Greek History
advertisement

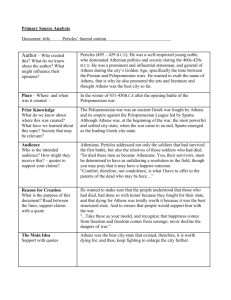
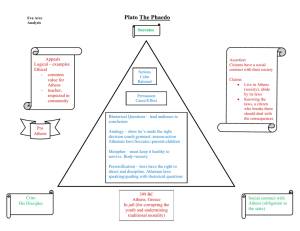
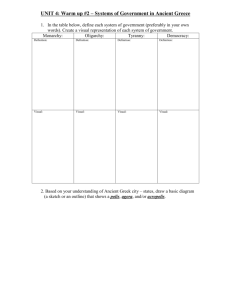
Greek History TSJCL Area F Comptetition Pflugerville High School February 26, 2011 1. The council of citizens in Athens in charge of running daily affairs was the _______. a. Boule b. Agora c. Acroterion d. Megaron 2. According to legend, two gods vied to be the patron god of Athens. These gods were Athena and: a. Zeus b. Hera c. Poseidon d. Hades 3. The war between Sparta and the Delian League was known as the _____ War. a. Punic b. Peloponnesian c. Peninsular d. Persian 4. In 405, ____ became the tyrant of Syracuse. a. Dionysus I b. Mitiades c. Antiochus III d. Nicias 5. After the death of Cyrus, who led The Ten Thousand, a band of Greek mercenaries, out of Persia? a. Alcibiades b. Iphicrates c. Philomelus d. Xenophon 6. Who was known as "The Father of History" because he was the first to organize his materials in a systematic way and to test their veracity? a. Leonidas b. Epimander c. Herodotus d. Euripides 7. What drunken, one-eyed king of Macedon was Alexander the Great's father? a. Cleitus b. Hegesias c. Philip II d. Neoptolemus 8. Knossos was the center of _____ culture. a. Mycenean b. Minoan c. Theban d. Doric 9. _________ was the name of Sparta's law-giver. a. Leonidas b. Socrates c. Solon d. Lycurgus 10. The Olympic games were first held in _____ B.C. a. 776 b. 657 c. 591 d. 314 11. The last major battle of the Peloponnesian War was a. Amphilochia b. Aegospotomi c. Mantinea d. Thermopylae 12. Athens' famous "wooden walls" were not walls at all but _____. a. barricades b. forests c. ships d. markets 13. Phormio led the Athenian fleet to victory over superior forces in 429 off the coast of a. Naupactus b. Megara c. Plataea d. Miletus 14. The Dark Age of Greece was brought about by the invasion of the ____. a. Macedonians b. Persians c. Pelasgians d. Dorians 15. The script of the early Myceneans is now referred to as _______. a. Linear A b. Linear B c.Archaic d. Pre-Classical 16. What city formed the "Sacred Band" composed of 150 pairs of comrade soldiers? a. Corinth b. Sparta c. Thebes d. Halicarnasus 17. In Sparta, the annually elected "overseers" were the ______. a. ephors b. sybota c. poletae d. kardakes 18. What Athenian orator vilified Philip and Alexander and tried to organize Greek opposition to them? a. Cleon b. Demosthenes c. Peisistratus d. Cimon 19. In 466, the Athenian admiral Cimon launched an offensive against Persia in Asia Minor and defeated the Persians in a double battle at the ______ River. a. Xanthus b. Pactolus c. Alphaeus d. Eurymedon 20. The "Peace of Callias" in 448 was between: a. Athens & Persia b. Athens & Sparta c. Thebes & Sparta d. Alexander & Athens 21. Alexander the Great loved his horse so much that he named several cities after it. In English, its name was "Ox-head." What was it in Greek? a. Pyxides b. Bucephalus c. Cottabus d. Parados 22. What historian recorded the events of the Peloponnesian War? a. Herodotus b. Xenophon c. Thucydides d. Plutarch 23. Who led the 300 Spartans at the battle of Thermopylae? a. Pericles b. Xanthippus c. Leonidas d. Lycurgus 24. At what battle in 388 did Philip defeat the Athenian and Theban forces? a. Mantinea b. Salamis c. Syracuse d. Chaeronea 25. Which happened first? a. Battle of Plataea b. Battle of Marathon c. execution of Socrates d. Peace of Nicias 26. Which of the following ruled Athens first? a. Cleisthenes b. Cimon c. Peisistratus d. Aristides 27. Who was the Milesian woman famous for her involvement with Pericles? a. Aspasia b. Sappho c. Hegesipyle d. Elpinice 28. The Spartan princess and first woman to enter a chariot at the Olympic games was _____. a. Tomyris b. Gorgo c. Cynisca d. Hypatia 29. The two hereditary kings of Sparta came from two families descended from Herakles: a. Atreid & Thyestid b.Agiad & Eurypontid c. Aeolid & Heraclid d. Perseid & Tisamenid 30. Who was the mother of Alexander the Great? a. Isodice b. Agariste c. Roxanne d. Olympias 31. In 427, what Athenian demagogue gained an evil reputation for pushing through a proposal to put to death the entire male population of Mytilene? a. Creon b. Pericles c. Demosthenes d. Cleon 32. The primary purpose of the Second Athenian Alliance was to defend Athens against a. Sparta b. Persia c. Thebes d. Rome 33. At what battle in 371 did Thebes defeat Sparta decisively? a. Leuctra b. Potidaea c. Aegea d. Mantinea 34. The Lelantine War in Euboea between 710 and 650 BC was primarily fought by ____ & ____. a. Larisa, Myceneae b. Corinth, Ephesus c. Chalcis, Eretria d. Miletus, Magnesia 35. The procedure during the Athenian democracy by which a citizen could be sent into exile for ten years was called______ a. pharmakos b. ostrakismos c. atimia d. koine 36. The pro-Spartan oligarchy imposed on Athens after her defeat in the Peloponnesian War was known as ___________. a. the Three Hundred b. archons c. epheroi d. the Thirty Tyrants 37. Who was the author of the first Athenian law code? a. Solon b. Peisistratus c. Draco d. Pericles 38. The ruler of Athens during the city's so-called Golden Age was_______. a. Solon b. Peisistratus c. Draco d. Pericles 39. The Greek mathematician that wrote a book called The Elements, which summarized all the knowledge of geometry up to his time, was _________. a. Euclid b. Eratosthenes c. Anaxagoras d. Aristotle 40. The chief city-state of the region called Attica was ___________. a. Athens b. Sparta c. Thebes d. Myceneae 41. What military genius of the Peloponnesian War was saved by Socrates at the Battle of Potidaea in 432, was exiled from Athens, went on to help Sparta for a while, later defected to Persia, then allowed to return to Athens, and was finally sent into exile again? a. Critias b. Xenophon c. Alcibiades d. Nicias 42. Who were the people enslaved by the Lacedaemonians? a. hoplites b. helots c. hubris d. hegemon 43. The father of Xerxes was ____. a. Cyrus b. Darius d. Artobazan c. Artaxerxes 44. Menelaus, son of Atreus, was the legendary king of ______. a. Athens b. Corinth c. Sparta d. Thebes 45. At which of the following battles did Themistocles fight? a. Aegospotomi b. Guagemela c. Amphilochia d. Salamis 46. Ionia was along the western coast of modern-day ___________. a. Greece b. Turkey c. Crete d. Albania 47. Which of the following was NOT Athenian? a. Lysander b. Aristides c. Cleisthenes d. Lysias 48. The mythical first king of Athens was_____. a. Draco b. Pericles c. Theseus d. Erectheus 49. When a Persian king wanted a Greek city-state to submit to his rule, he would send heralds to it to demand_________ and _________. a. earth, fire b. earth, water c. gold, silver d. gold, hostages 50. Which of the following is credited with reforming the Athenian constitution and setting it on democratic footing? a. Cleisthenes b. Critias c. Lysander d. Pericles Tie-Breakers—The following will be scored only in the event of a tie. Please mark the following answers using #96-100 on your Scantron. 96. The Mycenean Age belonged to what age of Greek history? a. Stone b. Golden c. Bronze d. Iron 97. Themistocles thought that Athens would become more powerful by focusing her attention on her________. a. army b. navy c. wealth d. alliances 98. Who commanded the Athenian forces at the Battle of Marathon? a. Alcibiades b. Lamachus c. Nicias d. Miltiades 99. What two sons of Peisistratus ruled Athens after their father's death? a. Ephialtes & Ictinus b. Hippias & Hipparchus c. Thepis & Phidias d. Cleon & Cimon 100. At the age of 32 or 33, Alexander the Great died in ________. a. Babylon b. Sussa c. Pella d. Alexandria