Lovejoy High School Biology Cell Test: Organelle Function and the
Lovejoy High School
Biology
Cell Test: Organelle Function and the Cell Theory
Review
For the following organelles:
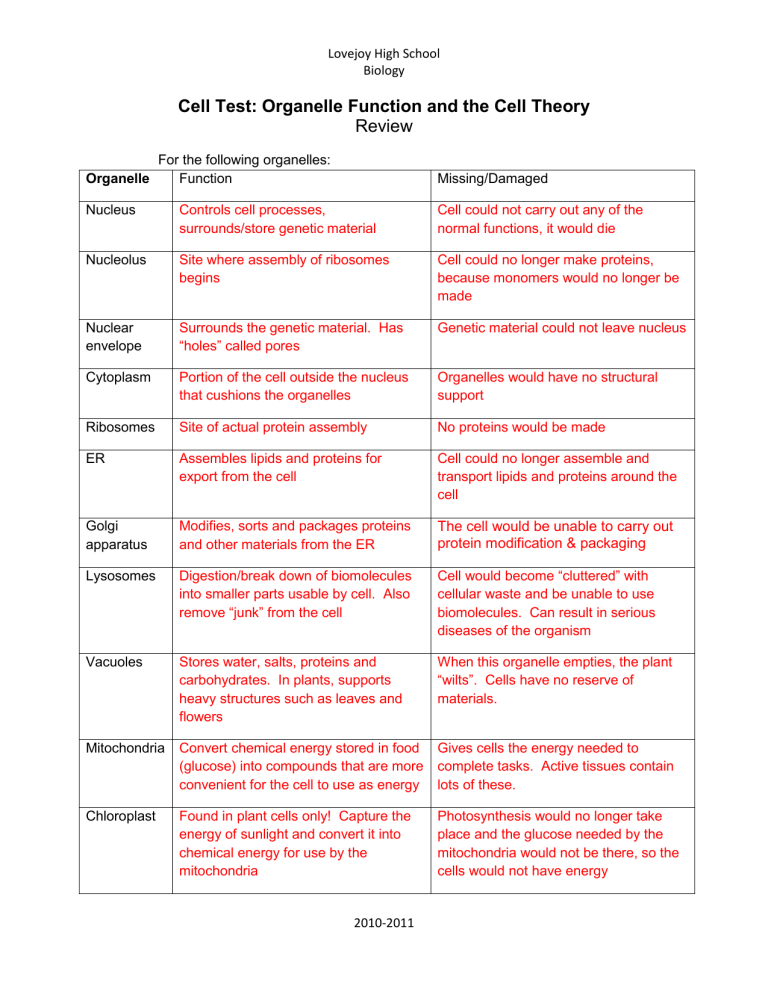
Organelle Function
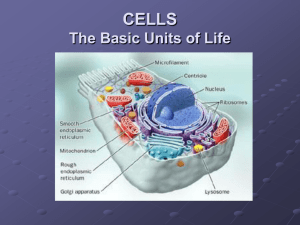
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Controls cell processes, surrounds/store genetic material
Site where assembly of ribosomes begins
Missing/Damaged
Cell could not carry out any of the normal functions, it would die
Cell could no longer make proteins, because monomers would no longer be made
Genetic material could not leave nucleus Nuclear envelope
Cytoplasm Portion of the cell outside the nucleus that cushions the organelles
Ribosomes Site of actual protein assembly
ER
Surrounds the genetic material. Has
“holes” called pores
Assembles lipids and proteins for export from the cell
Golgi apparatus
Modifies, sorts and packages proteins and other materials from the ER
Lysosomes Digestion/break down of biomolecules into smaller parts usable by cell. Also remove “junk” from the cell
Organelles would have no structural support
No proteins would be made
Cell could no longer assemble and transport lipids and proteins around the cell
The cell would be unable to carry out protein modification & packaging
Cell would become “cluttered” with cellular waste and be unable to use biomolecules. Can result in serious diseases of the organism
Vacuoles Stores water, salts, proteins and carbohydrates. In plants, supports heavy structures such as leaves and flowers
When this organelle empties, the plant
“wilts”. Cells have no reserve of materials.
Mitochondria Convert chemical energy stored in food
(glucose) into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use as energy
Gives cells the energy needed to complete tasks. Active tissues contain lots of these.
Chloroplast Found in plant cells only! Capture the energy of sunlight and convert it into chemical energy for use by the mitochondria
Photosynthesis would no longer take place and the glucose needed by the mitochondria would not be there, so the cells would not have energy
2010-2011
Lovejoy High School
Biology
Cytoskeleton Helps the cell maintain its shape by Cells would lose shape and die providing a network of protein filaments that help support the cell membrane and separate the organelles
Cell
Membrane
Regulates what enters and leaves the cell and provides protection and support for the cell
There would be no barrier between the internal parts of the cell and its environment
Cell Wall Provides support and protection for the cell. NOT IN ANIMAL CELLS!
Plant cells would not be able to support the tissues they made up. Bacterial cells would not have a protective barrier from their environment.
************************************************************************************************************
1. Describe cell specialization
Cells in a multicellular organism developing in different ways to perform different tasks.
2. Describe a prokaryotic cell and give an example organism of this cell type.
Do not contain a membrane around genetic material (nuclei) so it is not separated from the cytoplasm of the cell, nor do they contain organelles. Are much smaller and simpler than eukaryotic cells and are typically unicellular organisms. Ex. Bacteria and yeast
3. Describe a eukaryotic cell and give example organisms of this cell type.
Contain a membrane surrounding genetic material (nucleus) which separates it from the cytoplasm of the cell. Organelles are present. Highly specialized and can range from unicellular organisms to multicellular organisms. Ex. Plants, animals, fungi
4. Describe the cell theory
All living things are composed of cells
Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things
New cells are produced from existing cells
This fundamental concept of biology summarized the work of Schleiden, Schwann and
Virchow.
2010-2011
Lovejoy High School
Biology
Single celled organism
Do everything a living thing needs to do: grow, respond to environment, transform energy and reproduce
5. If an injury occurs in the lab, what is the first thing you should do, according to proper lab safety procedures? Tell the teacher
6. Describe proper focusing procedure of the microscope for low and high power.
When focusing on low power you use the coarse adjustment (big knob) and fine adjustment (small knob) to move the stage up and down and focus the objective lens.
However, when on high power you only use the fine adjustment .
7. Compare and contrast unicellular and multicellular organisms.
Unicellular Multicellular
Can be prokaryotic or eukaryotic
In terms of numbers, they dominate life on Earth
Example: yeast
Made of many cells
Go through cell specialization: cells throughout the organism develop in different ways to perform different tasks. These organisms depend on communication and cooperation among specialized cells
Are all eukaryotic
Are extremely diverse
Example: Animals
8. Compare and contrast a plant and animal cell.
Plant
Eukaryotic
Eukaryotic
Contain chloroplasts, large vacuole and cell wall
Photosynthesize
Found in multicellular organisms
Animal
No cell wall, small vacuole, no chloroplasts
Can not photosynthesize
Found in multicellular organisms
2010-2011