WH_Semester_1_Study_Guide
advertisement

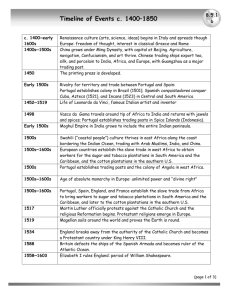
WORLD HISTORY Semester 1 Final Review Guide Name _____________________ Date _____________ Period ___ Vocabulary Genghis Khan Elizabeth I Hernan Cortez Byzantine Empire Inquisition Natural Right American Revolution Suffrage WORD BANK Mansa Musa Martin Luther Francisco Pizarro Feudalism Triangular Trade Network Nationalism Estate Urbanization Temperance Movement Henry VIII Christopher Columbus Mongols Scientific Revolution Columbian Exchange Republic Socialism Corporation SET 1: Early Civilization 1. Mali’s greatest leader who converted to Islam and created strong ties with Muslim states in the Middle East and Europe. 2. Central Asian group whose use of horses allowed them to control land from China to Eastern Europe in the early 1200s 3. Mongol leader 4. System during medieval Europe for protection 5. Formed from the Roman Empire and ruled for 1000 years in Eastern Europe SET 2: Renaissance and Absolutism 6. Church court that used secret testimonies, torture, and execution. 7. New way of thinking about the natural world using mathematical laws and careful observations 8. Reformation leader who questioned the actions of the Catholic Church and began the Protestant Reformation 9. Leader who broke away from the Catholic Church and formed the Church of England after his conflict with the Pope 10. Leader during the Renaissance who stabilized England as Protestant nation SET 3: Exploration, Conquest, and Trade 11. Spanish conqueror of the Inca 12. Spanish conqueror of the Aztecs 13. Italian explorer sent by the King and Queen of Spain in 1492 to seek trade routes to Asia. 14. Atlantic trade network that arose during the 1500s linking Europe, Africa, and the Americas. 2 15. Global exchange of goods, ideas, plants, animals, and disease in the 1500s. SET 4: Enlightenment and Revolutions 16. Strong feeling of pride and devotion in one’s country 17. Government ruled by elected representatives 18. Event that contributed to France’s debt before the revolution 19. Belongs to all humans at birth; including life, liberty, and property 20. Term for a social class in France SET 5: Industrial Revolution 21. Movement of people to the cities 22. System where the government has more control in the economy and provides the basic needs of the people 23. Business owned by many investors who buy shares of stock 24. Giving women the right to vote 25. Campaign to limit or ban the use of alcoholic beverages Multiple Choice Section Set 1: Early Civilization 26. Name the religion spread along trade routes between Middle East, Asia, and Africa as illustrated by the Mughal and Ottoman Empires. 27. Name the two highly valued items were most traded between West and North Africa. 28. Name the trade route East Africa was most connected to. 29. East Asian countries, such and Korea and Japan, were influenced by which major power? 30. What famous trade network ran from Asia to the Middle East? 31. Name the religion spread into East Asia from India. 32. Name the East Asian power that had a form of Feudalism similar to Medieval Europe. 33. Which institution held the most power in people’s lives in Medieval Europe? 3 34. What happened as a result of society becoming more stable and trade grew during the Middle Ages? 35. In the Middle Ages, which regions of the world did Europeans trade with? 36. What was an effect of the Black Death on Europe during the late Middle Ages? 37. The Crusades were a series of wars between____ and ____. 38. What was an impact of the Crusades on Europe? 39. Because of its connection with the Byzantine Empire, what was the dominant religion of Russia? 40. Name the main religion of the Ottoman Empire. SET 2: Renaissance and Absolutism 41. What was the name given to the time period associated with breakthroughs in perspective, engravings, and the European printing press that focused on a rebirth of classical learning of Greece and Rome? 42. How did Italy’s location help make it the starting point of the Renaissance? 43. How was Renaissance art different from the art of the Middle Ages? 44. What was an effect of the use of the printing press? 45. What factor led to the Protestant Reformation? 46. Describes the Catholic Reformation. 47. What new ideas developed during the Scientific Revolution? 48. A government where the ruler has complete control over the lives of its people is known as 49. What country had a Limited Monarchy? 4 50. Name Peter the Great’s goals for Russia. SET 3: Exploration, Conquest, and Trade 51. What was European motivation for exploration in the 1400s? 52. Who controlled trade between Asia and Europe in the 1400s? 53. How were the Portuguese able to gain a vast trading empire in the Indian Ocean in the early 1500s? 54. Why did Chinese traders demand payment for their goods in gold or silver? 55. Name the religion Spain worked to spread throughout the Americas in the 1500s. 56. Name the area of South America that was not controlled by the Spanish. 57. How did some West African kingdoms become powerful during the 1600s? 58. Who benefitted most from the Atlantic Slave Trade? 59. What was the overall impact of the Columbian Exchange on the Americas? 60. Which was a cause of the global population explosion? SET 4: Enlightenment and Revolutions 61. What did the European Enlightenment most want to change? 62. Who wrote that people have a natural right to overthrow a government that violates their rights? 63. Who would have opposed the Enlightenment? 64. What was the largest Estate in France? 65. Name the MAIN cause of the French Revolution. 5 66. Name of the document during the French Revolution that declared all men were equal under the law. 67. Name of prison in Paris attacked by the citizens to get gunpowder on July 14, 1789. 68. Name the period during the French Revolution was characterized by many arrests and executions, between September1793 to July 1794. 69. Celebrating a victory over Napoleon while focusing on the containment of France, creating lasting peace by establishing a balance of power, and protecting the system of monarchy describe the goals of which following event? 70. Name an effect Napoleon’s invasion of Spain had on Latin America. 71. What was an effect of national ideas in Latin America? SET 5: Industrial Revolution 72. “A gradual change in the way people lived and worked”, describes what time period? 73. What was a consequence of improved farming methods in the 1700s? 74. What two reasons did the Industrial Revolution begin in Britain? 75. What caused the growth of cities during the Industrial Revolution?