CONTEXT CLUES
advertisement

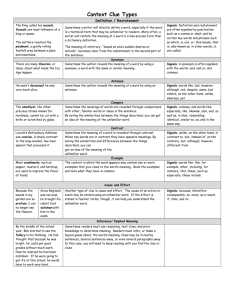
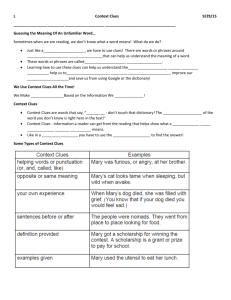
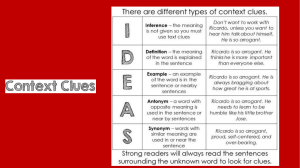
STRATEGIES FOR READING CONTEXT CLUES Having trouble with complete-the-sentence sections or determining what unfamiliar words mean while you’re reading? Have no fear! Skilled readers often use context clues to determine a word’s meaning. CONTEXT refers to the words or sentences before and/or after a certain word that hint at or clarify a word’s meaning. Below are examples of the different types of context clues to look for: Restatement, example, comparison, contrast, and cause/effect. RESTATEMENT Definitions or synonyms for a word are often repeated in a less precise way within some sentences. Look for the following signal words: SIGNAL WORDS Which is/means In other words That is Also known as Or Also called *Restatement context clues may also be signaled by a comma or other type of punctuation. FOR EXAMPLE: Jeanne trained herself to be an ambidextrous basketball player, which means she can shoot, pass, and dribble with both hands! EXAMPLE Examples of things that relate or are associated with a word are often given in a sentence. SIGNAL WORDS Like Including Such as For instance Especially Other This These These include For example FOR EXAMPLE: The work of an agronomist includes the selective breeding of crop plants and the development of methods to preserve oil. McDougal, Little. “Wordskills: Teacher’s Edition. Evanston, Illinois, 2000. COMPARISON By noting similarities between things described, the reader can get an idea of the meaning by comparing it to something more familiar. (*HINT: Synonyms may be used!) Like As In the same Similar to Resembling Just like SIGNAL WORDS Similarity Also Likewise Identical Related FOR EXAMPLE: Similar to the way a mother consoles a crying baby, my fears were assuaged when my teacher gave us an extension on my term paper. CONTRAST By noting contrasts between things described, the reader can get an idea of the meaning by contrasting it to something more familiar. (*HINT: Antonyms may be used!) SIGNAL WORDS On the other hand Different from/than In contrast to But Although On the contrary Dissimilar Unlike However FOR EXAMPLE: The intrepid child, unlike her more fearful playmates, never doubted her ability to climb to the top of the tree. CAUSE/EFFECT First the cause/action of a sentence will be stated, usually using an unfamiliar word. It will be followed by the effect or consequence of that initial action at the end in more familiar terms, which can be used to insinuate what the meaning is. Because Since Consequently Therefore SIGNAL WORDS When As a result “If…then” FOR EXAMPLE: Since both sides of the people arguing about the labor dispute were intransigent, now a federal mediator had to be brought in to help reach an agreement. Name:______________________________ English 2 APPL “SLANG” CONTEXT CLUES *DEFINITION OF WORD: 1) Restatement Sentence: 2) Example Sentence: 3) Comparison Sentence: 4) Contrast Sentence: 5) Cause/Effect Sentence: EXAMPLE “SLANG” CONTEXT CLUES *DEFINITION OF WORD: 1) Restatement Sentence: 2) Example Sentence: 3) Comparison Sentence: 4) Contrast Sentence: 5) Cause/Effect Sentence:

![Word Study [1 class hour]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007905774_2-53b71d303720cf6608aea934a43e9f05-300x300.png)