(NATIONAL CURRICULUM) IG 8 08
advertisement

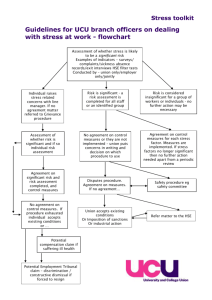
The EMT-Basic: National Standard Curriculum is established by the United States Department of Transportation, National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. The core curriculum follows national guidelines for training, both technical content and instructional strategies. The national curriculum must be followed; however, this template is being made available for your personal classroom notes/use. 21st Century Instructional Guide for Career Technical Education Emergency Medical Technician – Basic (EMT-B) Health Science Education Cluster Medical Emergency Preparation Concentration Title: Emergency Medical Technician – Basic (EMT-B) (0792) Standard Number: HSE.S.PTCB.1 Introduction to the Emergency Medical System Students will demonstrate basic knowledge and skills needed in the preparation for emergency medical care (i.e. introductory aspects of emergency medical care, importance of personal safety, medical, legal, and ethical issues pertaining to the EMT, structure and function of the human body, measuring and recording vital signs, completing a SAMPLE history, and techniques for lifting and moving patients). What is the relationship between having the knowledge and skills to perform emergency medical care and actually making the decision to perform emergency medical care? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: distinguish the roles and responsibilities of the EMT-B. articulate the importance of quality improvement. determine the importance of medical direction for the EMT-B. examine the role that stress management, critical incident stress debriefing, scene safety, body substance isolation, and personal protective equipment play in the EMT-B’s well-being. determine safety precautions that must be taken prior to performing the duties of the Essential Questions: Objectives: HSE.O.EMT.1.1 HSE.O.EMT.1.2 HSE.O.EMT.1.3 HSE.O.EMT.1.4 HSE.O.EMT.1.5 1 HSE.O.EMT.1.6 HSE.O.EMT.1.7 HSE.O.EMT.1.8 HSE.O.EMT.1.9 HSE.O.EMT.1.10 HSE.O.EMT.1.11 HSE.O.EMT.1.12 HSE.O.EMT.1.13 HSE.O.EMT.1.14 Standard Number: HSE.S.EMT.2 Essential Questions: EMT-B. relate the scope of practice for an EMT-B, including legal and ethical responsibilities. determine the meaning of advanced directives, consent, consent refusals, abandonment, negligence, duty to act, and confidentiality as applicable to the EMT-B. distinguish the EMT-B’s role and responsibilities in the case of organ donors and crime scenes. relate the meaning of basic topographic terms used with anatomy (i.e. medial, lateral, and proximal). examine the structure and functions of body organs and systems. demonstrate obtaining and recording baseline vital signs. generate and record a summary of the SAMPLE history for a given patient. demonstrate the proper use of body mechanics, explaining the rationale associated with the roles and responsibilities within the Emergency Medical Services. demonstrate techniques for lifting and moving patient, including the proper use of equipment. Airway Management Students will demonstrate knowledge and skills in: anatomy of the airway. physiology and pathophysiology in respiratory function. techniques for maintaining or restoring normal function. How does anatomy and physiology correlate with technique in emergency medical care? 2 Objectives: HSE.O.EMT.2.1 HSE.O.EMT.2.2 HSE.O.EMT.2.3 HSE.O.EMT.2.4 Standard Number: HSE.S.EMT.3 Essential Questions: Objectives: HSE.O.EMT.3.1 HSE.O.EMT.3.2 HSE.O.EMT.3.3 HSE.O.EMT.3.4 HSE.O.EMT.3.5 HSE.O.EMT.3.6 HSE.O.EMT.3.7 Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: examine anatomy and physiology of the respiratory system. determine methods to maintain an open airway including those for respiratory resuscitation. articulate the differences in the airway of infants, children, and adults. demonstrate the use of artificial airways, suction equipment, oxygen equipment, delivery systems, and resuscitation devices. Patient Assessment Students will: demonstrate knowledge and skills in assessments including reporting and documentation (i.e. scene size-up, initial assessment, detailed physical exam, and on-going assessment). communicate effectively, both orally and in writing. Discuss the effectiveness of oral communication in an emergency situation. Students will examine a scene for potential hazards, determining the need for additional assistance. relate potential or likely mechanisms of injury or natures of illnesses. articulate the components of the initial assessment, prioritizing patient care. implement the focused history and physical exam for both trauma and medical patients. characterize the detailed physical exam. outline the components of the on-going assessment, explaining the importance it plays in the delivery of quality patient care. differentiate the anatomical differences in infants and children as they relate to the Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: 3 assessment and treatment process. HSE.O.EMT.3.8 assess the components of the typical EMS communications system. HSE.O.EMT.3.9 demonstrate the proper use of communications equipment. HSE.O.EMT.3.10 characterize the need for accurate and confident verbal and interpersonal communications. HSE.O.EMT.3.11 articulate the components of a written medical report. HSE.O.EMT.3.12 examine implications of the legal medical report as it relates to patient refusal and special reporting situations. HSE.O.EMT.3.13 relate the importance that proper documentation plays in the improvement and quality of patient care. Standard Number: Medical/Behavioral Emergencies and Obstetrics and Gynecology HSE.S.EMT.4 Students will: demonstrate knowledge and skills in recognition and treatment of medical, behavioral, and Obstetrics and Gynecology emergencies. demonstrate knowledge and skills of pharmacological issues that may be encountered in Emergency Medical Services. Essential What are the possible relationships between behavioral management and medical management in Questions: emergencies? Objectives: Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: HSE.O.EMT.4.1 articulate a basic knowledge of pharmacology. HSE.O.EMT.4.2 determine guidelines for the proper administration of medications and/or assisting patients with self-administration. HSE.O.EMT.4.3 assess respiratory difficulty in patients. HSE.O.EMT.4.4 implement treatment for respiratory emergencies including the administration of prescribed inhalers. 4 HSE.O.EMT.4.5 HSE.O.EMT.4.6 HSE.O.EMT.4.7 HSE.O.EMT.4.8 HSE.O.EMT.4.9 HSE.O.EMT.4.10 HSE.O.EMT.4.11 HSE.O.EMT.4.12 HSE.O.EMT.4.13 HSE.O.EMT.4.14 HSE.O.EMT.4.15 HSE.O.EMT.4.16 HSE.O.EMT.4.17 HSE.O.EMT.4.18 HSE.O.EMT.4.19 prioritize signs and symptoms of cardiovascular disease. determine treatment of cardiovascular emergencies including the use of an automated external defibrillator or the administration of the patients’ nitroglycerin. recognize the signs and symptoms of a diabetic patient with an altered level of consciousness. determine the procedure for the administration of oral glucose. characterize signs and symptoms of an allergic reaction. initiate assistance with prescribed epinephrine auto-injectors in applicable cases of allergic reaction. recognize the signs and symptoms of poisoning and overdose. implement a plan to administer activated charcoal to treat poisoning. examine the signs and symptoms of environmental emergencies (i.e. heat and cold exposure, aquatic emergencies, bites, and stings). implement treatment of environmental emergencies given patient scenarios. characterize behavioral emergencies. determine methods to manage a disturbed patient including restraint of a combative patient. examine the anatomical and physiological changes occurring during pregnancy. compare normal and abnormal deliveries. examine signs and symptoms of common 5 HSE.O.EMT.4.20 Standard Number: HSE.S.EMT.5 gynecological emergencies. demonstrate neonatal resuscitation. Trauma Students will demonstrate knowledge and skills in the recognition and care of injuries involving bleeding, shock, tissue damage, head, and spine and their related conditions. Compare the severity of emotional impact with various types of trauma. Essential Questions: Objective Number: Objective: Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: HSE.O.EMT.5.1 differentiate internal and external bleeding including methods of controlling both. HSE.O.EMT.5.2 utilize data to identify and treat the signs and symptoms of shock related to hypoperfusion. HSE.O.EMT.5.3 examine the anatomy of skin. HSE.O.EMT.5.4 distinguish types and severity of soft tissue injuries. HSE.O.EMT.5.5 demonstrate care of soft tissue injuries. HSE.O.EMT.5.6 determine signs and symptoms of musculoskeletal injuries. HSE.O.EMT.5.7 demonstrate care of musculoskeletal injuries. Standard Number: Infants and Children HSE.S.EMT.6 Students will demonstrate knowledge and skills in the care of infants and children with common medical and trauma emergencies. Essential Should parent be permitted to stay with their child in the event of a medical or trauma emergency? Questions: Objectives: Student will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: HSE.O.EMT.6.1 differentiate developmental and anatomical differences in infants and children. HSE.O.EMT.6.2 examine common medical and trauma situations specific to infants and children. HSE.O.EMT.6.3 determine treatment of infants and children dependent on special technology. Standard Number: Operations 6 HSE.S.EMT.7 Essential Questions: Objectives: HSE.O.EMT.7.1 HSE.O.EMT.7.2 HSE.O.EMT.7.3 HSE.O.EMT.7.4 Standard Number: HSE.S.EMT.8 Essential Questions: Objectives: HSE.O.EMT.8.1 HSE.O.EMT.8.2 HSE.O.EMT.8.3 Students will: demonstrate safe ambulance operations and techniques for gaining access to patients demonstrate knowledge of hazardous materials, incident management systems, mass casualty situations and basic triage. Should access to patients in emergency situations be influenced by their ability to pay or the type of insurance coverage the patient possesses? Student will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: prioritize phases of an ambulance call (i.e. responding to the call, emergency vehicle operations, and transferring patients). differentiate emergencies requiring special means of access to patients. demonstrate equipment used to gain access to patients. demonstrate the removal of patients from emergencies such as hazardous materials spill or mass casualty situations. Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) The student will demonstrate knowledge and skills in the cardiopulmonary resuscitation of infants, children, and adults. Discuss the personal decision making process that must be made to perform CPR. Student will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: determine the importance of activating the appropriate emergency response system, performing CPR, using a barrier device, providing bag-mask ventilation, providing early defibrillation, and ensuring the arrival of early advanced care. demonstrate CPR according to established standards. examine the five major emergencies in adults that require CPR (i.e. heart attack, stroke, cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, and 7 HSE.O.EMT.8.4 HSE.O.EMT.8.5 Standard Number: HSE.S.EMT.9 Essential Questions: Objectives: HSE.O.EMT.9.1 HSE.O.EMT.9.2 Standard Number: HSE.S.EMT.10 Essential Questions: Objectives: HSE.O.EMT.10.1 HSE.O.EMT.10.2 HSE.O.EMT.10.3 HSE.O.EMT.10.4 21st Century Skills foreign body airway obstruction). determine strategies to prevent sudden infant death syndrome in infants. determine strategies to prevent injuries in children. Information Technology Applications Students will: use information technology applications. demonstrate use as appropriate to healthcare applications. How has the application of information technology impacted the delivery of emergency medical care? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: implement the use of software, hardware, and the Internet. utilize the Internet as a resource/research tool. Career and Technical Student Organization Students will participate in the local chapter of the Career and Technical Student Organization (CTSO). How does participation in a Career and Technical Student Organization (CTSO) impact professional development and lifelong learning? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: See www.HOSA.org. participate in the local chapter of the appropriate Career and Technical Student Organization (CTSO). See Robert’s Rules of Order. use parliamentary procedures in chapter meetings. demonstrate team membership/leadership and See HOSA Handbook. problem solving skills. See HOSA Handbook. participate in local, state, and national projects impacting healthcare and healthcare education. Learning Skills & Technology Tools Teaching Strategies Evidence of Culminating Activity Success Information and Communication 8 Skills: Thinking and Reasoning Skills: Personal, and Workplace, Skills: Learning Skills & Technology Tools Teaching Strategies Culminating Activity Evidence of Success Entrepreneurship Skills: GRASP Culminating Assessment: Industry Accreditation/ Certification Links and Other Resources Culminating Assessment You are working as an EMT-B and arrive at the scene of an accident. You will successfully assume the role of the EMT-B, performing all duties as required of an EMT-B, within the scenario provided. Technical Skills Performance Assessment at the completion of the core course within the concentration. Industry Accreditation/Certification CPR First Aid EMT-B Links and Other Resources Related Websites: HOSA http://www.hosa.org Center for Disease Control http://www.cdc.gov Pathways to Success http://careertech.k12.wv.us/pathwaystosuccess/ U.S. Department of Labor in the 21st Century http://www.dol.gov/ 9 Advanced Distributed Learning www.adlnet.org America's Career InfoNet www.acinet.org America's Job Bank www.ajb.org America's Service Locator www.servicelocator.org CareerOneStop www.careeronestop.org Employment & Training Administration www.doleta.gov The Job Accommodation Network (JAN) http://www.jan.wvu.edu Monthly Labor Review Online: Labor Force Archives http://www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/indexL.htm#Labor force Occupational Information Network www.doleta.gov/programs/onet Office of Disability Employment Policy www.dol.gov/odep Career Voyages http://www.careervoyages.gov/index.cfm Workforce West Virginia https://www.workforcewv.org/ 10 West Virginia Earn A Degree Graduate Early (EDGE) http://www.wvtechprep.wvnet.edu/edge.htm West Virginia Career and Technical Education http://careertech.k12.wv.us/ Contacts: Contacts HSE Teachers: See HSE Directory HSE Coordinators: Rebecca Davis rdavis@accesslk12.wv.us Cynthia Sundstrom scundstr@access.k12.wv.us OCTI Assistant Executive Director and EOCTST Coordinator: Donna Burge-Tetrick OCTI Executive Director: Gene Coulson 11