Force and Newton' s Laws Study Guide
advertisement

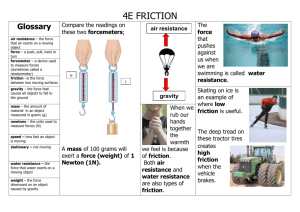
Force and Newton’s Laws Study Guide 1. State the law of universal gravitation. The force of gravity acts between all objects in the universe. 2. What is weight? Weight is the measure of the force of gravity on an object. 3. Why do scientists prefer to describe matter by its mass instead of weight? Weight can change with location but mass will stay constant. Mass is how much matter is in an object. 4. What are the two factors that affect the strength of gravity? a. mass b. distance 5. How do mass and distance affect the gravitational attraction between two objects? The more mass an object has, the greater the strength of its gravitational force; the greater the distance between two objects, the weaker the gravitational forces between them. 6. Using a Venn diagram, compare and contrast balanced and unbalanced forces. You should have a total of 4 contrasts and 2 similarities. Balanced – net force equals zero, does NOT change an object’s motion Same – push or pull, strength and direction Unbalanced – net force does NOT equal zero, changes an object’s motion 7. Explain static friction and give an example. Static friction is the friction that acts on objects that are not moving. Because of static friction, you must use an unbalanced force to start the motion of a stationary object. Example – trying to move a stalled car to the side of the road. The heavier the object, the more static friction it has. 8. Explain sliding friction and give an example. Sliding friction occurs when two solid surfaces slide over each other. Sliding friction is caused by the microscopic roughness of all objects. Example – throwing sand on an icy patch on the ground to help your footing. 9. Explain fluid friction and give an example. Fluid friction occurs when a solid object moves through a fluid (gas or liquid). This friction is much easier to overcome than sliding friction. Lubricants are used to help reduce sliding friction. Example – water on a water slide, applying oil to a squeaky gate hinge 10. Explain rolling friction and give an example. Occurs when an object rolls across a surface. This friction is much easier to overcome than sliding friction. Rolling friction reduces the amount of contact between surfaces because of curved shape of a sphere/circle/ Example – wheels, ball bearings 11. How is a force described? A force is described by its strength and direction. 12. What is net force? A combination of all forces acting on an object. 13.How can you find the net force if two forces act in opposite directions? You would subtract to find the net force. 14. Define Newton’s laws of motion. 1st Law - An object at rest will stay at rest and an object moving at a constant velocity (motion) will continue to move at a constant velocity (motion), unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. This law is also called the Law of Inertia. 2nd Law – The acceleration of an object depends upon the object’s mass and the net force acting on the object. acceleration = force/mass 3rd Law – For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. 15. When an object speeds up, slows down, or changes direction, why is an unbalanced force involved? If an unbalanced force was not involved then there would be no change in the object’s motion. 16.Draw the equation triangle for force, mass, and acceleration. Force mass acceleration 17. The force of gravity causes all objects near Earth’ surface to accelerate how fast? 9.8 m/s² or 32 ft/s² 18. What are the SI units for acceleration, force, and mass? acceleration = m/s² mass = kg force = N 19. What two factors affect the force of friction? a. the types of surfaces involved b. how hard the surfaces are pressed together 20. Identify one product of friction? Heat, wear, slows objects down 21. Two children are moving a wagon full of baseball equipment that has a mass of 35 kg. One child pulls with a force of 35 N and the other one pushes with a force of 60 N. The frictional force between the wagon and the ground is 20 N. What is the net force acting on the wagon? What is the forward acceleration of the wagon? Diagram the information in this question and show your work!!! 35 N + 60 N = 95 N 95 N – 20 N = 75 N of net force on the wagon acceleration = 75 N / 35 kg acceleration = 2.1 m/s² 22. Identify the action – reaction forces that are present. Walking – Action Force – Your foot pushes down and back on the ground Reaction Force – The ground pushes your foot up and forward A paddling a kayak – Action Force – The paddle pulls the water backwards. Reaction Force – The water pushes back onto the paddle causing the kayak to move forward. 23. What is the net force acting on a 0.15 kg hockey puck accelerating at a rate of 12 m/s²? **Show work** F = ma F = 0.15 kg X 12 m/s² F = 1.8 N 24.Thinking of Newton’s second law of motion, what are two ways to increase the acceleration of an object? a. Decrease the mass of the object b. Increase the force acting on the object 25. Define centripetal force. Any force that causes an object to move in a circular path. A center seeking force. 26. How does gravity affect objects that are moving horizontally? Gravity pulls objects that are moving horizontally toward the center of the Earth in the same way it pulls a dropped object. 27. Why can an object have a constant speed and still be accelerating. The object could be changing directions. 28. Define inertia. The tendency of an object to resist a change in its motion. 29. How is mass related to inertia? Give an example. The greater the mass, the greater the inertia. Example – An aquarium full of water versus an empty aquarium. The aquarium with water has more mass so it has more inertia. Therefore it is harder to move. 30. How does Newton’s first law explain what happens to passengers when a car stops quickly? When a car stops quickly a person’s body wants to continue forward in a straight line even though the car is stopped. This is the result of a body’s inertia. If a person doesn’t wear a seat belt their head could hit the dash board or the windshield. 31.Define momentum. A characteristic of a moving object that is related to the mass and velocity of the object. 32. When a rocket is launched, are the forces acting on it balanced or unbalanced? How do you know? The forces are unbalanced. I know because the rocket is accelerating and increasing in altitude. If the forces were balanced the rocket would still be on the launch pad. 33. Draw a diagram showing the motion of a satellite around Earth. Label the forces acting on the satellite. Is the satellite Your drawing should show Earth’s gravitational force accelerating? (centripetal force) directed toward the center of the Earth and perpendicular to the satellite’s motion. The forward velocity of the satellite is balanced by the force of gravity (centripetal force) which causes the object to be “held” in orbit. Remember the satellite is continuously falling around the Earth. The satellite is accelerating because it is changing direction.