Genetics Study Guide Final Exam
advertisement

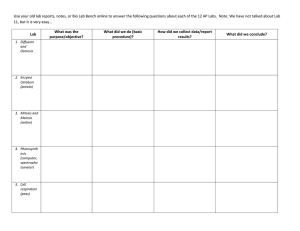
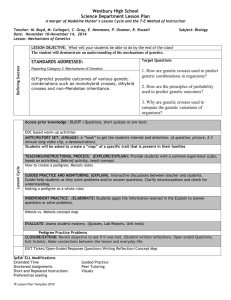
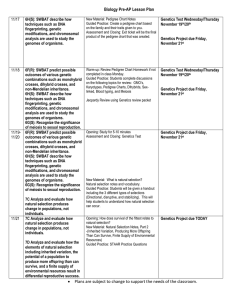
Genetics Final Exam Study Guide Molecular Genetics Information flow in molecular genetics (sequence relationship between DNA, RNA and protein), Open Reading Frame and how to use the genetic code Mutations -- missense (conservative, non-conservative), nonsense, silent and frame-shift, Loss-of-function, Gain-of-function. Mechanisms of mutagenesis Genetic Testing (RFLP analysis) Cytogenetics Meiosis (normal meiosis and non-disjunction meiosis) Meiotic basis for segregation and independent assortment. X chromosome inactivation Transmission Genetics Principles of segregation and independent assortment Pedigree analysis (autosomal and X-linked) Multiple alleles Co-dominance Recessive epistasis Linkage and mapping (two- point crosses, pedigree analysis) Population Genetics Calculating genotype and allele frequencies of a population Testing populations for genetic equilibrium Estimating the frequency of heterozygotes (or carriers) in a population. Human Evolution Basic terms related to phylogenetic trees Estimating number of mutations in an evolutionary lineage based on number of differences between existing similar sequences in different species.