Heeren book astronomy
advertisement

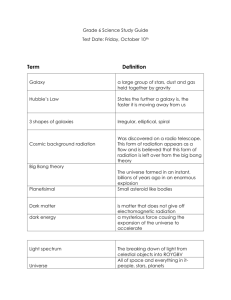
Heeren, Fred Show Me God, Vol 1. Day star Pub. Olanthe, Ka. 2004 Meteorites allegedly from Mars were fond in 1961 and later. In 1994 they were studied by David McKay who argued they had fossils or signs of life. (p5-30). Currently there is disagreement on whether they are fossils or just mineral and crystal deposits. There is now a known psychological disorder associated with alien abduction, associated with ones disillusionment with the present world and seeking deliverance. (P72,77) Copy p 76 on 12 arguments against there being life on other planets. The fist cause must be eternal (transcending time) p.91 Ex. 3:14 I am, John 8:58, Ps. 90:2 everlasting God. A finely tuned universe requires a creator with purpose and thus personhood p.95, Spinoza says first cause, God must be independent, unlimited and all powerful p.90. Scientists note that ¾ of the universe is hydrogen and ¼ is helium. However stars burning from the start of the universe would be able to convert only 3% of the hydrogen to helium; however the initial high density and temperature sate of the big bang could have created more helium.(p 104) The most distant galaxies appear irregular and immature and have some quasars. The nearer galaxies have spiral and elliptical shapes and appear middle aged. (p 104-5) Supporting the big bang or precise expansion is the smooth microware background radiation in all directions and the Hubble expansion.(107,111) According to Einstein’s equations, once matter crunches into a singularity as in a black hole, mater can never leave and neither can light. (113). This cause a problem for the universe banging from a singularity. S Hawking says gamma rays come out. An alternate explanation for observed gamma ray bursts is the merging of 2 neutron stars that produces bursts(114). Failed supernovae may become black holes. J. Ostriker, a Princeton cosmologist sated “If you extrapolate backing time, the universe will became so dense that you will need quantum mechanics. And we know we don’t have a quantum theory of gravity. At what time does this become a serious problem? At the Plank time. So we cannot extrapolate back our current theories before Plank time.” Plank time is 10-43 sec. after the big bang.(p 117) This science and space time does not go before the big bang, only philosophy can. John Mather, NASA’s principal scientist for cosmic background radiation, stated “We have equations that describe the transformation of one thing into another, but we have no equation whatever for creating space and time.”(p.119) Ps. 19:1-4 Three lines of evidence support creation: Thermodynamics, Einstein’s general theory of relativity, and the observation of astronomy. P.127 the 1st law of thermo. E=MC2 the conservation of mass and energy. Gen. 2:1 “Thus the heavens and the earth were completed in all their vast array.” The 2nd law says the contents of the universe are becoming less ordered and more random. The useful energy will be used up. The entropy (the amount of disorder) increases with time. The earth magnetic field is decreasing and its rotation is slowing. Ps. 102:25-26 “In the beginning you laid the foundations of the earth, and the heavens are the work of your hands. 26 They will perish, but you remain; they will all wear out like a garment. Like clothing you will change them and they will be discarded. “Isaiah 34:4 All the heavenly bodies will dissolve. The skies will roll up like a scroll, and their stars will all wither as leaves wither on the vine, and foliage on the fig tree.” Isa. 51:6 “There are 2 main points to be made about the theory of general relativity: 1. All the testable predictions that it makes have been proven correct, and 2. The equations of general relativity imply that the universe cannot be static, but must be expanding or contracting.” P.131 Einstein stated that gravity is a consequence of the effect of mass on space time and that mass curves the space time field. P 133 his equations for this have been proven true by observations. Large masses can slow down time and curve the path of light to follow the curved space time field. Einstein originally added a cosmological constant to his equations, so the universe could be static and the problem of a beginning avoided. In 1922 A. Friedmann found an algebraic error in the proofs for a static universe. Independently W. de Sitter found Einstein’s equations required that the universe be expanding. Later Einstein called his cosmological constant a great blunder and agreed that the universe was expanding and implied a beginning and God.p.135 Modern science’s most favored theory of beginnings, the big bang theory, describes a theory that defies atheism and pantheism, but harmonizes in some ways with the Bible. p140 George Smoot, leader of the COBE team, stated “There is no doubt that a parallel exists between the big bang as an event and the Christian notion of creation form nothing.” Astronomer Vesto Sipher first discovered in 1914 the red shifts and noted that the faint nebulae had red shifts while the closer stars did not.p141 Dr. Edwin Hubble studied the red shifts form 1920-1935 at Mt. Wilson observatory. He found that the universe was expanding and there was a linear relationship between distance and velocity with a galaxy twice as far away expanding away at twice the velocity.p.142-6 W. De Sitter found a solution to Einstein’s general relativity equations that implied this velocity distance relationship. Now the consensus is that the universe exploded and is slightly decelerating. P147 It is theorized that the Hubble constant, Ho, if known exactly, would determine the size and age of the universe. The latest estimates are universe is 13.7 billion yrs old and spans 27.4(visible universe) light yrs across. Age estimate range from 8-20 billion yrs as there is some variability in calibrating standards used. P 150 The precise relationship of distance to velocity in all directions points to common staring point. The known laws of physics break down at a density of 1096 times that of water and at the Planck time of 10-43 sec. old.p152 Such a density would be considered a singularity. G.Lemaitre is credited with being the father of the big bang theory in 1933. p152 R. Alpher and R. Herman calculated in 1948 that the big bang would leave microware radiation at temperature of about 50 Kelvin.183 In 1965 two Bell scientists, A. Penzias and R. Wilson, discovered by accident a microwave background in all directions of about 30 Kelvin.153 R. Dicke and other scientists had predicted that the big bang would leave a uniform microwave radiation.154 According to standard cosmology the temperature in the early bang would be too high for atoms and not until after 300,000 yrs would it decrease to 30000 the atoms could form. If the bang theory was true, the radiation would come from a blackbody as a perfect heat source. Any source like a star or supernova with light would not be like a blackbody. The radiation from a blackbody emits in a specific radiation intensity and wavelength pattern 158 In 1990 NASA’s COBE (Cosmic Background Explorer) satellite made precise measurements and confirmed an exact blackbody radiation curve in all directions. This supports the idea that the starting mass-energy was in equilibrium at a single temperature. In 1993 it was determined that the radiation varied by only .03% and thus accounts for 99.97% of the universe’s energy. p160 Other stars and universe bodies are not a source of this type of radiation. This forms a very strong argument for the big bang. The big Bang theory also predicts that the elements should be 75% hydrogen and about 25% helium and this is confirmed by spectroscopic measurements. P161 Helium does not form now from stars in these quantities, but the very hot temperatures of the bang account for the 25% Helium and small amounts of heavier elements. Quasars are also termed radio stars and are the most distant and powerful objects. They may have been created earliest and have a red shift of .16 and contain hydrogen.p162 Recent theories of cosmic background radiation say it should have very small ripples 1/90000. p165 This inhomogeneity is to account for the galaxies and not just uniform matter. This was found by careful examination of the COBE data and data form a U-2 plane with DMR. These ripples are also called the cosmic seeds or fingerprints of God which are very finely orchestrated. p 168. The U-2 data also indicated the milky was galaxy is being pulled throught space at about a million mph towards a great attractor in the Hydra-Centaurus super cluster. P169 The inflationary model of the big bang was put for by Alan Guth of MIT in 1979 and appears consistent with all observations. In this model there are many transformations in seconds and minutes and matter is formed over years and galaxies over thousand and billions of yrs.p170 Copy pg 171,175 models show that the COBE(light decoupled from matter) was created 300,000 yrs after the bang and the stars and galaxies after that. Other inflationary models are being worked on and it is a developing scinece.p172 Chuck Steidel of Caltech thinks he can see evidence of early galaxy formation by using different light filters and that the universe it changing. P384-6 Heeren argues that cosmology supports creation of the cosmos over ages.181-93 Some say that God created the universe with the appearance of age, but this would be deceptive. Some say that the speed of light changed during creation, but there is no evidence for this. The stars in the milky galaxy are 100,000 light yrs apart, and the observable universe must be at least 62 million light yrs across. He does not accept the ides that God created starlight in transit to give them the appearance of age.p186 C.I. Scofield proposed the gap theory and that the first creative act refers to a dateless past. A.H Strong also supports this view in his Systematic Theology and is Encyclopedia of Bible Difficulties. P187 Gen 2:4 uses the words “these are the generations of the heaven and earth when they were created.: A few other verses imply ages: Prov. 8:22-31; Ps. 104; Mica 6:3 and Habak. 3:6 He suggests the day age theory or the framework hypothesis. P189 He notes the symmetry of Days 1 and 4 light and stars, days 2 and 5 sea and sea cratures, and days 3 and 6, land and land creatures. Ps. 19:1-4 says God speaks to us thru his creation, and Rom. 1:19-20 as in natural revelation. The universe is expanding: Gen 1 expanse; Ps 19 stretched out; Job 26:7; Isa. 40:22, 42:5, 45:12; Jerem.10:12; Zech. 12:1 It takes ages for the C,N,O and the heavy elements to develop from stars.p248 It is a great miracle to move precisely thru the stages of inflation under God’s control. R. Gange agrees that the bang and inflation process argues for a fine tuned and guided creation. He is also aware of the space time warp.p388. p. 199 “The more we discover about how the universe works, the more we understand that our universe’s laws are set within very narrow, very critical parameters. Without a combination of the wildest possible coincidences, a universe capable of sustaining intelligent life would be impossible. Even unbelieving physicists have come to agree with the Bible’s assertion that our universe has been very precisely prepared for us; they routinely tell us that the universe’s conditions were very carefully chosen, adjusted or fine tuned.” Einstein wrote “That the harmony of natural law reveals an intelligence of such superiority that, compared with it, all the systematic thinking and acting of human beings is as utterly insignificant reflection.”p201 Evidence of fine tuning: 1. The elements for life like hydrogen, carbon, oxygen and nitrogen are incredibly fine tuned in their resonance and energy states and nuclear composition to allow life. Also the structure of the water molecule is very fined tuned as is the percent oxygen in the atmosphere. P205; 2. The ratio of the mass of the proton to the electron is also very fined tuned to allow molecules and life; 3.The relative strengths of the four fundamental forces is very fine tuned: gravity, electromagnetism, strong and weak nuclear force. For example if the strength of the gravitational force varied by one apart in1040, all stars would be red dwarfs of red giants; also its ratio to the electromagnetic force is very precise. 4. Several scientists had calculated the odds of random functional protein formation to be 1040,000 but there are only 1080 subatomic particles in the universe. It was then concluded that it is extremely unlikely that protein formation could occur by chance.; 5 The pattern of matter and energy and matter distribution in the universe is very fine tuned. The odds of this occurring by change are one in1030.; 6. The expansion force of our universe has been precisely balances by the gravitational force with time. If this would have varied form what occurred by one part in a million the universe would not exist.p.211; In 1985 at an international Astronomical society meting 59 scientists voted on how close the universe matched the critical mass that determines if the universe will continue to expand or collapse. All but 2 said the universe will continue to expand and gave a value near the 1080 subatomic particles. The ratio of universe actual density to the critical density is termed Omega Ω. P 214 Observation shows that visible stars give a value of .01 p.216 At Plank time the Ω must have been one. Rotating galaxies provide a clue that there is an additional up to 5% dark mater in them. This may consist of MACHO’s(massive compact halo objects), burned out stars, all(baryons): including protons, neutrons, and electrons. This leaves about 95% unknown matter. This is theorized to be cold dark matter(may clump into galaxies and attract hydrogen) and hot dark mater(may travel away at the speed of light).p128 7. When energy converts into mater it forms equal amounts of matter and antimatter. The opposite of electrons is positrons and there are also antiprotons It was theorized by S. Weinberg that at the big bang that energy was converted into mater and antimatter, but there was a very slight excess of matter.(one part in 1010) this also formed a great amount of photons of light that went onto form the cosmic background radiation. P221 G. Smoot noted 20-25 parameters that all look fine tuned. When you multiply the probabilities together, you find that it’s extremely unlikely that random chance could do this. P223 Omega Lambda form Wikipedia “In lieu of the cosmological constant itself, cosmologists often refer to the ratio between the energy density due to the cosmological constant and the critical density of the universe. This ratio is usually denoted ΩΛ. In a flat universe ΩΛ corresponds to the fraction of the energy density of the Universe due to the cosmological constant. Note that this definition is tied to the critical density of the present cosmological era: the critical density changes with cosmological time, but the energy density due to the cosmological constant remains unchanged throughout the history of the universe.” A positive vacuum energy density resulting from a cosmological constant implies a negative pressure, and vice versa. If the energy density is positive, the associated negative pressure will drive an accelerated expansion of empty space. (See dark energy and cosmic inflation for details.) Observations announced in 1998 of distance–redshift relation for Type Ia supernovae[3][4] indicated that the expansion of the universe is accelerating. When combined with measurements of the cosmic microwave background radiation these implied a value of ,[5] a result which has been supported and refined by more recent measurements. There are other possible causes of an accelerating universe, such as quintessence, but the cosmological constant is in most respects the most parsimonious solution. Thus, the current standard model of cosmology, the Lambda-CDM model, includes the cosmological constant, which is measured to be on the order of 10−35 s−2, or 10−47 GeV4, or 10−29 g/cm3,[6] or about 10−120 in reduced Planck units. In physical cosmology, astronomy and celestial mechanics, dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and tends to increase the rate of expansion of the universe.[1] Dark energy is the most popular way to explain recent observations and experiments that the universe appears to be expanding at an accelerating rate. In the standard model of cosmology, dark energy currently accounts for 74% of the total massenergy of the universe.[2] In astronomy and cosmology, dark matter is matter that is inferred to exist from gravitational effects on visible matter and background radiation, but is undetectable by emitted or scattered electromagnetic radiation.[1] Its existence was hypothesized to account for discrepancies between measurements of the mass of galaxies, clusters of galaxies and the entire universe made through dynamical and general relativistic means, and measurements based on the mass of the visible "luminous" matter these objects contain: stars and the gas and dust of the interstellar and intergalactic media. According to observations of structures larger than galaxies, as well as Big Bang cosmology interpreted under the "Friedmann equations" and the "FLRW metric", dark matter accounts for 23% of the mass-energy density of the observable universe, while the ordinary matter accounts for only 4.6% (the remainder is attributed to dark energy).[2] From these figures, dark matter constitutes 80% of the matter in the universe, while ordinary matter makes up only 20%. A small proportion of dark matter may be baryonic dark matter, astronomical bodies (such as massive compact halo objects) that are composed of ordinary matter, but which emit little or no electromagnetic radiation. However, the vast majority of the dark matter in the universe is believed to be nonbaryonic, and thus not formed out of atoms. It is also believed not to interact with ordinary matter via electromagnetic forces. The nonbaryonic dark matter includes neutrinos, and possibly hypothetical entities such as axions, or supersymmetric particles. Unlike baryonic dark matter, nonbaryonic dark matter does not contribute to the formation of the elements in the early universe ("big bang nucleosynthesis") and so its presence is revealed only via its gravitational attraction. In addition, if the particles of which it is composed are supersymmetric, they can undergo annihilation interactions with themselves resulting in observable by-products such as photons and neutrinos ("indirect detection").[4] Nonbaryonic dark matter is classified in terms of the mass of the particle(s) that is assumed to make it up, and/or the typical velocity dispersion of those particles (since more massive particles move more slowly). There are three prominent hypotheses on nonbaryonic dark matter, called Hot Dark Matter (HDM), Warm Dark Matter (WDM), and Cold Dark Matter (CDM); Isa. 40:25; 49:13-16 The Anthropic Principle- claims that we ourselves have somehow caused the universe to take the necessary form for our existence.p234 Multiple universes are proposed because our universe doesn’t offer enough time for thing to develop.p235 P330-60 Describe 50 godly scientists that made very great discoveries, greatly shaping and affecting our present scinece. Francis Bacon, the father of the scientific method.260 Recent discoveries: p.367 In 1967 A. Sakharov proposed the big bang theory with gust the right amount of mater over antimatter, resulting in the annihilation of antimatter, and forming the universe we see today. In 1970’s R Drake and J. Peebles say that Omega must be near one. In 2003 the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe views the universe’s early background radiation. They then say the age of the universe is 13.7 billion yrs. Data appear to support inflation and the universe composition of: 4% ordinary matter, 23% cold dark mater, and 73%dark energy ( this provides the energy for the expansion of the universe during the past 7 billion yrs.p368 J. Ostriker states the best way to measure the mass in the universe is by using gravity and Newton’s laws. The orbits of planets and galaxies tell us a lot. R Gange talks about possible time dilation p.389 time dilation A phenomenon predicted by the special theory of relativity in which the passage of time in the frame of reference of a moving object slows down as the object approaches the speed of light. Effectively, this makes it possible to spend energy to buy time. Time dilation has been experimentally confirmed using cesium clocks that can measure extremely small periods of time A potentially important consequence follows for future interstellar flight. Simply by traveling fast enough, an astronaut can reach any destination within a specified amount of (shipboard) time. The table below gives the travel times, as measured by onboard clocks, to Arcturus, located 36 light-years (11 parsecs) from the Sun, for a spacecraft traveling at various speeds (given as fractions of the speed of light, c). http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.daviddarling.info/images/time_dilation.gif&img refurl=http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/T/timedilation.html&usg=___2Gzharw3RUEXcbKFi0QOGWXFs=&h=284&w=403&sz=5&hl=en&start=1&zoom=1&um=1&itbs=1&tbn id=pPKXjbZWSdPN Shipboard travel times to Arcturus at various speeds Speed 0.1c 0.5c 0.9c 0.99c 0.999c Travel time 358.2 years 62.4 years 17.4 years 5.13 years 1.61 years Relative Velocity Time Dilation http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Time_dilation When two observers are in relative uniform motion, and far away from any gravitational mass, the point of view of each will be that the other's (moving) clock is ticking at a slower rate than the local clock. The faster the relative velocity, the greater the magnitude of time dilation. This case is sometimes called special relativistic time dilation. It is often interpreted as time "slowing down" for the other (moving) clock. But that is only true from the physical point of view of the local observer, and of others at relative rest (i.e. in the local observer's frame of reference). The point of view of the other observer will be that again the local clock (this time the other clock) is correct, and it is the distant moving one that is slow. From a local perspective, time registered by clocks that are at rest with respect to the local frame of reference (and far from any gravitational mass) always appears to pass at the same rate.[1] Clocks which are far from massive bodies (or at higher gravitational potentials) run faster, and clocks close to massive bodies (or at lower gravitational potentials) run slower. This is because gravitational time dilation is manifested in accelerated frames of reference or, by virtue of the equivalence principle, in the gravitational field of massive objects. It can also be manifested by any other kind of accelerated reference frame such as an accelerating dragster or space shuttle. Spinning objects such as merry-go-rounds and ferris wheels are subjected to gravitational time dilation as an effect of their angular momentum. Gravitational Time dilation: This is supported by the general theory of relativity due to the equivalence principle that states that all accelerated reference frames are physically equivalent to a gravitational field of the same strength. For example, a person standing on the surface of the earth experiences the exact same effect as a person standing in a space ship accelerating at 9.8 N/kg (the gravitational field strength of Earth). According to general relativity, inertial mass and gravitational mass are the same. Not all gravitational fields are "curved" or "spherical"; some are flat as in the case of an accelerating dragster or spacecraft. Any kind of g-load contributes to gravitational time dilation. In an accelerated box, the equation with respect to an arbitrary base observer is o o o , where Td is the total time dilation at a distant position, g is the acceleration of the box as measured by the base observer, and h is the "vertical" distance between the observers. When gh is much smaller than c2, the linear "weak field" approximation Td + gh / c2 may also be used. =1 Outside a non-rotating sphere http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gravitational_time_dilation A common equation used to determine gravitational time dilation is derived from the Schwarzschild metric, which describes spacetime in the vicinity of a non-rotating massive spherically-symmetric object. The equation is: , where t0 is the proper time between events A and B for a slow-ticking observer within the gravitational field, tf is the coordinate time between events A and B for a fast-ticking observer at an arbitrarily large distance from the massive object (this assumes the fast-ticking observer is using Schwarzschild coordinates, a coordinate system where a clock at infinite distance from the massive sphere would tick at one second per second of coordinate time, while closer clocks would tick at less than that rate), G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the object creating the gravitational field, r is the radial coordinate of the observer (which is analogous to the classical distance from the center of the object, but is actually a Schwarzschild coordinate), c is the speed of light, and r0 = 2GM / c2 is the Schwarzschild radius of M. If a mass collapses so that its surface lies at less than this radial coordinate (or in other words covers an area of less than 4πG2M2 / c4), then the object exists within a black hole. Einstein's Equivalence Principle states that accelerations are equivalent to gravitational fields. This means that there is no experiment in a fairly small sized room that you can do to determine which one of the following two circumstances are true: We imagine we have two clocks, labelled 1 and 2, that are fixed and stationary relative to the surface of the Earth. We are in a reference frame that is in free fall towards the surface of the earth, and we have our own clock, stationary with respect to us. Note that since we are in free fall, we are floating. According to the Equivalence Principle, our reference frame is inertial, and therefore our clock can do good measurements of time. Note that any other clock, stationary relative to us, at some other location is not necessarily doing good measurements of time, since the Equivalence Principle is only true locally. Thus we will compare the rates of the Earth clocks to ours only when we pass right by them. When we pass by Clock 1, it is moving with respect to us. Therefore, Special Relativity tells us that it is running slowly relative to our clock. Similarly when we pass by Clock 2, since it is moving with respect to us it will be running slowly compared to our clock. The horizon problem is a problem with the standard cosmological model of the Big Bang which was identified in the 1970s. It points out that different regions of the universe have not "contacted" each other due to the great distances between them, but nevertheless they have the same temperature and other physical properties. This should not be possible, given that the exchange of information (or energy, heat, etc.) can only take place at the speed of light. The horizon problem may have been answered by inflationary theory, and is one of the reasons for that theory's formation. Another proposed, though less accepted theory is that the speed of light has changed over time, called Variable speed of light.[1] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Horizon_problem When we look at the CMB it comes from 46 billion comoving light years away. However when the light was emitted the universe was much younger (300,000 years old). In that time light would have only reached as far as the smaller circles. The two points indicated on the diagram would not have been able to contact each other because their spheres of causality do not overlap. Inflationary theory allows for a solution to the problem (along with several others such as the flatness problem) by positing a short 10 − 32 second period of exponential expansion (dubbed "inflation") within the first minute or so of the history of the universe. During inflation, the universe would have increased in size by an enormous factor. If the Universe is only 14 billion years old, how can we see objects that are now 47 billion light years away? http://www.astro.ucla.edu/~wright/cosmology_faq.html#DN When talking about the distance of a moving object, we mean the spatial separation NOW, with the positions of both objects specified at the current time. In an expanding Universe this distance NOW is larger than the speed of light times the light travel time due to the increase of separations between objects as the Universe expands. This is not due to any change in the units of space and time, but just caused by things being farther apart now than they used to be. What is the distance NOW to the most distant thing we can see? Let's take the age of the Universe to be 14 billion years. In that time light travels 14 billion light years, and some people stop here. But the distance has grown since the light traveled. The average time when the light was traveling was 7 billion years ago. For the critical density case, the scale factor for the Universe goes like the 2/3 power of the time since the Big Bang, so the Universe has grown by a factor of 22/3 = 1.59 since the midpoint of the light's trip. But the size of the Universe changes continuously, so we should divide the light's trip into short intervals. First take two intervals: 7 billion years at an average time 10.5 billion years after the Big Bang, which gives 7 billion light years that have grown by a factor of 1/(0.75)2/3 = 1.21, plus another 7 billion light years at an average time 3.5 billion years after the Big Bang, which has grown by a factor of 42/3 = 2.52. Thus with 1 interval we got 1.59*14 = 22.3 billion light years, while with two intervals we get 7*(1.21+2.52) = 26.1 billion light years. With 8192 intervals we get 41 billion light years. In the limit of very many time intervals we get 42 billion light years. With calculus this whole paragraph reduces to this. Another way of seeing this is to consider a photon and a galaxy 42 billion light years away from us now, 14 billion years after the Big Bang. The distance of this photon satisfies D = 3ct. If we wait for 0.1 billion years, the Universe will grow by a factor of (14.1/14)2/3 = 1.0048, so the galaxy will be 1.0048*42 = 42.2 billion light years away. But the light will have traveled 0.1 billion light years further than the galaxy because it moves at the speed of light relative to the matter in its vicinity and will thus be at D = 42.3 billion light years, so D = 3ct is still satisfied. If the Universe does not have the critical density then the distance is different, and for the low densities that are more likely the distance NOW to the most distant object we can see is bigger than 3 times the speed of light times the age of the Universe. The current best fit model which has an accelerating expansion gives a maximum distance we can see of 47 billion light years. H. Ross; A Beginner's-and Expert's-guide to the Big Bang: Sifting Facts From Fictions http://www.reasons.org/astronomy/astronomy-and-bible Wisdom reposes in the heart of the discerning and even among fools she lets herself be known. Proverbs 14:33 “Proverbs 1:7 indicates that knowledge begins with respectful submission to the biblical God and that rejection of wisdom and biblical instructions inevitably to irrationality – to foolishness” (40). 20For since the creation of the world God's invisible qualities—his eternal power and divine nature—have been clearly seen, being understood from what has been made, so that men are without excuse. 21For although they knew God, they neither glorified him as God nor gave thanks to him, but their thinking became futile and their foolish hearts were darkened. 22Although they claimed to be wise, they became fools 23and exchanged the glory of the immortal God for images made to look like mortal man and birds and animals and reptiles. Rom. 1:20-23 New Internat. 20 From the creation of the world (A) His invisible attributes, that is, His eternal power and divine nature, have been clearly seen, being understood through what He has made. (B) As a result, people [a] are without excuse. 21 For though they knew God, they did not glorify Him as God or show gratitude. Instead, their thinking became nonsense, and their senseless minds [b] were darkened. (C) 22 Claiming to be wise, they became fools (D) 23 and exchanged the glory of the immortal God for images resembling mortal man, birds, fourfooted animals, and reptiles. (E) Holman Bible