitude and latitude. Knows the different representation of the Earth and what they are used for. Distinguishes the imaginary lines and their use in order to find a specific point. Finds different points on Earth by using the meridian and parallel lines. Identifies and classifies the different types of maps. GRADING CRITERIA – – Description of the most commonly used symbols on maps and explanation of the meaning of the different elements. Carrying out exercises and presentations both individually and in groups, involving the search for, collection and organisation of texts of a geographical nature. METHODOLOGY MATERIALS AND RESOURCES – – – Student’s book Social Science 5, edebé Flashcards Posters Online resources – Interactive Digital Book – Listening exercises – Flashcards – Art and Science Other resources – Activity book Social Science 5, edebé – Digital whiteboard – Educational resources – Perishable materials SPACES - TIMES – – Classroom; other spaces. Approximate time: three weeks. METHODOLOGICAL STRATEGIES The proposed methodology promotes the structure of significant learning based on the sequence: • Suitability of the presentation of the content to the linguistic competency of the students in the English language. • Initial motivation and evocation of prior knowledge. • Progressive and careful inclusion of contents by means of examples taken from everyday and contextualised situations to enable the transfer, generalisation and expansion of learning, and which connect with the skills identified. • Application of what is learnt to different activities: Applying, reasoning, working with skills and multiple intelligences, projects, cooperative group, interactive activities, reinforcement and in greater depth activities..., sequenced by levels of difficulty, and which facilitate the skills and the different cognitive styles of the students. • Different kinds of digital resources, using the digital whiteboard and the computer. These resources include activities integrated into the learning sequence, interactive activities and carefully selected Internet links. Lesson 2 STRUCTURE: – The lesson work begins with an image related to the content of the lesson and includes work eliciting prior knowledge (Look and think). – The content to be worked on is presented. – The content is developed sequentially, which is based on the image, which relates to essential realities for understanding what is being explained. – Each sequence includes a range of oral and written learning activities, for working on the content (Facts, Notebook Activities, Talk about it, Online). – Investigate is a proposal located at the end of every second lesson. This is an experimental activity linked to the content in question, which alludes to the main stages of scientific method. – An integrated task or The challenge is presented with activities for working and evaluating skills and multiple intelligences. Contextualised activities are proposed, referring to real and everyday situations for the student/s, in which they must show initiative and apply what they have learnt. During these activities different abilities and learning styles are taken into account (reading, reasoning, movement, dramatization, artistic representation...). – Final activities, both theory-based (Mental maps, Glossary) and practical (Key concepts, Test your knowledge, Pastimes) in which the student can revise the content studied. EVALUATION PROCEDURES AND TOOLS WRITTEN – – Wide-ranging student tasks carried out in the daily activities of the class. Wide-ranging student evaluation activities (book, photocopiable files...). Group work. ICT activities: interactive, Internet links. Individual dossier. ORAL – – – – Individual and collective questions. Dialogue. Oral presentation. Oral individual test. OTHERS Programming and teaching instructions Guides for continuous evaluation – Skills work / Multiple intelligences. – Evaluation of skills / Multiple intelligences. Individual record. – Portfolio contents. Valuation of the approach and processes employed Observation and valuation of the degree to which each – Evaluation report. as well as the result obtained. student participates and the quality of their involvement. – – – EVALUATION OF THE TEACHING ADAPTATION OF THE PLANNING There is consistency between what is programmed and the actual classes. There is a balanced distribution over time. The classes are adapted to the characteristics of the group. Significant learning objectives have been taken into account. Use of suitable Interdisciplinarity is considered (during activities, handling contents, etc.). methodology The methodology promotes motivation and develops the skills of students. Degree of monitoring of students. Regulation of the teaching Suitability of resources used in class to the learning. in practice The promotion criteria are agreed between the teachers. The criteria for positive evaluations are linked to the objectives and contents. Evaluation of what is learnt The evaluation tools enable the registration of numerous learning variables. The grading criteria are suited to the typology of planned activities. and the resulting information supplied to The evaluation criteria and the grading criteria are made available: students and families To the students. To the families. Measures are taken in advance to become familiar with learning difficulties. Employment of measures A response is made to different learning speeds and skills. There are sufficient measures and resources available. for attending diversity Application of special measures recommended by the teaching staff in response to psycho-pedagogical reports. Class preparation and educational materials ACADEMIC RESULTS SUGGESTIONS FOR IMPROVEMENTS PROGRAMMING SUPPORTING SEN – – – – – – … Individualised attention in the classroom for the execution of the proposed activities. Adaptation of the activities of the programme. Individualised attention inside and outside the classroom for the execution of adapted activities. Significant curricular adaptation due to SEN. Curricular adaptation for high intellectual capacity. Adaptations made to the curricular material for late inclusion in the Education System. 1 … ... 2 … … 3 … … Students 4 5 6 … … … … … … 7 … … 8 … … … Lesson 3. Climate and Landscape 1. Objectives in terms of skills and in relation with the multiple intelligences 1. Recognise the characteristics that are observed and measured in order to know about and forecast the atmospheric weather. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist science. Logic - Mathematics) 2. Know about the different climates in the world, their location and characteristics. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist science) 3. Know the climates of Spain, their location, their characteristics and the landscape that defines them. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist science) 4. Know the symbols of the Spanish state. (Awareness and cultural expressions / Visual and spatial) 5. Know what rights are, as well as duties and freedom, and reflect on the relation that exists between them. (Social science and civics / Interpersonal) 6. Know the organisation of the territory in Spain (autonomous communities and cities, provinces and townships). Find the autonomous communities and cities and the provinces on a map of Spain. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist science) 7. Participate in group activities, demonstrating a cooperative attitude and responsible participation, accepting differences with respect and tolerance of the ideas and contributions made from others. (Social science and civics. Initiative and entrepreneurial spirit. To learn how to learn / Intrapersonal) 2. List of contents / Evaluation criteria / Learning standards Contents • Observing and commenting on images. P Evaluation criteria • Identify some basic characteristics of the different types of climate of the Spanish territory. • Appreciating the opinion of others. V • Factors of atmospheric weather: temperature, wind, humidity and precipitation. C • The climate and its factors: altitude, latitude and distance with respect to the sea. C • Climates and temperatures according to the latitude. C • Climates and landscapes in Spain. C • Meteorological factors and of the landscape for each climate zone. P • Awareness of the effects of global warming. V • Explain the most relevant characteristics of temperatures and rainfall of the climates found in Spain, and identify the characteristics of landscapes that are typically found in each climatic zone. Learning standards • Identifies and understands how climate factors act: proximity to the equator, altitude over sea level and the influence of the climate. • Relates relief and altitude with the influence of the sea in its action as climatic factors. • Explain the consequences that human actions have on climatic change. • Describes the different climates: oceanic, subtropical, Mediterranean, continental and high mountainous and associates them with the areas of land where they are found. • Identify the most important political institutions in Spain, its functions and the different rights and freedoms that are found in the constitution. • Identifies different types of elections as a way to participate in the running of the township, the autonomous community and Spain. • Identify and assess the cultural and popular manifestations that coexist in the area, recognising their evolution in time and assessing them as social cohesion elements. • Develops his sense of empathy towards cultural manifestations that enrich the life of our society. • Participates in group activities, adopting a responsible, constructive and supportive attitude, respecting the basic principles of democracy. INTERDISCIPLINARY TEACHING • Culture of peace: respect for the diversity of opinions. • Our heritage: identification of actions with which the emission of harmful emissions in the atmosphere can be reduced. – – – – – – – – – – – LEARNING ACTIVITIES Learn what time is and some of its elements: temperature, humidity, wind, air pressure and precipitation. Know what a climate consists of and which factors influence it. Study the climatic zones and their characteristics. Locate countries in the corresponding climatic zone. Learn what a climograph is, what it is used for and how to read it. Study the different climates that exist in Spain and their main characteristics. Draw climographs representing different types of climate. Investigate plants that exist in each climatic zone of Spain. Reflect on global climate change and its causes. Identify human actions that release harmful emissions into the atmosphere. Consider some initiatives with which the amount polluting gases produced can be reduced. OTHER ACTIVITIES INITIAL EVALUATION MOTIVATION SKILLS AND MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES SUPPLEMENTARY ACTIVITIES Class group – Brainstorm the key contents of the lesson to focus the attention and enable the activation of necessary prior knowledge (in this case, to reflect on the climate and the adaptation of plants and animals to the climate). – Explain to students that in this lesson they will learn about weather, climate, climatic zones, climographs and the different climates in Spain, and they will learn about global climate change, its causes, consequences and ways in which it can be prevented. THE CHALLENGE: Make a weather station! The students will build a weather station in order to study the climate of their local area: including an anemometer, a pluviometer, as well as other instruments. The teacher will encourage them to create other instruments that may be useful found at the proposed links. Finally, they will make a table in which they will write down the information about the climate in their area for a week. – Cool it down: encourage students in the learning of the lesson by means of a song about global warming. – Story: The Wind and the Sun: access the proposed link and reflect on the message that is conveyed by the story being told. – Atmospheric phenomena: learn about the causes and effects of different climatic phenomena. The teacher will write the following words on the board: earthquakes, volcanoes, hurricanes, tornadoes, wildfires, sea geyser. In work groups, the students will choose one of the climatic phenomena with the aim to carry out an investigation, which should then be presented to their classmates. – Autochthonous plants: encourage the students to find out which of the plants in their local area are native. They should choose one, draw it, colour it in, and write the most important information about it. – My climate zone map: draw a climatic map of Spain using a colour code to represent the different climate zones. The students should indicate the corresponding autonomous communities and add brief sentences describing the climate of each community. – Global warming essay: check that the students have understood the content of the lesson studied. After carefully watching the video from the online activity, the students should write an essay, which will later be stuck to a poster. ATTENDING DIVERSITY CURRICULAR ADAPTATION: Photocopiable reinforcement files: – Complete the sentences. – Match each term with the corresponding explanation. Photocopiable consolidation files: – Look for information about different climates and write about them. – Write all of the information known by the student about the greenhouse effect. EVALUATION OF THE LESSON Evaluation resources (materials for teachers) – Photocopiable evaluation file: • Draw a climograph and answer the questions. • Answer various questions. • Describe the celebration held for the patron saint of their city. OF SKILLS/MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES Programming and teaching instructions Guides for continuous evaluation – Skills work / Multiple intelligences. – Evaluation of skills / Multiple intelligences. Individual record. – Portfolio contents. – Evaluation report. ACTIVITIES PROMOTING READING AND DEVELOPMENT OF ORAL/WRITTEN EXPRESSION Reading Employing strategies for reading skills. - Silent reading (self-regulation of comprehension). - Reading aloud. Reading texts comprehensively. Reading other written texts, digitalised texts, interactive activities… to obtain information, learn, have fun and communicate. Reading parts of a text. Oral/written expression Oral activities for breaking the ice to create an appropriate atmosphere and introduce the topic. Expressing what is learnt orally/in writing appropriately by using precise vocabulary. Responding to questions linked to the contents of the lesson in writing. Listening to sounds corresponding to objects and actions and identifying them. Looking at images and commenting on them. Using open questions, information search tasks, games… Singing songs. ICT ACTIVITIES Online resources (www.edebe.com) – Interactive Digital Book. Web links Looking at a climate map of the world (http://links.edebe.com/pzsdw). Activity to encourage students to learn the lesson content (http://links.edebe.com/c9t). MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS FOR A POSITIVE EVALUATION – – – – – – Explains the difference between atmospheric weather and climate. Understands the concept of climate and learns about the factors that it depends on. Identifies and understands how these climate factors behave: the proximity to the equator, the altitude over sea level and the influence of the sea. Knows what a climograph is and how to read it. Knows and differentiates between different types of climates in Spain. Is aware of the causes and consequences of climate change. GRADING CRITERIA – – – Identification and understanding of climate factors: the proximity to the equator, the altitude over sea level and the influence of the sea. Knowledge of the relation between relief, altitude and the influence of the sea in its action as climatic factors. Description of different climates: oceanic, subtropical, Mediterranean, continental and high mountainous and the association between these climates and the areas that have such climates. METHODOLOGY MATERIALS AND RESOURCES – – – Student’s book Social Science 5, edebé Flashcards Posters Online resources – Interactive Digital Book – Listening exercises – Flashcards – Art and Science Other resources – Activity book Social Science 5, edebé – Digital whiteboard – Educational resources – Perishable materials SPACES - TIMES – – Classroom; other spaces. Approximate time: three weeks. METHODOLOGICAL STRATEGIES The proposed methodology promotes the structure of significant learning based on the sequence: • Suitability of the presentation of the content to the linguistic competency of the students in the English language. • Initial motivation and evocation of prior knowledge. • Progressive and careful inclusion of contents by means of examples taken from everyday and contextualised situations to enable the transfer, generalisation and expansion of learning, and which connect with the skills identified. • Application of what is learnt to different activities: Applying, reasoning, working with skills and multiple intelligences, projects, cooperative group, interactive activities, reinforcement and in greater depth activities..., sequenced by levels of difficulty, and which facilitate the skills and the different cognitive styles of the students. • Different kinds of digital resources, using the digital whiteboard and the computer. These resources include activities integrated into the learning sequence, interactive activities and carefully selected Internet links. Lesson 3 STRUCTURE: – The lesson work begins with an image related to the content of the lesson and includes work eliciting prior knowledge (Look and think). – The content to be worked on is presented. – The content is developed sequentially, which is based on the image, which relates to essential realities for understanding what is being explained. – Each sequence includes a range of oral and written learning activities, for working on the content (Facts, Notebook Activities, Talk about it, Online). – Investigate is a proposal located at the end of every second lesson. This is an experimental activity linked to the content in question, which alludes to the main stages of scientific method. – An integrated task or The challenge is presented with activities for working and evaluating skills and multiple intelligences. Contextualised activities are proposed, referring to real and everyday situations for the student/s, in which they must show initiative and apply what they have learnt. During these activities different abilities and learning styles are taken into account (reading, reasoning, movement, dramatization, artistic representation...). – Final activities, both theory-based (Mental maps, Glossary) and practical (Key concepts, Test your knowledge, Pastimes) in which the student can revise the content studied. EVALUATION PROCEDURES AND TOOLS WRITTEN – – Wide-ranging student tasks carried out in the daily activities of the class. Wide-ranging student evaluation activities (book, photocopiable files...). Group work. ICT activities: interactive, Internet links. Individual dossier. ORAL – – – – Individual and collective questions. Dialogue. Oral presentation. Oral individual test. OTHERS Programming and teaching instructions Guides for continuous evaluation – Skills work / Multiple intelligences. – Evaluation of skills / Multiple intelligences. Individual record. – Portfolio contents. Valuation of the approach and processes employed Observation and valuation of the degree to which each – Evaluation report. as well as the result obtained. student participates and the quality of their involvement. – – – EVALUATION OF THE TEACHING ADAPTATION OF THE PLANNING There is consistency between what is programmed and the actual classes. There is a balanced distribution over time. The classes are adapted to the characteristics of the group. Significant learning objectives have been taken into account. Use of suitable Interdisciplinarity is considered (during activities, handling contents, etc.). methodology The methodology promotes motivation and develops the skills of students. Degree of monitoring of students. Regulation of the teaching Suitability of resources used in class to the learning. in practice The promotion criteria are agreed between the teachers. The criteria for positive evaluations are linked to the objectives and contents. Evaluation of what is learnt The evaluation tools enable the registration of numerous learning variables. The grading criteria are suited to the typology of planned activities. and the resulting information supplied to The evaluation criteria and the grading criteria are made available: students and families To the students. To the families. Measures are taken in advance to become familiar with learning difficulties. Employment of measures A response is made to different learning speeds and skills. There are sufficient measures and resources available. for attending diversity Application of special measures recommended by the teaching staff in response to psycho-pedagogical reports. Class preparation and educational materials ACADEMIC RESULTS SUGGESTIONS FOR IMPROVEMENTS PROGRAMMING SUPPORTING SEN – – – – – – … Individualised attention in the classroom for the execution of the proposed activities. Adaptation of the activities of the programme. Individualised attention inside and outside the classroom for the execution of adapted activities. Significant curricular adaptation due to SEN. Curricular adaptation for high intellectual capacity. Adaptations made to the curricular material for late inclusion in the Education System. 1 … ... 2 … … 3 … … Students 4 5 6 … … … … … … 7 … … 8 … … … Lesson 4. Spain and Europe 1. Objectives in terms of skills and in relation with the multiple intelligences 1. Recognise the characteristics that are observed and measured in order to know about and forecast the atmospheric weather. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist science. Logic - Mathematics) 2. Know about the different climates in the world, their location and characteristics. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist science) 3. Know the climates of Spain, their location, their characteristics and the landscape that defines them. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist science) 4. Know the symbols of the Spanish state. (Awareness and cultural expressions / Visual and spatial) 5. Know what rights are, as well as duties and freedom, and reflect on the relation that exists between them. (Social science and civics / Interpersonal) 6. Know the organisation of the territory in Spain (autonomous communities and cities, provinces and townships). Find the autonomous communities and cities and the provinces on a map of Spain. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist science) 7. Participate in group activities, demonstrating a cooperative attitude and responsible participation, accepting differences with respect and tolerance of the ideas and contributions made from others. (Social science and civics. Initiative and entrepreneurial spirit. To learn how to learn / Intrapersonal) 2. List of contents / Evaluation criteria / Learning standards Contents • Observing and commenting on images. P Evaluation criteria • Identify some basic characteristics of the different types of climate of the Spanish territory. • Appreciating the opinion of others. V • Knowledge of the political organisation of Spain as a democratic country. C • Autonomous communities in Spain. P • Autonomous government, autonomous parliament and High Courts of Justice. P • Provinces and townships of Spain. C • Explain the most relevant characteristics of temperatures and rainfall of the climates found in Spain, and identify the characteristics of landscapes that are typically found in each climatic zone. Learning standards • Identifies and understands how climate factors act: proximity to the equator, altitude over sea level and the influence of the climate. • Relates relief and altitude with the influence of the sea in its action as climatic factors. • Explain the consequences that human actions have on climatic change. • Describes the different climates: oceanic, subtropical, Mediterranean, continental and high mountainous and associates them with the areas of land where they are found. • Identify the most important political institutions in Spain, its functions and the different rights and freedoms that are found in the constitution. • Identifies different types of elections as a way to participate in the running of the township, the autonomous community and Spain. • Identify and assess the cultural and popular manifestations that coexist in the area, recognising their evolution in time and assessing them as social cohesion elements. • Develops his sense of empathy towards cultural manifestations that enrich the life of our society. • Knowledge of the cultural diversity in Spain. C • Identification of the European Union as an economic and political union of 28 states. C • Rights and obligations as a Spanish and European citizen. C • Scientific method: hypothesis, experimentation, analysis of results and conclusion. P • Communication technology. P • Participates in group activities, adopting a responsible, constructive and supportive attitude, respecting the basic principles of democracy. INTERDISCIPLINARY TEACHING • Culture of peace: respect for the diversity of opinions. Identification of duties and rights as Spanish and European citizens. LEARNING ACTIVITIES – – – – – – – – – – – Know Spain: the constitution of 1978 and the general elections. Study the separation of powers: executive power (President of the government and Council of Ministers), legislative power (Congress of Deputies and the Senate) and judicial power (Supreme Court and Constitutional Court). Know how Spain is organised administratively: the autonomous communities, the Statute of Autonomy and the automatic elections. Identify the similarities between the organisation of an autonomous community and that of Spain. Know the provinces and how they are divided: city councils and the local elections. Identify festivities and traditions in Spain and their cultural importance. Recognise different languages that are spoken in Spain. Know about the European Union: origin and structure. Study the single market: the Euro. Learn which are European institutions, and their characteristics and operation. Reflect on our rights and obligations as Spanish and European citizens. OTHER ACTIVITIES INITIAL EVALUATION MOTIVATION SKILLS AND MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES SUPPLEMENTARY ACTIVITIES Class group – Brainstorm the key contents of the lesson to focus the attention and enable the activation of necessary prior knowledge (in this case, to reflect on Spain as a democratic country and on the European Union). – Explain to the students that in this lesson they will study how Spain is organised politically, its autonomous communities and provinces, the European Union and its institutions, as well as the rights and obligations of Spanish and European citizens. THE CHALLENGE: Make a weather station! The students will build a weather station in order to study the climate of their local area: including an anemometer, a pluviometer, as well as other instruments. The teacher will encourage them to create other instruments that may be useful found at the proposed links. Finally, they will make a table in which they will write down the information about the climate in their area for a week. – Ode to Joy: identify the countries belonging to the European Union by means of watching a video. – Flag picture: draw the flags of Spain and the European Union, writing on each one some important historical information. – Giant map of Spain: draw the silhouette of the map of Spain on a poster. The students will draw the autonomous communities with a pencil. The poster will be completed little by little as more information is obtained about the country. – Election day: organise elections to be held in class with the help of your teacher. Two or three candidates should be presented, which will choose a group of people so that they work together on writing their speeches. A day will be dedicated to the elections. Simple pamphlets will be used for voting and the votes will be counted. – Spain’s festivities and traditions: know the traditions and festivities of a province or autonomous community by means of looking up information. The students should present the most important information to the class. – What is the EU?: reinforce what has been learnt in the lesson by means of the access to the proposed link. The students should copy the most important sentences onto a poster, which will be hung up in the classroom under a poster made between them all with the heading: European Union. – Human Rights investigation: carry out an investigation about human rights by means of working in groups. The students will be able to choose any topic related with the activity, the information for which will be presented on a large poster. ATTENDING DIVERSITY CURRICULAR ADAPTATION: Photocopiable reinforcement files: – Draw and colour in the map of the Iberian peninsula. – Draw and write the names of the autonomous communities. Photocopiable consolidation files: – Draw a conceptual map, defining the organisation of Spain: Spanish citizens and parliamentary monarch. EVALUATION OF THE LESSON Evaluation resources (materials for teachers) – Photocopiable evaluation file: • Draw a climograph and answer the questions. • Answer various questions. • Describe the celebration held for the patron saint of their city. OF SKILLS/MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES Programming and teaching instructions Guides for continuous evaluation – Skills work / Multiple intelligences. – Evaluation of skills / Multiple intelligences. Individual record. – Portfolio contents. – Evaluation report. ACTIVITIES PROMOTING READING AND DEVELOPMENT OF ORAL/WRITTEN EXPRESSION Reading Employing strategies for reading skills. - Silent reading (self-regulation of comprehension). - Reading aloud. Reading texts comprehensively. Reading other written texts, digitalised texts, interactive activities… to obtain information, learn, have fun and communicate. Reading parts of a text. Oral/written expression Oral activities for breaking the ice to create an appropriate atmosphere and introduce the topic. Expressing what is learnt orally/in writing appropriately by using precise vocabulary. Responding to questions linked to the contents of the lesson in writing. Listening to sounds corresponding to objects and actions and identifying them. Looking at images and commenting on them. Using open questions, information search tasks, games… Singing songs. ICT ACTIVITIES Online resources (www.edebe.com) – Interactive Digital Book. Web links Solve a puzzle (http://links.edebe.com/7mu23v). Watch the video called Capitals of Europe, music: European anthem (http://links.edebe.com/mesa). MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS FOR A POSITIVE EVALUATION – – – Identifies the most important Spanish political institutions. Learns about the most important democratic principles established in the constitution. Identifies the different types of elections as a way of participating in the running of the township, the autonomous community and the State. GRADING CRITERIA – – – Identification of the different types of elections as a way of participating in the running of the township, the autonomous community and Spain. Developing empathy towards cultural manifestations that enrich the life of our society. Participation in group activities adopting a responsible, constructive and supportive attitude, respecting the basic principles of democracy. METHODOLOGY MATERIALS AND RESOURCES – – – Student’s book Social Science 5, edebé Flashcards Posters Online resources – Interactive Digital Book – Listening exercises – Flashcards – Art and Science Other resources – Activity book Social Science 5, edebé – Digital whiteboard – Educational resources – Perishable materials SPACES - TIMES – – Classroom; other spaces. Approximate time: three weeks. METHODOLOGICAL STRATEGIES The proposed methodology promotes the structure of significant learning based on the sequence: • Suitability of the presentation of the content to the linguistic competency of the students in the English language. • Initial motivation and evocation of prior knowledge. • Progressive and careful inclusion of contents by means of examples taken from everyday and contextualised situations to enable the transfer, generalisation and expansion of learning, and which connect with the skills identified. • Application of what is learnt to different activities: Applying, reasoning, working with skills and multiple intelligences, projects, cooperative group, interactive activities, reinforcement and in greater depth activities..., sequenced by levels of difficulty, and which facilitate the skills and the different cognitive styles of the students. • Different kinds of digital resources, using the digital whiteboard and the computer. These resources include activities integrated into the learning sequence, interactive activities and carefully selected Internet links. Lesson 4 STRUCTURE: – The lesson work begins with an image related to the content of the lesson and includes work eliciting prior knowledge (Look and think). – The content to be worked on is presented. – The content is developed sequentially, which is based on the image, which relates to essential realities for understanding what is being explained. – Each sequence includes a range of oral and written learning activities, for working on the content (Facts, Notebook Activities, Talk about it, Online). – Investigate is a proposal located at the end of every second lesson. This is an experimental activity linked to the content in question, which alludes to the main stages of scientific method. – An integrated task or The challenge is presented with activities for working and evaluating skills and multiple intelligences. Contextualised activities are proposed, referring to real and everyday situations for the student/s, in which they must show initiative and apply what they have learnt. During these activities different abilities and learning styles are taken into account (reading, reasoning, movement, dramatization, artistic representation...). – Final activities, both theory-based (Mental maps, Glossary) and practical (Key concepts, Test your knowledge, Pastimes) in which the student can revise the content studied. EVALUATION PROCEDURES AND TOOLS WRITTEN – – Wide-ranging student tasks carried out in the daily activities of the class. Wide-ranging student evaluation activities (book, photocopiable files...). Group work. ICT activities: interactive, Internet links. Individual dossier. ORAL – – – – Individual and collective questions. Dialogue. Oral presentation. Oral individual test. OTHERS Programming and teaching instructions Guides for continuous evaluation – Skills work / Multiple intelligences. – Evaluation of skills / Multiple intelligences. Individual record. – Portfolio contents. Valuation of the approach and processes employed Observation and valuation of the degree to which each – Evaluation report. as well as the result obtained. student participates and the quality of their involvement. – – – EVALUATION OF THE TEACHING ADAPTATION OF THE PLANNING There is consistency between what is programmed and the actual classes. There is a balanced distribution over time. The classes are adapted to the characteristics of the group. Significant learning objectives have been taken into account. Use of suitable Interdisciplinarity is considered (during activities, handling contents, etc.). methodology The methodology promotes motivation and develops the skills of students. Degree of monitoring of students. Regulation of the teaching Suitability of resources used in class to the learning. in practice The promotion criteria are agreed between the teachers. The criteria for positive evaluations are linked to the objectives and contents. Evaluation of what is learnt The evaluation tools enable the registration of numerous learning variables. The grading criteria are suited to the typology of planned activities. and the resulting information supplied to The evaluation criteria and the grading criteria are made available: students and families To the students. To the families. Measures are taken in advance to become familiar with learning difficulties. Employment of measures A response is made to different learning speeds and skills. There are sufficient measures and resources available. for attending diversity Application of special measures recommended by the teaching staff in response to psycho-pedagogical reports. Class preparation and educational materials ACADEMIC RESULTS SUGGESTIONS FOR IMPROVEMENTS PROGRAMMING SUPPORTING SEN – – – – – – … Individualised attention in the classroom for the execution of the proposed activities. Adaptation of the activities of the programme. Individualised attention inside and outside the classroom for the execution of adapted activities. Significant curricular adaptation due to SEN. Curricular adaptation for high intellectual capacity. Adaptations made to the curricular material for late inclusion in the Education System. 1 … ... 2 … … 3 … … Students 4 5 6 … … … … … … 7 … … 8 … … … Lesson 5. Population 1. Objectives in terms of skills and in relation with the multiple intelligences 1. Know factors that intervene in the evolution of a population. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Logic, Mathematics. Naturalist science) 2. Know how to calculate the birth rate, death rate and natural growth, net migration and actual growth. (Mathematics. Science and technology. Digital / Logic, Mathematics. Naturalist science) 3. Know the different types of graphs used to represent the data for a population. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist science. Visual and spatial) 4. Know the different types of immigration and reflect on the causes and consequences of the immigration. (Social science and civics / Interpersonal) 5. Locate the Middle Ages in history and know the historical facts that mark a start and an end. (Social science and civics / Interpersonal) 6. Know the origin of Al-Andalus, their social organisation and the different phases of Muslim presence in the Iberian Peninsula. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist science) 7. Participate in group activities by demonstrating a cooperative attitude and responsible participation, accepting the differences with respect and tolerance towards ideas and the contributions of others. (Social science and civics. Initiative and entrepreneurial spirit. To learn how to learn / Interpersonal) 2. List of contents / Evaluation criteria / Learning standards Contents • Observing and commenting on images. P • Population density. P • Death rate, birth rate and natural growth. C • Population graphs: bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, pictograms, pyramids. C • Work population and sectors. C • Respect for diversity. V Evaluation criteria • Explain the Spanish and European demographic distribution, representing population pyramids, bar charts and pie charts. • Describe the migratory movements of the Spanish population by means of a conceptual map that includes the rural exodus, the emigration to Europe and the arrival of emigrants to our country. • Describe the most important historical stages of the Middle Ages in the Iberian Peninsula, and differentiate, after the collapse of the Visigoth monarchy, the evolution of Al-Andalus and the Christian Kingdoms. • Explain the influence of the influence of the Arabic civilisation in Spain and specify their artistic, cultural and economic legacy. Learning standards • Explains the concept of population density and knows how to work it out. • Reads a population pyramid and describes the demographic factors of population growth. • Explains his opinion about the influence of the immigrants on the social changes that occur in the affected countries. • Locates the most important historical phases of the Middle Ages in the Iberian Peninsula: Visigoth Kingdom, Al-Andalus and the Christian Kingdoms. • Describes the artistic, cultural and economic legacy of Al-Andalus. INTERDISCIPLINARY TEACHING • Culture of peace: respect for the diversity of people without establishing differences based on culture, religion or ethnic group. Identification of the causes of emigration, like for example poverty, starvation or war. – – – – – – – – – – – LEARNING ACTIVITIES Know the population density and how to calculate it: population density in Spain. Identify the change of population with the passing of time. Learn how to calculate the birth rate, the death rate, natural growth, migratory growth and total growth. Study different types of graphs in order to represent a population and its suitability: bar chart, line graph, pie chart, pictogram, pyramid. Analyse how the population in Spain has changed. Know what the population in Europe is like and its characteristics. Observe the factors that cause population growth in Europe. Identify the relation between population and work: active and inactive population. Recognise which are the productive sectors and their relation with the population. Reflect on diversity and respect towards other people without establishing differences based on their culture, religion or ethnic group. Identify some causes for which people are obliged to emigrate. OTHER ACTIVITIES INITIAL EVALUATION MOTIVATION SKILLS AND MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES SUPPLEMENTARY ACTIVITIES Class group – Brainstorm the key contents of the lesson to focus the attention and enable the activation of necessary prior knowledge (in this case, to reflect on the population on Earth and human needs like food or education). – Explain to the students that in this lesson they will study population density, growth rate, death rate, natural growth, migratory growth and total growth, the different types of graphs used to represent the population, population in Europe, as well as the relation between population, work and productive sectors. THE CHALLENGE: Discover the history of the place where you live! The students will look for information about the city, province or autonomous community where they live. To do so, they should work in pairs and choose a place of interest or building in the Middle Ages and the age of discoveries and looking for information and pictures about it. Finally, they will create a digital archive that contains the collected information and they will present it before their classmates. – Population Equation Song: encourage students in the learning of the lesson content by means of a song. The students should write the most important sentences from the content on colour posters that will be presented to the class. – Emigration: carry out a brief investigation about the emigration of the Spanish in the 1950s, 1960s and 1970s. The students will look up information about the topic they are designated and will be able to include all of the most important historical data. – Population graphs: check that students know how to read a population graph. Observe the information from the proposed link and answer the questions together. – Human numbers through times: access the proposed link and read the information about the worldwide population with the aim to discuss it. – Getting Geographic: carry out the activity on the link. The students will make a graph representing Canada and Bolivia and will compare the information obtained. – Overpopulation: know the problems involved with overpopulation by means of watching the proposed link. The students, after discussing the most important information, will be split into groups and will carry out a research task about the consequences of overpopulation. The information should be presented on a poster or in a power point presentation. – Racism: the teacher will ask students about the meaning of the term to then have a brief debate about it. The students should carry out a research task about racism, in which the causes and consequences of racism will be included... ATTENDING DIVERSITY CURRICULAR ADAPTATION: Photocopiable reinforcement files: – Calculate the population density of some cities based on the data provided. – Calculate the natural growth, migratory growth and total growth of various cities by means of the data provided. Photocopiable consolidation files: – Look for information about the meaning of the words and write four causes of emigration. – Write down jobs from the primary, secondary and tertiary sectors. EVALUATION OF THE LESSON Evaluation resources (materials for teachers) – Photocopiable evaluation file: • Write the definition of a population pyramid and explain how many types of pyramids exist. • Calculate natural growth, migratory growth and the total growth for various situations given. • Identify the main artistic characteristics and name a piece of artwork. OF SKILLS/MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES Programming and teaching instructions Guides for continuous evaluation – Skills work / Multiple intelligences. – Evaluation of skills / Multiple intelligences. Individual record. – Portfolio contents. – Evaluation report.. ACTIVITIES PROMOTING READING AND DEVELOPMENT OF ORAL/WRITTEN EXPRESSION Reading Employing strategies for reading skills. - Silent reading (self-regulation of comprehension). - Reading aloud. Reading texts comprehensively. Reading other written texts, digitalised texts, interactive activities… to obtain information, learn, have fun and communicate. Reading parts of a text. Oral/written expression Oral activities for breaking the ice to create an appropriate atmosphere and introduce the topic. Expressing what is learnt orally/in writing appropriately by using precise vocabulary. Responding to questions linked to the contents of the lesson in writing. Listening to sounds corresponding to objects and actions and identifying them. Looking at images and commenting on them. Using open questions, information search tasks, games… Singing songs. ICT ACTIVITIES Online resources (www.edebe.com) – Interactive Digital Book. Web links Activity about population growth (http://links.edebe.com/tk). Indicative map of the European population (http://links.edebe.com/crz). History of the coexistence between porcupines (http://links.edebe.com/czia8). Video Population Equation Song (http://links.edebe.com/bgv5). Activity about a population graph (http://links.edebe.com/riz3gw). Activity about the worldwide population (http://links.edebe.com/xvd). Activity about a population pyramid (http://links.edebe.com/32). Activity about overpopulation (http://links.edebe.com/w3). MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS FOR A POSITIVE EVALUATION – – – – – Knows how to calculate population density. Identifies the phenomena that cause population change. Knows how to calculate the natural growth rate, migratory movement rate and actual growth rate. Defines the different economic sectors and identifies activities that belong to each sector. Reads and understands different types of population pyramids and graphs. GRADING CRITERIA – – Explanation of the concept of population density and calculating it. Reading a population pyramid and describing the demographic factors of population growth. – Explaining personal opinion about the influence of immigrants on social changes that occur in the affected countries. METHODOLOGY MATERIALS AND RESOURCES – – – Student’s book Social Science 5, edebé Flashcards Posters Online resources – Interactive Digital Book – Listening exercises – Flashcards – Art and Science Other resources – Activity book Social Science 5, edebé – Digital whiteboard – Educational resources – Perishable materials SPACES - TIMES – – Classroom; other spaces. Approximate time: three weeks. METHODOLOGICAL STRATEGIES The proposed methodology promotes the structure of significant learning based on the sequence: • Suitability of the presentation of the content to the linguistic competency of the students in the English language. • Initial motivation and evocation of prior knowledge. • Progressive and careful inclusion of contents by means of examples taken from everyday and contextualised situations to enable the transfer, generalisation and expansion of learning, and which connect with the skills identified. • Application of what is learnt to different activities: Applying, reasoning, working with skills and multiple intelligences, projects, cooperative group, interactive activities, reinforcement and in greater depth activities..., sequenced by levels of difficulty, and which facilitate the skills and the different cognitive styles of the students. • Different kinds of digital resources, using the digital whiteboard and the computer. These resources include activities integrated into the learning sequence, interactive activities and carefully selected Internet links. Lesson 5 STRUCTURE: – The lesson work begins with an image related to the content of the lesson and includes work eliciting prior knowledge (Look and think). – The content to be worked on is presented. – The content is developed sequentially, which is based on the image, which relates to essential realities for understanding what is being explained. – Each sequence includes a range of oral and written learning activities, for working on the content (Facts, Notebook Activities, Talk about it, Online). – Investigate is a proposal located at the end of every second lesson. This is an experimental activity linked to the content in question, which alludes to the main stages of scientific method. – An integrated task or The challenge is presented with activities for working and evaluating skills and multiple intelligences. Contextualised activities are proposed, referring to real and everyday situations for the student/s, in which they must show initiative and apply what they have learnt. During these activities different abilities and learning styles are taken into account (reading, reasoning, movement, dramatization, artistic – representation...). Final activities, both theory-based (Mental maps, Glossary) and practical (Key concepts, Test your knowledge, Pastimes) in which the student can revise the content studied. EVALUATION PROCEDURES AND TOOLS WRITTEN – – Wide-ranging student tasks carried out in the daily activities of the class. Wide-ranging student evaluation activities (book, photocopiable files...). Group work. ICT activities: interactive, Internet links. Individual dossier. ORAL – – – – Individual and collective questions. Dialogue. Oral presentation. Oral individual test. OTHERS Programming and teaching instructions Guides for continuous evaluation – Skills work / Multiple intelligences. – Evaluation of skills / Multiple intelligences. Individual record. – Portfolio contents. Valuation of the approach and processes employed Observation and valuation of the degree to which each – Evaluation report. as well as the result obtained. student participates and the quality of their involvement. – – – EVALUATION OF THE TEACHING ADAPTATION OF THE PLANNING There is consistency between what is programmed and the actual classes. There is a balanced distribution over time. The classes are adapted to the characteristics of the group. Significant learning objectives have been taken into account. Use of suitable Interdisciplinarity is considered (during activities, handling contents, etc.). methodology The methodology promotes motivation and develops the skills of students. Degree of monitoring of students. Regulation of the teaching Suitability of resources used in class to the learning. in practice The promotion criteria are agreed between the teachers. The criteria for positive evaluations are linked to the objectives and contents. Evaluation of what is learnt The evaluation tools enable the registration of numerous learning variables. The grading criteria are suited to the typology of planned activities. and the resulting information supplied to The evaluation criteria and the grading criteria are made available: students and families To the students. To the families. Measures are taken in advance to become familiar with learning difficulties. Employment of measures A response is made to different learning speeds and skills. There are sufficient measures and resources available. for attending diversity Application of special measures recommended by the teaching staff in response to psycho-pedagogical reports. Class preparation and educational materials ACADEMIC RESULTS SUGGESTIONS FOR IMPROVEMENTS PROGRAMMING SUPPORTING SEN – – – – – – … Individualised attention in the classroom for the execution of the proposed activities. Adaptation of the activities of the programme. Individualised attention inside and outside the classroom for the execution of adapted activities. Significant curricular adaptation due to SEN. Curricular adaptation for high intellectual capacity. Adaptations made to the curricular material for late inclusion in the Education System. 1 … ... 2 … … 3 … … Students 4 5 6 … … … … … … 7 … … 8 … … … Lesson 6. Medieval times and the Age of Discovery 1. Objectives in terms of skills and in relation with the multiple intelligences 1. Know factors that intervene in the evolution of a population. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Logic, Mathematics. Naturalist science) 2. Know how to calculate the birth rate, death rate and natural growth, net migration and actual growth. (Mathematics. Science and technology. Digital / Logic, Mathematics. Naturalist science) 3. Know the different types of graphs used to represent the data for a population. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist science. Visual and spatial) 4. Know the different types of immigration and reflect on the causes and consequences of the immigration. (Social science and civics / Interpersonal) 5. Locate the Middle Ages in history and know the historical facts that mark a start and an end. (Social science and civics / Interpersonal) 6. Know the origin of Al-Andalus, their social organisation and the different phases of Muslim presence in the Iberian Peninsula. (Mathematics. Science and technology / Naturalist science) 7. Participate in group activities by demonstrating a cooperative attitude and responsible participation, accepting the differences with respect and tolerance towards ideas and the contributions of others. (Social science and civics. Initiative and entrepreneurial spirit. To learn how to learn / Interpersonal) 2. List of contents / Evaluation criteria / Learning standards Contents • Observing and commenting on images. P • Appreciating the opinion of others. V • Different cities in the Iberian Peninsula. C • Territorial distribution of the Christian cities and those of Al-Andalus. C • Social groups and life in the times of Al-Andalus. C • The Christian Monarchs: evolution and society. C • The early Middle Ages: society. C • Romanic art. C • The late Middle Ages: cities and professions. C • Mudejar art. C • Route of Santiago de la Compostela. C • The Age of Discovery. C • The Catholic Monarchs and the Reconquista. C Evaluation criteria • Explain the Spanish and European demographic distribution, representing population pyramids, bar charts and pie charts. • Describe the migratory movements of the Spanish population by means of a conceptual map that includes the rural exodus, the emigration to Europe and the arrival of emigrants to our country. • Describe the most important historical stages of the Middle Ages in the Iberian Peninsula, and differentiate, after the collapse of the Visigoth monarchy, the evolution of Al-Andalus and the Christian Kingdoms. • Explain the influence of the influence of the Arabic civilisation in Spain and specify their artistic, cultural and economic legacy. Learning standards • Explains the concept of population density and know how to work it out. • Reads a population pyramid and describe the demographic factors of population growth. • Explains his opinion about the influence of the immigrants on the social changes that occur in the affected countries. • Locates the most important historical phases of the Middle Ages in the Iberian Peninsula: Visigoth Kingdom, Al-Andalus and the Christian Kingdoms. • Describes the artistic, cultural and economic legacy of Al-Andalus. • Identification of the main characteristics of the empire. C • Domestic and foreign policy of the empire. C • Expansion of the empire. C • Renaissance, baroque, the Golden Age. C • An attitude that demonstrates interest and participation. V • Information and communication technology. P • Active participation. V INTERDISCIPLINARY TEACHING • Culture of peace: respect for the different religions, cultures and traditions and adopting positive and compassionate attitudes regarding people from other countries or cultures. – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – LEARNING ACTIVITIES Study when the Middle Ages in the Iberian Peninsula take place and the cultural principles that were experienced during that period: the Visigoths. Analyse what Al-Andalus was: origin and development. Learn what the Al-Andalus society was like and the different religions that existed. Understand what the lifestyle in the times of Al-Andalus were like: architecture, science, technology and agriculture. Study the Christian Kingdoms and the end of the Middle Ages: the Castilla Crown, the Crown of Aragon and the Navarra Kingdom. Learn what the society was like during the times of the Christian Kingdoms. Reflect on the multi-culturalism in Medieval Times: the coexistence of Jews, Christians and Muslims. Analyse the evolution of the Christian Monarchs during the Middle Ages: rural feudalism and the Roman style in the development of the cities and the Gothic style. Study the main characteristics of the Mudejar style. Know what the Order of San George was: the route of Santiago de la Compostela. Analyse the age of discovery: technical advances. Know the different explorations made by Castilla and Portugal. Study the Catholic Monarchs and the main historical milestones of their reign: the Know about Christopher Columbus; the discovery of America. Analyse the Spanish Empire and its evolution since 1516 until 1580. Know the domestic and foreign policy during the age of the reign of Charles I and Philip II. Study the American colonies and their development. Learn about what the renaissance and baroque consisted of and their artistic repercussions. Analyse what the Spanish Golden Age was and identify some of its main characteristics. OTHER ACTIVITIES INITIAL EVALUATION MOTIVATION SKILLS AND MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES SUPPLEMENTARY ACTIVITIES Class group – Brainstorm the key contents of the lesson to focus the attention and enable the activation of necessary prior knowledge (in this case, to reflect on the Middle Ages and the medieval society). – Explain to students that in this lesson they will study the Middle Ages in Spain, Al-Andalus, the Christian Kingdoms, the Roman, Gothic and Mudejar styles; the Order of Saint George and the route to Santiago de la Compestela; the Catholic Monarchs; Christopher Columbus and the discovery of America; the Spanish Empire and the Golden Age. THE CHALLENGE: Discover the history of the place where you live! The students will look for information about the city, province or autonomous community where they live. To do so, they should work in pairs and choose a place of interest or building in the Middle Ages and the age of discoveries and looking for information and pictures about it. Finally, they will create a digital archive that contains the collected information and they will present it before their classmates. – Rats and the plague song: know in detail about the causes and consequences of the black death. Watch the video of the proposed link. The teacher will ask students, in pairs, to investigate the said epidemic. – The Rise of the Christian Kingdom: copy, draw and colour in the four maps and the time line from the student's book, scale, and stick them together with the pyramid of Al-Andalus from the previous activity. The students, in groups, will expand the information with the help of the book and they will present it on posters that will be stuck together with the corresponding map. – Mural Work: gather all of the possible information in order to make a gigantic poster where the teacher will draw a pyramid like the one in the student's book. In groups, they will focus on various aspects (clergy, noblemen y peasants) and they will present the information collected on posters that will be stuck together with the pyramid. – The Way of St. James: acquire more knowledge about the route of Santiago de Compostela based on watching the documentary video. The students will write a brief essay about it that will be presented to the class. – King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella of Spain: know the history of the Catholic Monarchs by watching a video. The students should write down the most important information and share their ideas. ATTENDING DIVERSITY – The Spanish Empire: watch the video from the proposed link. The students should write down important information that will be shared at the end of the video. The teacher will ask students to write the most important sentences in order to form mobiles. – The Golden Age: look for information about the Spanish Golden Age and write a brief essay about it. CURRICULAR ADAPTATION: Photocopiable reinforcement files: – Complete a text with the terms provided. – Answer various questions. Photocopiable consolidation files: – Look for information on the internet and write a text about the Reconquista of the Christian Kingdom. – Look on the internet for works of art or inventions corresponding with different historic periods. EVALUATION OF THE LESSON Evaluation resources (materials for teachers) – Photocopiable evaluation file: • Write the definition of a population pyramid and explain how many types of pyramids exist. • Calculate natural growth, migratory growth and the total growth for various situations given. • Identify the main artistic characteristics and name a piece of artwork. OF SKILLS/MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES Programming and teaching instructions Guides for continuous evaluation – Skills work / Multiple intelligences. – Evaluation of skills / Multiple intelligences. Individual record. – Portfolio contents. – Evaluation report. ACTIVITIES PROMOTING READING AND DEVELOPMENT OF ORAL/WRITTEN EXPRESSION Reading Employing strategies for reading skills. - Silent reading (self-regulation of comprehension). - Reading aloud. Reading texts comprehensively. Reading other written texts, digitalised texts, interactive activities… to obtain information, learn, have fun and communicate. Reading parts of a text. Oral/written expression Oral activities for breaking the ice to create an appropriate atmosphere and introduce the topic. Expressing what is learnt orally/in writing appropriately by using precise vocabulary. Responding to questions linked to the contents of the lesson in writing. Listening to sounds corresponding to objects and actions and identifying them. Looking at images and commenting on them. Using open questions, information search tasks, games… Singing songs. ICT ACTIVITIES Online resources (www.edebe.com) – Interactive Digital Book. Web links Map of the territories governed by the Umayyad Caliphate (http://links.edebe.com/7cq). The routes of Christopher Columbus (http://links.edebe.com/qz). Looking at a map of the Maya, Aztec and Inca Empires (http://links.edebe.com/3w). Video about the black death (http://links.edebe.com/jp). Activity about the history of Islam in Spain (http://links.edebe.com/qkr7). Activity about the Order of Saint George (http://links.edebe.com/h9). Activity about the Catholic Monarchs (http://links.edebe.com/ja4g). Activity about the Spanish Empire (http://links.edebe.com/6texfx). MINIMUM REQUIREMENTS FOR A POSITIVE EVALUATION – – – – – – Locates events that took place in space and time in the history of Spain in the Middle Ages. Places the most important historical phases of the Middle Ages in the Iberian Peninsula in chronological order. Explains the process of the Reconquista and repopulation of the Christian Kingdoms. Describes the artistic and cultural legacy of Al-Andalus. Knows about and explains the importance of the route of Santiago de la Compostela. Describes and differentiates between the three monotheisms: Judaism, Christianity and Islam. GRADING CRITERIA – – Locating the most important historical phases of the Middle Ages in the Iberian Peninsula: Visigoth Kingdom, Al-Andalus and the Christian Kingdoms. Description of the artistic, cultural and economic legacy of Al-Andalus. METHODOLOGY MATERIALS AND RESOURCES – – – Student’s book Social Science 5, edebé Flashcards Posters Online resources – Interactive Digital Book – Listening exercises – Flashcards – Art and Science Other resources – Activity book Social Science 5, edebé – Digital whiteboard – Educational resources – Perishable materials SPACES - TIMES – – Classroom; other spaces. Approximate time: three weeks. METHODOLOGICAL STRATEGIES The proposed methodology promotes the structure of significant learning based on the sequence: • Suitability of the presentation of the content to the linguistic competency of the students in the English language. • Initial motivation and evocation of prior knowledge. • Progressive and careful inclusion of contents by means of examples taken from everyday and contextualised situations to enable the transfer, generalisation and expansion of learning, and which connect with the skills identified. • Application of what is learnt to different activities: Applying, reasoning, working with skills and multiple intelligences, projects, cooperative group, interactive activities, reinforcement and in greater depth activities..., sequenced by levels of difficulty, and which facilitate the skills and the different cognitive styles of the students. • Different kinds of digital resources, using the digital whiteboard and the computer. These resources include activities integrated into the learning sequence, interactive activities and carefully selected Internet links. Lesson 6 STRUCTURE: – The lesson work begins with an image related to the content of the lesson and includes work eliciting prior knowledge (Look and think). – The content to be worked on is presented. – The content is developed sequentially, which is based on the image, which relates to essential realities for understanding what is being explained. – Each sequence includes a range of oral and written learning activities, for working on the content (Facts, Notebook Activities, Talk about it, Online). – Investigate is a proposal located at the end of every second lesson. This is an experimental activity linked to the content in question, which alludes to the main stages of scientific method. – An integrated task or The challenge is presented with activities for working and evaluating skills and multiple intelligences. Contextualised activities are proposed, referring to real and everyday situations for the student/s, in which they must show initiative and apply what they have learnt. During these activities different abilities and learning styles are taken into account (reading, reasoning, movement, dramatization, artistic representation...). – Final activities, both theory-based (Mental maps, Glossary) and practical (Key concepts, Test your knowledge, Pastimes) in which the student can revise the content studied. EVALUATION PROCEDURES AND TOOLS WRITTEN – – Wide-ranging student tasks carried out in the daily activities of the class. Wide-ranging student evaluation activities (book, photocopiable files...). Group work. ICT activities: interactive, Internet links. Individual dossier. ORAL – – – – Individual and collective questions. Dialogue. Oral presentation. Oral individual test. OTHER Programming and teaching instructions Guides for continuous evaluation – Skills work / Multiple intelligences. – Evaluation of skills / Multiple intelligences. Individual record. – Portfolio contents. Valuation of the approach and processes employed Observation and valuation of the degree to which each – Evaluation report. as well as the result obtained. student participates and the quality of their involvement. – – – EVALUATION PROCEDURES AND TOOLS ADAPTATION OF THE PLANNING There is consistency between what is programmed and the actual classes. There is a balanced distribution over time. The classes are adapted to the characteristics of the group. Significant learning objectives have been taken into account. Use of suitable Interdisciplinarity is considered (during activities, handling contents, etc.). methodology The methodology promotes motivation and develops the skills of students. Degree of monitoring of students. Regulation of the teaching Suitability of resources used in class to the learning. in practice The promotion criteria are agreed between the teachers. The criteria for positive evaluations are linked to the objectives and contents. Evaluation of what is learnt The evaluation tools enable the registration of numerous learning variables. The grading criteria are suited to the typology of planned activities. and the resulting information supplied to The evaluation criteria and the grading criteria are made available: students and families To the students. To the families. Measures are taken in advance to become familiar with learning difficulties. Employment of measures A response is made to different learning speeds and skills. There are sufficient measures and resources available. for attending diversity Application of special measures recommended by the teaching staff in response to psycho-pedagogical reports. Class preparation and educational materials ACADEMIC RESULTS SUGGESTIONS FOR IMPROVEMENTS PROGRAMMING SUPPORTING SEN – – – – – – … Individualised attention in the classroom for the execution of the proposed activities. Adaptation of the activities of the programme. Individualised attention inside and outside the classroom for the execution of adapted activities. Significant curricular adaptation due to SEN. Curricular adaptation for high intellectual capacity. Adaptations made to the curricular material for late inclusion in the Education System. 1 … ... 2 … … 3 … … Students 4 5 6 … … … … … … 7 … … 8 … … …