school of technology - Central Connecticut State University
advertisement

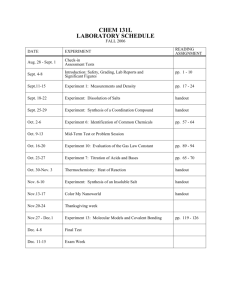
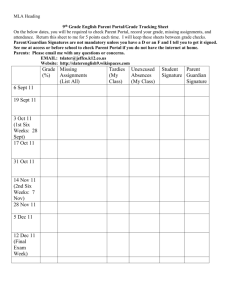
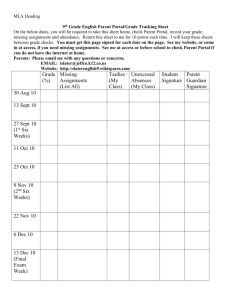
CENTRAL CONNECTICUT STATE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY Engineering Technology Department 1615 Stanley St., New Britain, CT 06050 ENGR 251 - 01 Engineering Mechanics I - Statics 3 SH (revision 08/30/02 – Peter F. Baumann) FACULTY: Prof. Peter F. Baumann OFFICE: Copernicus 21208 EMAIL:baumannp@CCSU.edu OFFICE TELEPHONE: 860-832-0086 OFFICE HOURS: Mon 3:15-4:15p, Tue/Thu 10:15a-12:15p CLASSROOM: NC 22406 LAB.: None TIME: Tues/Thur 2:00-3:15p COURSE DESCRIPTION: Engineering vector mechanics of equilibrium (statics), covering force resolution and composition, force moments and couples, and equilibrium equations for analysis. Forces and moments acting on structures and machines, centroids, and moments of inertia, are evaluated. COURSE PREREQUISITES: ENGR 150, MATH 221, PHYS 125 LEARNING OUTCOMES: Upon the completion of this class, the student will be able to: Analyze any statics problem in a simple and logical manner and apply to its solution a few well-understood basic principles. Use vector methods and techniques to more simply and concisely solve three-dimensional mechanics of particle problems as well as those concerned with rigid bodies. Draw free-body diagrams and solve associated equilibrium problems. Use engineering method and format for problem solving and solution presentation. Use both customary and international (SI) units of measurement to solve statics problems. Find centroids and centers of gravity. Analyze trusses, frames and machine structures. Find internal forces in structural members, and for beams prepare shear and bending moment diagrams. Find moments of inertia. Undertake follow-up courses in mechanics of materials and dynamics as required by discipline. REQUIRED TEXTBOOKS: Beer and Johnston., 2004, Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics, 7 Edition, McGraw-Hill, ISBN:0-07th 230491-X. REQUIRED MATERIALS: Engineering paper; a calculator capable of performing trigonometric and exponential functions and square and cube roots; a protractor, ruler or scale. PERFORMANCE CRITERIA READING ASSIGNMENTS: Shall be completed per assigned schedule. HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS: Shall be completed using the engineering method for problem solving and solution presentation according to the assigned schedule. EXAMINATIONS: Shall be taken per the assignment schedule. Since exam problems will reflect homework assignments, appropriate use of the engineering method for problem solving and solution presentation is expected. SPECIAL NEEDS: If you need course adaptations or accommodations because of a disability, you must file appropriate documentation with Dr. George Tenney in the Office of Special Services. If you have emergency medical information that needs to be shared with the instructor, or require special arrangements in case the building must be evacuated, please inform the instructor. ATTENDANCE: (class policy) Students shall arrive for class in a timely manner. Attendance in class is very important and checks will be made and may be considered in "borderline" cases. If you are unable to attend class on the day of a test, notify the instructor before the class meeting. Make-up tests are possible for excused absences only and must be scheduled with the instructor. ASSESSMENT CRITERIA EXAMINATIONS: Appropriate use of the engineering method for problem solving and solution presentation, application of correct theories (formulae) to any problem solution with follow-through to final results properly expressed in numerical form with appropriate units. GRADE COMPUTATION: EXAM 1: EXAM 2: EXAM 3 FINAL EXAM : 25% 25% 25% 25% Topical Outline – Class Schedule – Assignment – Fall 200X: (Instructor reserves the right to modify this policy statement and syllabus. Students will be notified of any changes before they are made. Week 1 Topic Date Sept 3 Sept 5 Sept 10 Sept 12 Sept 17 Sept 19 Sept 24 Sept 26 Oct 1 Oct3 Oct 8 Oct 10 Oct 15 Oct 17 Oct 22 Oct 24 Oct 29 Oct 31 Nov 5 Nov 7 Nov 12 Nov 14 Nov 19 Nov 21 Nov 26 Reading Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Distributed Forces: Moments of Inertia Dec 3 Dec 5 Dec 10 Dec 12 Chapter 9 FINAL EXAM Dec 19 Introduction Statics of Particles 2 3 4 5 Rigid Bodies: Equivalent System of Forces EXAM 1 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies 6 7 8 9 Distributed Forces: Centroids and Centers of Gravity EXAM 2 Analysis of Structures 10 11 12 13 14 Forces in Beams and Cables EXAM 3 Friction 15 16 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Problems Assigned 2.5, 2.16, 2.25, 2.36, 2.45, 2.50, 2.61, 2.66, 2.71, 2.82, 2.85, 2.98, 2.104, 2.110, 2.123, 2.128 3.1, 3.10, 3.21, 3.32, 3.37, 3.48, 3.61, 3.71, 3.83, 3.87, 3.99, 3.104, 3.110, 3.123, 3.128 4.1, 4.12, 4.15, 4.26, 4.31, 4.36, 4.47, 4.52, 4.61, 4.75, 4.76, 4.88, 4.93, 4.98, 4.109, 4.114, 4.121, 4.130, 4.133 5.1, 5.10, 5.27, 5.36, 5.43, 5.45, 5.63, 5.68, 5.75, 5.84, 5.92, 5.102, 5.113, 5.117, 5.129, 5.133 Chapter 6 6.1, 6.10, 6.26, 6.29, 6.45, 6.54, 6.65, 6.70, 6.75, 6.88, 6.99, 6.112, 6.123, 6.130, 6.145, 6.152 Chapter 7 7.3, 7.8, 7.17, 7.24, 7.35, 7.46, 7.49, 7.58, 7.65, 7.70, 7.81, 7.90 Chapter 8 8.3, 8.16, 8.39, 8.54, 8.65, 8.70, 8.84, 8.121, 8.128, 8.141, 8.144 9.1, 9.10, 9.15, 9.26, 9.32, 9.42, 9.53, 9.58, 9.72, 9.81, 9.86, 9.93, 9.98, 9.107, 9.111, 9.120, 9.135, 9.148, 9.151, 9.155, 9.169, 9.174