syllabus
advertisement

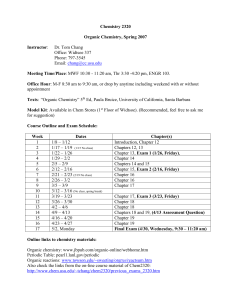
CHE 312 Organic Chemistry II Instructor: Dr. James L. Lyle Office: NSM D-323 Phone: (310) 243-3388, (310) 243-3376 e-mail: jlyle@csudh.edu Office hours: MW 9-10:00 am; TTh 12-1:00 pm; open door policy. Text: Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition, Morrison & Boyd. Study Guide for... Model kit 1. Grading: Traditional letter grades will be assigned. A = 100-93%, A- = 92-90%, B+ = 89-88, etc. Daily exams = 100 4 exams @100 pts = 400 final exam = 100 600 2. Exams. No make up exams will be given. 3. Final exam. The final exam will be will be comprehensive. 4. Homework. Homework is very important to doing well in this class and mastering organic chemistry. Homework is not going to be collected, but it should be done on a regular basis. Suggested problems are attached. Many of these problems are lengthy. You should be selective in which ones you do. If you have any questions, see the instructor. 5. Office hours. The instructor is available at any time outside of class for questions, etc. Do not hesitate to seek help if there is anything you do not understand! 6. Prerequisite. Completion of the first semester of Organic Chemistry, lecture and laboratory. Corequisite is enrolment in CHE-313. 7. Academic Integrity. Please review the statement on Academic Integrity in your University Catalog. Cheating will not be tolerated. 8. Course goals, objectives and requirements are covered in the rest of this syllabus. 9. Attendance is expected. Two of the daily exams scores will be dropped to allow for unavoidable absences. 10. The schedule, homework, etc. can be found: http://chemistry.csudh.edu CHE-312 meeting 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 45. TENTATIVE SCHEDULE Spring '03 date subject 1/27 1/29 2/3 2/5 2/10 2/12 2/17 2/19 2/24 2/26 3/3 3/5 3/10 3/12 3/17 3/19 3/24 3/26 3/31-4/4 4/7 4/9 4/14 4/16 4/21 4/23 4/28 4/30 5/5 5/7 5/12 5/14 TBA Infrared Spectroscopy 17.1,17.3-17.7 Nucl. Mag. Resonance 17.9-17.13,17.22 Aldehydes & Ketones text 18 no class EXAM I Carboxylic acids 19 Functional derivatives 19/20 Carbanions I 21 Carbanions II Michael Addition EXAM II Amines, syntheses 25 27 Spring Break, no class Amines, reactions Phenols Aryl halides EXAM III Molecular Orbitals Polynuclear Aromatics Heterocyclics Carbohydrates EXAM IV FINAL EXAM 22 23 24 26 28 30 34 CHE-312 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS Athough homework is not required to be turned in, it is required that you do it. You will not pass this course if you do not conscientiously do the homework assignments. Some of the following problems have multiple parts. It may not be necessary to do every part, but you should be able to do any homework problem, or problems similar to them, on the exams. The answers are in the Study Guide and should be consulted. You should also do the homework on a regular basis after every lecture. There is too much to do and learn if you put it off. If you have any questions see the instructor. Subject Assignment IR: please note that in some later printings Of the text the problems in this chapter are off by .1; 17.2 (which starts What is... ) may be 17.3 in your text, 17.3 (which starts give the... ) may be 17.4, etc., 17.5. (Note: spectra are analyzed at the end of the Study Guide.) Handout. nmr: 17.8(a-f),17.11,17.13,17.12,17.15,17.16,17.29, p. 643: 1(a thru i). aldehydes & ketones p. 701: 1,2, outline syntheses of each of the compounds in problem 2 using as many methods as possible for each from your choice of starting materials. p. 702: 3,4,5,18.16,6,10(a thru h). p. 706: 30,32,33. Outline all steps in the mechanisms for nucleophilic addition and acid catalyzed nucleophilic addition. Which mechanisms go with which reactions of aldehydes & ketones? carboxylic acids p. 747: 1,2,3,4,6,7,13,15(a,b,c),27. func. deriv. p. 787: 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,20,21. Outline all steps in the mechanisms for nucleophilic acyl substitution and acid catalyzed nucleophilic acyl substitution for appropriate reactions. carbanions: 21.11(mechanisms), 21.18,p 817: 1,2,3,6, mechanism for 6(a,d),25.1(a),25.8,25.10(a,b,c),25.16, 25.19(a-d),25.20(a-d),27.1,p.985: 2,3,7. amines: p.843: 1,2,22.5,22.6,3. p.878: 1,2,4,5,9,7,11,12,29,30,32. phenols: p.913: 1,4,5,8,33. aryl halides: p. 968: 1,2,3,8. Outline mechanisms for nucleophilic aromatic substitution (bimolecular) and the benzyne mechanism. molecular orbitals: handout, 28.3,28.6,28.7,28.10. heterocycles: know the names of common heterocycles. p 1074: 1,2. polynuclear aromatics: 1. Reactions. Predict the structures and names of the products (if any) of naphthalene with: a) CrO3, acetic acid b) O2,V2O5 c) Na,C2H5OH,reflux d) Na,C5H11OH,reflux e) H2,Ni,heat,pressure f) HNO3,H2SO4 g) Br2 o h) conc. H2SO4, 80 i) conc. H2SO4, 160o j) acetyl chloride,AlCl3,CS2 k) acetyl chloride,AlCl3,C6H5NO2 l) succinic anhydride,AlCl3,C6H5NO2 2. Reactions. Predict the structures and names of the products of the reaction of: anthracene with: a) K2CrO7,H2SO4 b) Na,C2H5OH,reflux c) Br2 phenanthrene with: a) K2CrO7,H2SO4 b) Na,C5H11OH,reflux c) Br2 d) Br2,FeBr3 3. Predict the products of nitration of the following compounds: a) 1-methylnaphthalene b) 2-methylnaphthalene c) 1-nitronaphthalene d) 2-nitronaphthalene e) 1-naphthalenesulfonic acid f) 2-naphthalenesulfonic acid g) N-(1-naphthyl)acetamide h) N-(2-naphthyl)acetamide i) alpha-naphthol j) beta-naphthol 4. Outline syntheses of the following from naphthalene: a) alpha-naphthol b) beta-naphthol c) alpha-naphthylamine d) beta-naphthylamine e) 1-iodonaphthalene f) 2-iodonaphthalene g) 1-nitronaphthalene h) 2-nitronaphthalene i) alpha-naphthoic acid j) beta-naphthoic acid k) 4-(1-naphthyl)butanoic acid l) alpha-naphthaldehyde m) beta-naphthaldehyde n) 1-phenylazo-2-naphthol o) 4-amino-1-naphthol p) 1-bromo-2-methoxynaphthalene q) 1,5-diaminoanaphthalene r) 4,8-dibromo-1,5-diiodonaphthalene s) 5-nitro-2-naphthalenesulfonic acid t) 1,2-diaminonaphthalene u) 1,3-diaminonaphthalene v) ortho-aminobenzoic acid w) phenanthrene x) anthracene y) 9,10-anthroquinone 5. Haworth syntheses of the following starting with compounds with fewer rings: a) 2-methylnaphthalene b) 1-methylnaphthalene c) 1,4-dimethylnaphthalene d) 1,7-dimethylnaphthalene e) 1,6-dimethylnaphthalene f) 1,4,6-trimethylnaphthalene g) 1-phenylnaphthalene h) anthracene i) phenanthrene j) 9-methylanthracene k) 2-methylanthracene l) 9-methylphenanthrene m) 4-methylphenanthrene n) 1-methylphenanthrene carbohydrates: define the following terms and give examples: carbohydrate monosaccharide, disaccharide,polysaccharide aldose, ketose pentose reducing sugar Tollen's reagent Fehling's reagent Benedict's solution epimers Ruff degradation Kiliani-Fischer synthesis D, L glucoside alpha-glucoside beta-glucoside anomers Additional Homework for Molecular Orbital Chapter: 1. Electrocyclic reactions. Predict the products of the following electrocyclic reactions showing the stereochemistry in the products. Is the motion conrotatory or disrotatory? hv hv 2. Cycloadditions. Predict the products of the cycloaddition reactions listed below and then indicate if the reaction is allowed or forbidden by conservation of molecular orbital symmetry and why or why not. [4+2] + [2+2] + 3. Does a [1,3] sigmatropic rearrangement of an alkyl group proceed with retention or inversion of configuration? Show you reasoning using molecular orbitals.