vocabulary-definitions
advertisement

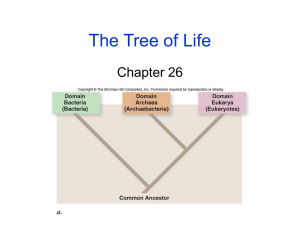
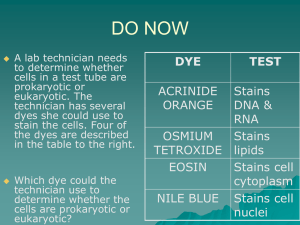
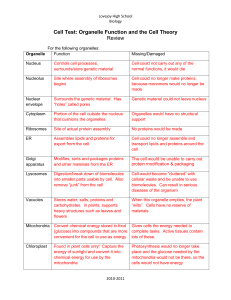
Taxonomy- the scientific study of how living things are classified. Kingdom- The highest classification into which living organisms are grouped. Phylum- is the second of the major groups into which biologists classify members of a kingdom. It ranks below kingdom. Class- a group of organisms ranking above order and below phylum. Order- A group of organisms ranking above a family and below a class. Family- A group of organisms ranking above a genus and below an order. Genus- A group of organisms ranking above a species and below a family. Part of the scientific name, which is always captalized. Species- A group of organisms having many characteristics in common and ranking below a genus. Organisms that reproduce sexually and belong to the same species interbreed and produce fertile offspring. Archaebacteria- are single celled microorganisms in the domain Archaea, which are genetically different from bacteria and eukaryotes, and often live in extreme environmental conditions. Eubacteria- is a unicellular, prokaryotic group of bacteria. It has its own kingdom because of its unique chemical makeup. Eubacteria is the one of the oldest forms of life, which may be the way it is the most familiar. Protista/Protists- are a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms consisting mostly of unicellular organisms but some are multicellular. Fungi- a eukaryotic organism lacking chlorophyll and feeding on organic matter; ranging from unicellular or multicellular organisms. Plantae (Plants)- any multicellular eukaryotic organism with a cell wall and chloroplasts that performs photosynthesis to obtain its nutrition. Animalia (Animals)- a major group of eukaryotic multicellular organisms that are heterotrophic, must ingest their food and are motile, moves independently. Chemosynthesis- the synthesis of organic compounds within an organism, with chemical reactions providing the energy source. Photosynthesis- is the process in which plants, algae, and some bacteria use water along with sunlight and carbon dioxide to make their own food in the chloroplasts . Binomial nomenclature- is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts. Unicellular- made of a single cell. Multicellular- consists of many cells. Autotroph (Autotrophic)- an organism that makes its own food. Heterotroph (Heterotrophic)- an organism that cannot make its own food. Prokaryote (Prokaryotic)- an organism whose cells lack a nucleus and some other cell structures. Eukaryote (Eukaryotic)- an organism whose cells contain nuclei. Dichotomous Key- a key used to identify a plant or animal in which each stage presents descriptions of two distinguishing characters, with a direction to another stage in the key, until the species is identified. Classification- the process of grouping things based on their similarities.