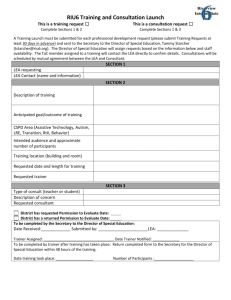
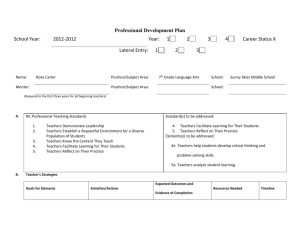
APPENDIX A: Educational Technology Planning Toolkit
advertisement

REVISED 9/14/2006 TO ADD K-4 INTEGRATED ACTIVITIES TO GOAL 1, BULLET 2 CONNECTICUT STATE DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY PLAN TEMPLATE July 1, 2006 – June 30, 2009 ED 616 Section 254(h)(1)(B), of the Telecommunications Act of 1996, and FCC Order 97-157, Paragraph 573 Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) P.L. 107-110 Published: August 2005 Submissions to RESCs for review due before April 15, 2006 Submission to SDE due June 30, 2006 CONNECTICUT STATE DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION Dr. Betty J. Sternberg Commissioner of Education IT IS THE POLICY OF THE CONNECTICUT STATE BOARD OF EDUCATION THAT NO PERSON SHALL BE EXCLUDED FROM PARTICIPATION IN, DENIED THE BENEFITS OF, OR OTHERWISE DISCRIMINATED AGAINST UNDER ANY PROGRAM INCLUDING EMPLOYMENT, BECAUSE OF RACE, COLOR, RELIGIOUS CREED, SEX, AGE, NATIONAL ORIGIN, ANCESTRY, MARITAL STATUS, SEXUAL ORIENTATION, MENTAL RETARDATION AND PAST/PRESENT HISTORY OF MENTAL DISORDER, LEARNING DISABILITY AND PHYSICAL DISABILITY. TABLE OF CONTENTS OVERVIEW OF EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY PLANNING 1 EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY PLAN APPROVAL PROCESS 3 COVER PAGE 4 TECHNOLOGY PLAN PREPARATION CHECK-OFF PAGE 5 LEA FEDERAL GRANT PROGRAM COMPLIANCE FORM 6 YOUR DISTRICT’S CURRENT STATUS LEA Profile Technology Planning Committee Vision Statement Needs Assessment ADDRESSING STATE AND DISTRICT GOALS Technology Funding Sources 7-13 7 8-9 10 11-13 14-50 51-55 CHILDREN’S INTERNET PROTECTION ACT (CIPA) CERTIFICATION 56 APPENDIX A: Educational Technology Planning Toolkit 57 APPENDIX B: Technology Plan Review Guide 58 OVERVIEW OF EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY PLANNING What skills, attitudes and attributes do our students need to succeed in our 21st century, information intense society? Literacy in the 21st century requires more than the ability to read, write and compute. The State Board of Education believes that every student must develop strong technological skills and continually use them in order to function adequately in our 21st century world. Connecticut schools must ensure that technology resources are integrated across the curriculum in preK-12 and become part of the fabric of instruction. Students must use appropriate technologies to access worldwide resources in order to become more productive learners as part of their regular classroom routine. They must be able to use the many forms of technology to access, understand, manage, interpret, evaluate and create information. They also must be able to analyze information for content, relevancy and accuracy and be able to present that information in a variety of formats, including those with technology platforms. An education that is technologically rich produces high school graduates with the tools, competencies and level of sophistication necessary to be successfully employed in an everchanging global economy. Such an education enables all students to understand and use current and emerging technologies in their personal, academic and work environments. For many students, especially those with disabilities, technology often provides access to the general curriculum and allows them to perform tasks or demonstrate skills they would otherwise be unable to do. 1 In order to help students be successful in a technologically rich economy: Educational leaders must establish a vision for this transformed view of teaching and learning, and they must model this transformation in their own learning and work experiences. Learners and their families must have equal access to tools that support their learning. The locus of control for learning must shift from teacher directed to student directed learning. Learners must master the information literacy skills to access, investigate, and apply information. Every classroom in Connecticut must be connected to the statewide network with access to digital resources and curricula. Learners must demonstrate their understandings and skills relative to measurable performance standards. Technology must be a vital link among the staff, students, parents, and expanded community.2 This template is designed to help every school district use technology effectively by developing a comprehensive educational technology plan that addresses: district strategic initiatives, curriculum development and implementation, professional development, infrastructure, hardware, technical support, software, community involvement, fiscal planning, data management, monitoring and evaluation as they relate to the teaching and learning process. 1 High-quality comprehensive educational technology plans must be collaborative and include ideas and suggestions from all members of the educational community. These stakeholders may include: faculty, staff, parents, students, and others. The planning process must be a shared activity that not only involves schools and school districts, but also the community-at-large. Resources and links have been provided in the appendices to assist in the development of local educational technology plans. Please refer to them as you begin the planning process. 1 2 CSDE Board of Education Position Statement on Educational Technology and Information Literacy, 12/4/04 CAPSS Technology Position Statement, 12/14/01 2 EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY PLAN APPROVAL PROCESS 1. Complete your local technology plan using the template that follows on pages 5-21. 2. Once completed, your local technology plan must be reviewed by your RESC before submission to the CSDE. Submit two hard copies of your plan by April 15, 2006, to the following RESC staff for an initial review: Staff RESC Region Phone Fax ACES Josh Smith 203-407-4454 203-407-4590 CES Esther Bobowick 203-365-8883 203-365-8878 CREC Scott Nierendorf 860-524-4042 860-246-3304 EASTCONN Jane Cook 860-455-0707 860-455-0691 Education Connection Sean Kavanaugh 860-567-0863 860-567-3381 LEARN Kirsten Hoyt 860-434-4800 860-434-4871 Email jsmith@aces.k12.ct.us bobowice@ces.k12.ct.us snierendorf@crec.org jcook@eastconn.org kavanaugh@educationconnection.org khoyt@learn.k12.ct.us 3. When your local plan has been reviewed, necessary revisions have been completed, and it has been signed off as recommended for approval on the cover page by the appropriate RESC staff, submit a hard copy and a CD-ROM version of your plan by June 30, 2006, for final review/state certification. Send to: Arthur Skerker Connecticut State Department of Education 165 Capitol Avenue Hartford, CT 06106 4. Upon review and approval by the CSDE, a letter of approval/state certification will be sent by the CSDE to the Superintendent of Schools with a copy to the educational technology plan contact. 3 Cover Page EDUCATIONAL TECHNOLOGY PLAN – July 1, 2006-June 30, 2009 District/Agency: East Lyme Public Schools District Code: 045 Technology Plan Contact: Dr. Lloyd A. Johnson, Assistant Superintendent Phone: 860-739-3966 Fax: 860-739-1215 Email: lloyd.johnson@eastlymeschools.org Address: P.O. Box 176, 165 Boston Post Road, East Lyme, CT 06333 Name of Superintendent: Paul Smotas, Ph.D. Email: paul.smotas@eastlymeschools.org Signature of Superintendent: Date: Date Submitted to Board of Education: Date Approved by Board of Education: For RESC/SDE Use Only: RESC Regional Reviewer: RESC Recommendation for Approval: Date: Yes / No / Conditional SDE Authorization: Date: Date: 4 Technology Plan Preparation Check-Off Page The submitted plan has the following: Cover Page Technology Plan Preparation Check-Off Page LEA Federal Grant Program Compliance Form LEA Profile Technology Planning Committee Vision Statement Needs Assessment Goal 1 Goal 2 Goal 3 Goal 4 Goal 5 Goal 6 Goal 7 Technology Funding Sources and Costs CIPA Certification Signature of Authorized LEA Agent Date 5 LEA Federal Grant Program Compliance Form East Lyme Public Schools Name of Local Education Agency (LEA), i.e. School District, Consortium or Charter School submitting this plan. If Consortium, list all members in the space below. Developing a comprehensive technology plan based on the educational goals of the school system will ensure that the most appropriate technologies are effectively infused into your instructional and/or administrative programs. Thorough planning also ensures that all parties have equitable access and achieve the greatest benefit from routine use of educational technology. The comprehensive technology plan should demonstrate clear targets for technology use, spell out desired goals for learners, create visions for future directions, build "buyin" from stakeholders, and demonstrate to those who might provide funding that a district or charter holder is ready to act. School Districts, Consortia or Charter Schools (LEAs) who apply for technology funding through any Federal grant program are required to have developed a comprehensive, three-year plan, which outlines how the agency intends to utilize and integrate educational technology. The applying agency (check all that apply) is compliant with the provisions of the Children’s Internet Protection Act (CIPA). [Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) P.L. 107-110, Section 2441] will be CIPA compliant by this date. has applied for E-Rate Funding for FY 2006. The LEA’s comprehensive technology plan must be approved by the local board of education. Date the plan was approved: OR Date the plan is to be submitted for board approval: June 12, 2006 Certified by: _____________________________________ Signature of Superintendent ______________ Date of Signature Printed Name of Superintendent 6 LEA Profile This information should provide a “snapshot” of your district and help planners and reviewers to understand areas of need. This information will also assist the State to establish priorities in the provision of resources to districts. The SDE is particularly interested in the capability that each LEA has to access resources that will be placed onto the Connecticut Education Network (CEN) and additionally, the capability of each district to access online versions of the CMT and CAPT. LEA NAME: East Lyme Public Schools If CMT and CAPT are administered online at some point in the future, certain testing conditions would be desirable at every school. Ideally these include the following: All of the students in each grade level have access to the state assessment at the same time; Students are grouped in clusters of no more than thirty and all have access to the assessment at the same time (classrooms with only one or two computers would not be appropriate for testing); Students remain in their own school; and The computers have high-speed internet access. Your completion of the chart below will help the CSDE to better understand the state’s technical readiness for online testing. Maximum number of grade 4 students who could be accommodated under the above conditions 88 Percentage of grade 4 students who could be accommodated under the above conditions (number accommodated/total number of grade 4 students) 42% Maximum number of grade 6 students who could be accommodated under the above conditions 200 Percentage of grade 6 students who could be accommodated under the above conditions (number accommodated/total number of grade 6 students) 85% Maximum number of grade 8 students who could be accommodated under these conditions 200 Percentage of grade 8 students who could be accommodated under the above conditions (number accommodated/total number of grade 8 students) 82% Maximum number of grade 10 students who could be accommodated under the above conditions 175 Percentage of grade 10 students who could be accommodated under the above conditions (number accommodated/total number of grade 10 students) 53% 7 TECHNOLOGY PLANNING COMMITTEE The Technology Planning Committee should represent all stakeholders. Development of the technology plan and implementation of the plan should enable parents, educators, students and community members to benefit from the investment in technology and all should have representation on the committee. Member Title Constituency Represented Lloyd A. Johnson Assist. Superintendent Central Office Karen Costello District Curriculum Marie Shaw Program Improvement Administrator Library Media Specialist Rosetta Fremont Computer Consultant East Lyme High School Edward Beckwith Network Administrator District Network Kathy Cietanno Library Media Specialist East Lyme Middle School Jill Curioso Computer Consultant East Lyme Middle School Grace DeGrooth Computer Consultant Haynes & Niantic Center Schools Beth Schultz Computer Consultant Flanders & Niantic Center Schools 8 East Lyme High School Technology Planning Committee East Lyme’s commitment to providing resources for technology education and integration is long standing and substantial. There are five library media/learning resource specialists and four computer consultants for five schools who work with classroom teachers on instructional programming; a network manager; and two computer technicians who repair and install equipment. There are district-wide funds for the network infrastructure and each school budgets funds for equipment, software and training. District-wide, grant and building funds are made available for professional development for both the technology and instructional staff. The district has implemented both a student data base program (Admin Plus) and a special education electronic IEP (SEMSnet) program that tracks students data and created the opportunity for student assessment analysis. The Technology Committee has been charged with managing and guiding these efforts. In addition to the members listed, the Assistant Superintendent and the Administrator for Program Improvement attend and participate in the committee’s meetings. The following plan was developed by the committee and reviewed by the district’s administrative staff. The committee meets monthly to monitor network performance, respond to requests, develop network expansion priorities, determine district and building software and hardware needs, plan professional development activities for themselves and review building professional development needs to determine if other buildings could benefit from the same training activities. 9 Technology Vision and Mission Statements Vision East Lyme is committed to ensuring technology literacy for all students to become productive members of our rapidly changing global society. One of the greatest challenges of this century is to embed information technology in a culture that supports democracy, freedom of expression, tolerance, diversity, and complexity of opinion.* The East Lyme Public Schools are dedicated to this vision and are committed to ensuring technology literacy for all students. Mission Statement Students today need to be users of multiple educational technologies. East Lyme Public Schools strive to provide a curriculum enriched with technological experiences. Furthermore, the East Lyme Public Schools in partnership with the community, enable each student to learn the following information and skills necessary to be productive members in a global society: Establishing high standards and developing a preK-12 technology plan that is integrated across all content areas and incorporates 21st century skills and competencies Providing equal access to technological tools provided by the district for all students Selecting curriculum resources and providing course offerings that prepare students with 21st century skills Providing ongoing professional development that promotes the integration of technology across the curriculum Ensuring that teachers and educational leaders are highly qualified in the application of appropriate technology in all curricular areas Providing up-to-date equipment and programs and prompt, expert technical assistance Implement policies for safe and acceptable use of technology resources Informing families of ways in which technology can be used effectively and safely by their children Teaching students how to use technology in order to communicate information and ideas, conduct research, organize data, solve problems and create original work Staying current with the capabilities of emerging technologies Requiring that students responsibly use technology by demonstrating appropriate network etiquette, taking necessary security measures, assessing the validity of online resources and following rules for copyright and citation Ensuring that teachers incorporate technology into instruction across all curriculum areas in order to respond to complex problems and broaden content mastery Requiring students to use technology in order to communicate information and ideas, conduct research, organize data, solve problems and create original work East Lyme Schools is committed to ensuring technology literacy for all students. *Sherry Turkle, Professor of Social Studies and Technology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology 10 NEEDS ASSESSMENT Curriculum Integration Presently, computer generated student products are used to assess student learning in a variety of places throughout the grades and disciplines. This assessment process allows teachers to determine how to revise curriculum, materials and instructional strategies to improve student outcomes. In addition, CMT and CAPT test results are analyzed using both the printed reports and the computer disc version. Testing objectives not mastered by 20 or more percent of the students taking the assessment are identified for increased attention through curriculum, materials acquisition and instructional strategy development. Finally, the East Lyme K-12 Curriculum Mapping Project allows the analysis of student outcomes electronically. The curriculum guides template and completed guides are available online for staff reference. The East Lyme curriculum development protocol includes a requirement to address the integration of technology in the instructional and assessment phases of courses of study in a comprehensive and sequential manner. In the past, the implementation of these requirements varied according to the training and interest level of the teacher. As each major discipline area is reviewed and new curriculum documents developed, this discrepancy/need is being addressed. Presently, revised Connecticut State Department of Education Curriculum Frameworks include goals which incorporate technology. Therefore, East Lyme curricula guides, which recently have been revised, incorporate technology applications as recommended and all guides to be developed in the future will also. The current technology plan indicates technology activities currently occurring and plans for future implementations. The following Plan also illustrates with much specificity how teachers are integrating technology into their lessons including ways technology is presently used for the entire classroom and for small group instruction. Currently, the East Lyme student body is consistently using technology as an integral component in developing subject area reports, creating demonstrations and conducting research on-line. See Goal 1, Bullet 1 for specific examples. Professional Development To date, many technology professional development activities have occurred in East Lyme Schools. Such activities are ongoing and in response to both teacher and administrator perceived needs. A partial list includes: use of the district network for document storage, email and internet access, use of Microsoft Office components such as Power Point (for both staff and students), using various applications with students: Inspiration, Kidspiration KidPicks and Board Maker, and using the PPT and IEP forms software SEMSNET. Regarding the use of equipment and on-line capability, teachers at various level and buildings have been trained on on-line 11 conferencing, virtual meetings, use of email, efficient internet searches, use of assistive technology (see goal 4, Bullet 2) and classroom management strategies (i.e. grade Quick). On a district-wide basis, a National Study for School Evaluation (NSSE) Teacher Technology On-line Survey was conducted in February, 2006 to identify areas in need of further training by level: elementary, middle school, high school. Initial analysis of this survey’s results identified the following items the staff at each level identified as the items they felt least competent in: Elementary: “I can design an assignment in which students evaluate the accuracy, relevance, appropriateness, and bias of electronic information sources.” “I can use students’ test results from computer-based assessments to evaluate student learning from software.” “I can create my own World Wide Web pages to be accessed by my students as part of a lesson.” Middle School: “I can design a lesson in which students create web pages to share their reports or writings outside the classroom.” “I can create my own World Wide Web pages to be accessed by my students as part of a lesson.” “I can teach students to create digital portfolios of their learning using media such as HyperStudio or the Web.” “I can teach a lesson addressing district and state standards as well as the ISTE National Educational Technology Standards for Students.” “I can protect privacy and security when publishing students’ writing or images on the Web.” High School: “I can design a lesson in which students create web pages to share their reports or writings outside the classroom.” “I can create my own World Wide Web pages to be accessed by my students as part of a lesson.” “I can use students’ test results from computer-based assessments to evaluate student learning from software.” “I can protect privacy and security when publishing students’ writing or images on the Web.” “I can teach students to create digital portfolios of their learning using media such as HyperStudio or the Web.” The District Technology Committee will discuss these needs and identify additional technology skills and various applications that require training. At the building level, computer consultants poll teachers regarding PD activities. Included in our curriculum development process is an expectation that the integration of 12 appropriate technology is a component of all discipline areas. An outgrowth of these processes is the identification of technology implementation expectations that have PD implications. The District Technology Committee is a body that facilitates the identification and scheduling of PD and interacts with the District’s Professional Development Steering Committee. The Steering Committee is responsible for advising the District’s Leadership Team and assists in coordinating and implementing PD activities on designated days. The effectiveness of technology PD activities is determined by teacher feedback to the building computer consultants who convey those impressions to the District Technology Committee. Equitable Use of Technology The district is dedicated to equitable access to technology by staff and students. The lack of a district-wide or capital improvement budget to address the replacement and acquisition of new technology hardware has resulted in individual building efforts. Due to the previous lack of a hardware replacement and acquisition plan, inconsistencies in the prioritization in meeting these needs have resulted in inequities. This plan addresses those inequities. So also, are there discrepancies among the three elementary schools regarding time allocated for technology training and completion of integrated projects. This plan addresses this inconsistency. Students with disabilities are provided the technology tools requested by Pupil Placement Teams (PPT) through Assistive Technology Assessments and staff recommendations. Those tools include but are not limited to personal computers (usually laptop), specialized software (such as text-to-voice, Board Maker), equipment that converts print text to Braille text, FM units, and communication devices (such as Speech Boards). In general, East Lyme PPTs are supported in efforts to seek Assistive Technology Assessment and the Director of Special Services Office is completely responsive in acquiring the recommended devices or software. The following matrix may be used to determine the extent technology is available to staff. Please include information about the type and availability of staff access both on and off campus. All have a desktop or laptop computer connected to the district network and internet for Administrators their use. All have a desktop or laptop computer connected to the district network and internet for Teachers (pre-school) their use. All have a desktop computer connected to the district network and internet for their use. Teachers All secretaries have a desktop computer connected to the district network and internet for their use. All paraprofessionals have access to a desktop computer connected to the district Non-certified staff network and internet for their use. 13 The following matrix may be used to determine the extent technology is available to students. Please include information about availability in classrooms, the library-media center and all other areas where students have access. Mention the extent of supervised access before and after school. All classrooms have a desktop computer connected to the district network and internet. Students (pre-school) All classrooms have at least two desktop computers connected to the district network and internet. In addition, there is a computer lab for large group instruction and project work. In general, each elementary class has one lesson a week by the school’s computer Students (elementary) consultant. All four classroom clusters (12 in the school) have a common area called the Kiva which contains 20 desktop computers connected to the district network and internet. In addition Students (middle school) there is a computer lab for large group instruction and project work. All classrooms have at least two desktop computers connected to the district network and internet. In addition, there are numerous computer labs dedicated to specific and general Students (high school) use. All classrooms for students with disabilities have at least two desktop computers connected to the district network and internet. Additional Assistive Technology devices/software Students (with disabilities) may be in the room if provided for in the individual student’s IEP. Infrastructure and Telecommunications Each classroom has voice and data drops with access to the internet. Our goal is a minimum of two data drops per classroom. Video conferencing equipment and necessary bandwidth is available to grades 5 to 12. This plan extends this service to the three elementary schools. Recent contracts with SBC and CEN resulted in improved access, bandwidth and speed to all schools. The plan also increases the number of data drops to meet present and future needs of various programs and schools. The E-rate has supported the development, installation and growth of our district’s network. Administrative Needs All administrators have up-to-date equipment and access to our network, the internet and network-based programs like Admin Plus. Administrators completed the NSSE Online Survey and also convey their training needs to their building computer consultant. They use their technology for communicating with staff via email, researching topics on the internet, receiving email based professional updates (ie ASCD’s Smart Briefs), reviewing/analyzing student test data, using AdminPlus to analyze student demographic data, and using SEMSNET to record and publish State required PPT meeting minutes and IEPs. 14 PLAN IMPLEMENTATION LEA Technology Goals and Strategies The goals listed below are the State Goals as identified in the State Technology Plan (draft of new plan is expected to be available by September 2005). The LEA technology plan should be aligned to the State Plan and include the State Goals. The LEA may include any additional goals that apply to their technology plan. Goal 1: Improve student academic achievement through the use of technology in elementary and secondary schools with a target of fully integrating technology into the academic curriculum by December 2006. Goal 2: Ensure that all educators are proficient in the use and integration of technology and ongoing professional development activities are provided. Goal 3: Ensure that all K-12 educational institutions have the capacity, infrastructure, staffing, and equipment to meet academic and business needs for effective and efficient operations. Goal 4: Ensure that K-12 resources are available for all students, regardless of race, ethnicity, income, geographical location, or disability, so they can become technologically literate by the end of eighth grade and achieve their academic potential. Goal 5: Develop a continuous process of evaluation and accountability for the use of educational technology as: a teaching and learning tool, a measurement and analysis tool for student achievement, and a fiscal management tool. Goal 6: Develop a schema of current and future financing requirements to support the LEA’s Technology Plan. . Goal 7: Develop a telecommunications services plan that will support both instructional needs and administrative requirements. 15 Goal 1: Improve student academic achievement through the use of the technology in elementary and secondary schools with a target of fully integrating technology into the academic curriculum by December 2006. The following must be addressed: Bullet 1: Describe how the LEA will ensure all students have educational opportunities to achieve academic success through proven strategies of researched-based successful practices; Objective Strategy ELPS will provide equity and accessibility to technological tools for all students ELPS will allocate resources (staff, equipment and learning materials) equitably across the district so that each student has access to the tools necessary to succeed. ELPS will continue to develop a student’s potential to use technology both in innovative and creative ways to meet the state and national standards ELPS will revise their K-12 student Technology Competency Standards to align with the local, state and national curriculum frameworks. ELPS will teach students how to use technology in order to communicate information and ideas, conduct research, organize data, solve problems, create original work and use technology as an effective assessment tool. ELPS will pilot and adopt curriculum resources that support technology integration skills so students that will be prepared to be viable members in our global society. 16 Accountability Measure Provide up-to-date equipment (one computer per every three students), programs and prompt, expert technical assistance. Timeline Objective will be achieved by 2009. Multiple teacher assessment of student work through a variety of tools such as school wide rubrics, performance objectives, and grades. Teacher assessment through a variety of tools such as school wide rubrics. Develop the technology competency rubrics in year one. Assess and revise student competency document by end of year two. Objective will be ongoing and student progress will be monitored annually for both ELPS graduation competency requirement and NEASC accreditation measure. Students will observe ELPS policies for safe and acceptable use of technology resources. ELPS will require all students to responsibly use technology by demonstrating appropriate network etiquette, taking necessary security measures, assessing the validity of online resources and following rules for copyright and citation. ELPS will share knowledge and resources via technology for student and family use at home. ELPS will develop and maintain websites for communication, research, and new learning opportunities. ELPS will purchase on-line resources for student and family use. Information and Media 5/6 Language Arts Literacy: Sample Lesson Plan: In grades 5/6, students Students integrate will know how to locate their Social Studies and access different and Language Arts types of information project studying the using library resources Middle East and will online data bases. make a newspaper. Students are shown Included is an different research tools expository piece on and are shown how to an independent state. create information A persuasive article using a variety of forms on any environmental of media. issue. An 17 ELPS provides filtering software, on-line plagiarism software, student and parent sign AUP (acceptable use policy) contract, and teacher monitoring of student computer technology use. Appropriate reinforcement of school policies when students transition between and among schools within ELPS. Provide a highstandard of information and service via the web (i.e. teacher webpages, active links, communications) Completed interdisciplinary projects that show application of technology objectives in grade and curricula areas. Objective will be achieved by end of 8th grade. Objective timeline are subject to looping and multiage levels in 3 tiers of house configuration. Many presentation projects are to be delivered in a public speaking format. Objective will be ongoing including the district updating the filtering software, publishing the Board of Education approved AUP in faculty and student handbooks, providing professional development focusing on strategies to ensure technology compliance by all users in the community. Objective will be ongoing and continually assessed for relevancy. Communication Skills: In grades 5/6 students will experience teleconferencing to interact with experts and peers. They will start to get comfortable with public speaking and using effective oral and written and multimedia communications Critical Thinking: In grades 5/6 students will be able to organize thoughts and topics using Inspiration software to make a thoughtful progression on topics and put into a word processed document. Organize observations and data into table and charts for interpretation. They also will unitize Terrapin Logo software to learn basic programs skills Problem Identification and Solutions: In grades 5/6, students should be able to make observations about real problems and discuss a solution using print, presentation and graphing tools. Creativity and Intellectual Curiosity: In grades 5/6, students using digital cameras, projectors, presentation software and video conferencing will share and communicate new entertainment piece that must be relevant to the location and customs. An actual current event and last, a Dear Abby section where you would write a real life problem and then write the reader an answer based on how you would help or advise them. 5/6 Social Studies Sample Lesson Plan: Students studying colonial times researched and wrote pieces on a particular historical figure and had to explain why this particular person played and important role in history 5/6 Science Sample Lesson Plan: Students had to research different careers in Oceanology and take on those roles as they study the oceans and the responsibilities that come with the understanding and protecting the world’s oceans and marine life 5/6 Math Sample Lesson Plan: Students will gather data from surveying fellow students or family members and make graphs using Excel. They are 18 Graded with rubric and teacher assessments. Objectives are ongoing and student progress will be monitored annually. Yearly survey and meeting with teams of teachers are conducted to ensure that each team covers each technology competency. These surveys are conducted by the media specialist and computer coordinator. Objectives are constantly evolving with new and emergent technology. ideas and thoughts using any or all of the above tools to express their results of a project based assignment. Social Responsibility: In grades 5/6, students should be able to make a practical decision selecting which piece of technology would be best suited for a particular situation. They are taught to have respect for others when using network resources and email. The safety and dangers of the internet and the appropriateness of personal online information are taught Information and Media Literacy: In grades 7/8, students will know how to analyze, access and manage information they have found using all types of research tools including internet, online data bases, historical fiction, electronic correspondence and multimedia resources. They should be able to take the information and evaluate and integrate this into finished product. Communication Skills: In grades 7/8, students will have several teleconferencing experiences and will have public speaking experiences within shown different types of graphs and asked to determine what graph explains their information best and why. 7/8 Sample Language Arts Lesson Plan: Students will be researching a philanthropic organization using the internet in order to analyze the validity and credibility of internet websites. They need to give 8 examples of how to check the information on a website, e.g. who is the author and what is his purpose. In the end they will create a presentation on their organization and give details on who founded it, when, why, what the organization does to benefit people in society, how it operates and how it is 19 Completed interdisciplinary projects that show application of technology objectives in grade and curricula areas. Many presentation projects are to be delivered in a public speaking format. Objective will be achieved by end of 8th grade. Objective timelines vary in the 3 house configurations. Objectives are ongoing and student progress will be monitored annually. Yearly survey and meeting with teams of teachers are conducted to ensure that each team covers each technology competency. Graded with rubric and teacher assessments larger group setting to effectively deliver a persuasive presentation to a specific audience. Create a multimedia presentation representing clear ideas, plans, results and conclusion. Select and organize materials digital and print funded. 7/8 Sample Social Studies Lesson Plan: Students will research civil rights and create a web page based on a particular person that stood for civil Critical Thinking: liberties. They must include graphics and In grades 7/8, students will use graphing cite all sources used. calculators, scientific In the end they must probes, to form analysis also create a rubric and hypothesis for their assignment formulation. They will based on format, continue to utilize facts, accuracy and organizational graphs grammatical errors. and charts. 7/8 Sample Science Problem Identification Lesson Plan: and Solutions: Students collect real time data from the In grades 7/8, students will be using various weather station and tools including using observational, databases, email probes and presentation and measurement tools to calculators to identify gather and organize and solve real life and record data on problems that include the local weather and inquiry and rainfall. This is observational steps and charted and graphed compiling data. to summarize and analyze and then used to see how it plays a role in different parts of the Creativity and earth. Intellectual Curiosity: In grades 7/8, students will use brainstorming and web-based software to present to a specific audience a problem and how it is solved in today’s society. 20 These surveys are conducted by the media specialist and computer coordinator. Objectives are constantly evolving with new and emergent technology. Social Responsibility: In grades 7/8, students are reminded of the dangers of personal information along with the rules governing intellectual properties and copyright laws, fair use and plagiarism 7/8 Math Sample Lesson Plan: Students develop a budget using a spreadsheet. They examine the student’s fixed, variable, and periodic expenses and revise to adjust for cash flow problems that appear on the first spreadsheet. This lesson is to increase student awareness and appreciation of the formulas that a spreadsheet can perform and calculate. 21 Goal 1: Improve student academic achievement through the use of the technology in elementary and secondary schools with a target of fully integrating technology into the academic curriculum by December 2006. The following must be addressed: Bullet 2: Describe how the LEA will meet the Student Computer Technology Competency Standards; The East Lyme Curriculum Council designed a Curriculum Template and acts as a clearing house to review every new curriculum developed. The revised Connecticut State Department of Education Curriculum Frameworks, which include goals that incorporate technology, is used in the development of curriculum guides in all academic areas as required by the Curriculum Template. The East Lyme curriculum development format also includes a requirement to address the integration of technology in the instructional and assessment phases of courses of study in a comprehensive and sequential manner. Science and Language Arts curriculum documents are completed and include those computer technology competency student outcomes. Other curriculum areas, such as Mathematics, Visual Arts, music, Physical Education and library Media Learning resources are in progress. Planned to begin in the summer of 2006 are World Languages, Social Studies and Health Education. Currently, many teachers are integrating technology into their lessons and unit plans. East Lyme students are consistently using technology as an integral component in developing subject area reports, creating demonstrations and conducting research on-line. This plan will ensure that these expectations are universal, systematic and sequential in nature. Each elementary teacher has been given a list of Technology Competencies and is expected to incorporate them into assigned projects. At ELMS, there is a team Technology Assessment for each grade level. In addition, there is a graduation requirement for Technology Competency for an ELHS diploma that meets local, state and national standards. Objective Students will know how to: Elementary: Kindergarten: Many technology objectives for kindergarten students are across the curriculum areas. These are: 1. Mouse control: Strategy: Impart a process to allow students to think and work independently 22 Accountability Measure Completed interdisciplinary projects that show application of technology objectives in grade and curricula Timeline Double clicking Dumping paint into area Placing suitable stamps Dragging Undo 2. Keyboard introduction: Letter identification Shift Key Delete Key 3. Beginning paint skills: Palette and brush size selection Illustrating curriculum concepts 4. Opening documents 5. Exiting Program Curriculum Specific Objectives: Language Arts: Identifying Letters; writing name, words, and eventually sentences; first and last sounds of words Math: Identifying, sorting and creating shapes sequencing counting and number identification and numeric representation Social Studies farm, city extension activities (writing, drawing), seasonal and calendar activities Science: beach, ocean, space extension activities Physical Education: Field Day extension activities areas: Using the keyboard letters and keys – shift, space, backspace and period; internet activities Internet activities, paint and drawing software Grade 1: Many technology objectives for first grade students are across the curriculum areas. These 23 E.G. Using paint or drawing program, produce a seasonal or shape picture with a describing sentence. are: 1. Continue skills from K 2. Keyboard familiarization: Space Bar Return Key 3. Desktop and window contents: Folders Windows – Opening, Closing, Scroll Bar 4. Writing and illustration of curriculum (math, science, language arts) contents Paint tool familiarization 5. Word Processing Flashing insertion point Navigating in document Punctuation 6. Opening and closing Applications Appropriate use of CD Rom Quitting and ejecting CD’s 7. Saving and retrieving documents Curriculum Specific Goals: Language Arts: o Extension of writing skills from Kindergarten; phonetic spelling; beginning, middle, end story sequencing; short and long vowel Math: o Money, representing math problems; bar graph; sequencing and grouping math; sorting by attribute; measuring, clock reading Social Studies: o Family chart; community helpers; calendar and seasonal activities self portrait with writing; Science: o field trip extension activities –– apple Extension of keyboard E.G. skills; Space bar, Using paint or drawing period. program, make a classroom book that consists of a short vowel word and illustration. Internet activities, word processing, Teacher monitored and paint and drawing observed on-line software activities via the intranet (ex. www.Starfall.com and www.little-g.com) that involve sorting letters into alphabetical order, telling time, and measuring. 24 orchard, pond, ocean; illustrate and label science concepts – solid/liquid, ocean, field, forest, and pond animals and plants, butterfly life cycle Internet virtual field trips Grade 2: Many technology objectives for second grade students are across the curriculum areas. These are: 1. Continue skills from Grade 1 2. Saving by navigating to personal folder 3. Word Processing and Painting curriculum concepts 4. Object manipulation: Creating shapes Resizing, moving Pictographs, Bar Graphs Labeling with text objects 5. Presentation of class writing, Wordprocessed and audio recordings 6. Opening applications, folders, and documents 7. Creating slide shows with text, drawing, animation, and audio recording Curriculum Specific Goals: Language Arts: Writing and illustrations of great grabbers and snapshots, poetry Math: Illustrating math problems; Social Studies: Web exploration on Iditarod website; photo insertion and writing about self Science: Writing and illustrations about whales, rabbits; graphs on animal measurements Extension of keyboard skills; Grade 3: Many technology objectives for third grade students are across the curriculum areas. These are: Internet activities, word processing, paint, drawing software and Internet activities, word processing, paint and drawing software Slide show retelling stages of readings with illustrations, sound and transitions greeting cards with graphics; Web-graphic organizing software bar graphs, pictographs; fraction activities 25 E.G. Using multimedia software, create a slide show of a student’s story that includes illustrations and voice recordings. Drawing geometrical shape designs and writing about them; 1. Continue skills from Grade 2 2. Word Processing Page Alignment Spacing Font adjustment Spell Check Copy/Cut/Paste 3. Illustrations Advanced paint tools Text Wrap 4. Keyboarding introduction and reinforcement 5. Opening multiple applications and navigating between applications 6. Accessing pre-saved websites Reading for content Taking notes Organizing information 7. Presentation of information Writing, illustrating, and importing images into presentation application Creating multiple slides and cards in presentation applications Choosing transitions and creating animations 8. Math and science concepts illustrated and labeled 9. Webquests related to curriculum objectives Curriculum Specific Goals: Language Arts: Writing and illustrations of stories; slide show creation of stories with illustrations, animations, transitions, and sound; poetry; Math: Bar graphs; Pictographs; Drill and practice on addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division; making and labeling geometric shapes; tangrams Social Studies: Inuits, Arctic Animals, Canada, Japan, Mexico; Science: Inquiry web activities and scavenger hunts presentation software. Keyboard instruction and practice throughout school year Via the intranet connect to online tangram activities (www.classbrain.com) Inquiry web activities and scavenger hunts 26 on specific websites: Rocks and Minerals, Habitats; creating a book about science areas Grade 4: Many technology objectives for fourth grade students are across the curriculum areas. These are: 1. Word Processing/ keyboarding/ Saving + Retrieving files (all ongoing) 2. Graphs on Spreadsheets: bar, pie, and line graph (over time) Explaining significance of graph with text. 3. Search Terms and formulating appropriate questions for research. 4. Citing sources 5. Cut and paste graphics/ create electronic poster or book with text, graphics, illustrations, data, etc. 6. HyperStudio, AppleWorks, and PowerPoint slideshow presentation skills 7. Webquests related to curriculum objectives 8. Websites – reading for content, taking notes, organizing information 9. Painting and drawing as a tool used to express knowledge of subject 10. Database 10. Electronic Portfolio in PowerPoint of years activities Curriculum Specific Goals: Language Arts: Poetry; Writing and illustration of on specific websites; virtual field trips Internet activities, word processing, paint, drawing software and presentation software. Word Processing programs, presentation software, desktop publishing software Keyboard instruction and practice throughout the year Portfolio Slideshow elaborating on Fourth Grade Year including Text, Word Art, Hypertext links, Clip Art, photos, and sound; database (list and review) of books read; book reviews with scanned book cover; 27 E.G. Using Kidspiration, create a graphic organizer about habitats. Native American Stories; Math: Construct charts and graphs to display survey data .tessellation creation and written explanation, geometry vocabulary illustrated and labeled; online CMT prep Social Studies: Native American writing and illustration, time lines; state population graphs; state research and slide shows with clip art, photos, and information; brochure Web based inquiry on the human body, simple machines; graphing of science data; Nature’s Classroom brochures with images, text, and word art, integrated technology projects on electricity, magnetism, biomes, endangered species, and earth changes Spreadsheet graphing – bar graphs, line graphs (over time); Complete an inquirybased Webquest asking students to complete activities that emphasize content Conduct a research project using online resources 28 E.G. Using Excel, input the data from the survey collected in class of M&M colors and then produce a chart/graph. Goal 1: Improve student academic achievement through the use of the technology in elementary and secondary schools with a target of fully integrating technology into the academic curriculum by December 2006. The following must be addressed: Bullet 3: Describe how the LEA will provide resources that reflect scientifically-based research and best practices focused on improving student achievement; East Lyme’s commitment to providing resources for technology education and integration is long standing and substantial. There are five library media/learning resource specialists and four computer consultants for five schools who work with classroom teachers on instructional programming; a network manager; and two computer technicians who repair and install equipment. There are district-wide funds for the network infrastructure and each school budgets funds for equipment, software and training. District-wide, grant and building funds are made available for professional development for both the technology staff and instructional staff. The district has implemented both a student data base program (Admin Plus) and a special education electronic IEP (SEMSnet) program that tracks student data and created the opportunity for student assessment analysis. The benefits of having Admin Plus and SEMSnet in our district include: Elimination of 95 percent of IEP procedural compliance issues; A drop in average IEP prep time for more than one hour to 15 minutes; A major shift in compliance activities; staff’s primary focus is evaluating quality of service instead of checking compliance errors. 29 Goal 1: Improve student academic achievement through the use of the technology in elementary and secondary schools with a target of fully integrating technology into the academic curriculum by December 2006. The following must be addressed: Bullet 4: Describe how the LEA will encourage the development and utilization of innovative strategies for the delivery of specialized or rigorous academic courses and curricula through the use of technology. Objective Strategy ELPS K-12 curricula will continually be evaluated by subject specialists for technology integration and area content. Develop innovative strategies for maximizing the CEN (Connecticut Education Network) resources. Accountability Measure Curricula will be revised through a variety of methods including teacher and department recommendations based on research and best practice. Assessing curriculum based on the global changes that technology innovations offer. Promote the use of the CEN by staff and students and encourage the participation the various opportunities that the CEN offers. 30 The ELPS Curriculum Council approves new courses and curricula changes. Key technology innovators in buildings will promote educational and creative use of technology as well as introducing new technology to the staff and students. The use of CEN resources and their integration into curriculum and professional development will be assessed by key personnel such as administrators, department chairs, library media specialists and computer consultants. Timeline The objective will be ongoing following the district’s curricula approval process. The objective will be ongoing as new resources are added to the CEN. Goal 1: Improve student academic achievement through the use of the technology in elementary and secondary schools with a target of fully integrating technology into the academic curriculum by December 2006. The following must be addressed: Bullet 4 (continued): Include any plans to promote technology-based distance learning opportunities to meet the educational needs of those who have limited access to such courses and curricula due to geographical isolation or insufficient resources; Objective ELPS will offer a variety of courses and learning opportunities to students outside of the school building via online technology. ELPS intra-district distance learning opportunities will be established for appropriate students’ learning/ placement. Strategy Accountability Measure Establish and maintain partnerships with other schools, consortia, and higher education. Example of current online learning: VHS (virtual high school), Bridgeport partnership, satellite offerings and various distance learning opportunities. Maximize the infrastructure connection with fiberoptics that deliver high speed accessibility to five schools in the district. 31 Instructors of online courses (VHS) are responsible for course content and student achievement and grades are reported on transcripts. ELPS also monitor student participation and academic success. ELPS will continue to solicit other distance learning opportunities, K-12. Student’s progress will be monitored by teachers and administrators. Infrastructure will be maintained by the network administrator and the Board of Education will allocate the appropriate budget to maintain the connectivity. Timeline The objective is ongoing as new courses are introduced and new distance learning contacts are established. The objective will be ongoing as well as the support of the connectivity. Goal 2: Ensure that all educators are proficient in the use and integration of technology and ongoing professional development activities are provided. The following must be addressed: Bullet 1: Describe how the LEA will provide all teachers, (including library-media specialists, bilingual and ESL teachers, special and alternative education teachers) non-instructional staff, principals, and administrators, incentives to become technologically competent; The East Lyme Technology Committee has made arrangements to use a National School Study Evaluation program’s on-line staff survey focusing on the technology status of the school system. The results of this survey, which includes questions about the staff members’ knowledge and use of technology, will be used to identify areas/skills in need of further training. The committee also plans to take the 2001 Connecticut Teacher Technology Competency rubric matrix for Educational Technology Concepts and Operations and use it on an ongoing basis in a checklist form with teachers by discipline to further identify specific skills in need of training. Teachers will be encouraged to focus Teacher Supervision Growth Plans on their technology competency needs. Teachers who have passed BEST requirements will be encouraged to include technology topics or integration activities in their yearly Teacher Supervision Professional Growth Plans. Teachers who have demonstrated they have developed their technological literacy and have integrated those skills into their instruction will be the first ones in their school or department to receive updated equipment. Over time, the district budget will support and advance teacher’s technology competencies by sponsoring two teachers on an annual basis to attend a regional or national conference at no expense to them. 32 Goal 2: Ensure that all educators are proficient in the use and integration of technology and ongoing professional development activities are provided. The following must be addressed: Bullet 2: Describe how the LEA will monitor staff technological literacy. Indicate how the LEAs monitoring of technological literacy impacts professional development; During January 2006, all certified staff participated in a National Study for School Evaluation (NSSE) Teacher Technology Survey. Analysis of the results of this survey will be used to assess the technological literacy of the staff by level (high school, middle school and elementary) and to inform the District Technology Committee and building professional committees in order to plan needed and appropriate training. Technology workshops related to student learning are aligned with the CT Technology Standards for teachers are CEU-able; therefore, attendance is monitored as well as attainment of the outcomes of the PD offering by central office administration. Once training is completed and projects or software applications are delineated in the curriculum guides, principals will monitor the inclusion of those technology related student learning outcomes in teachers’ classes by examination of representative student portfolios as a component of the district’s Curriculum Monitoring Process. Also, technology competency plans will be part of each certified staff’s growth plan, and monitored by the certified staff’s evaluator. 33 Goal 2: Ensure that all educators are proficient in the use and integration of technology and ongoing professional development activities are provided. The following must be addressed: Bullet 3: Describe how the LEA will provide specific research-based professional development opportunities to all staff; Time during Professional Development days will be devoted to Technology Literacy upon the recommendation the District Technology Committee. Analysis of the results of the National Study for School Evaluation (NSSE) Teacher Technology Survey will be used to identify specific topics to be offered in PD programs by level. Computer consultants in individual buildings will offer technology training on topics identified through building surveys before or after school. Individual or small groups of teachers will receive training on an as needed basis during planning or release time. Teacher lessons involving the integration of technology will be video taped and made available to staff for training at their own convenience. 34 Goal 2: Ensure that all educators are proficient in the use and integration of technology and ongoing professional development activities are provided. The following must be addressed: Bullet 4: Describe how the LEA will provide specific research-based professional development opportunities to all staff; Objective All students, teachers, staff and administrators will have equal access to technology appropriate for their grade level, subject area or responsibilities. Strategy Accountability Measure See Goal 3; the district is committed to improving access and technology availability in an equitable manner for staff and students. All curriculum and program guides are district-wide with learner expectations developed for all students regardless of their race, ethnicity, income or disability. 35 Implementation of technology education and Library Media Learning Resources Program activities and assessments will be monitored by building principals or their designees. Timeline Equipment equalization by June of 2009 Curriculum Guide implementation by Sept. 2007 Goal 3: Ensure that K-12 educational institutions have the capacity, infrastructure, staffing and equipment to meet academic and business needs for effective and efficient operations. The following must be addressed: Bullet 1: Describe how the LEA will ensure that all facilities meet minimum standards of technology infrastructure and provide connectivity to the Connecticut Education Network (CEN); Currently some of the schools in the district do not meet the minimum requirement of student to computer ratio (1 computer to 3 students). The district will continue to work on meeting this minimum computer ratio requirement. The LEA will also compile a list of specifications for future computer purchases in order to standardize the equipment purchased. Continue to address the need for more drops in one of the elementary schools (one additional per instructional area) as well as additional drops in instructional area of the high school. Propose to the Board of Education the purchase of the equipment necessary to facilitate videoconferencing at the elementary level by purchasing one unit per year over three years. The LEA currently has connection to CEN and will continue to utilize the CEN connectivity. 36 Goal 3: Ensure that K-12 educational institutions have the capacity, infrastructure, staffing and equipment to meet academic and business needs for effective and efficient operations. The following must be addressed: Bullet 2: Describe how the LEA will ensure continued maintenance and support of existing infrastructure and end user technology; and The LEA will secure a yearly contract with an outside computer vendor to evaluate and recommend updates to the existing infrastructure. The LEA will construct an RFP (Request for Proposal) as a guideline for the vendor to evaluate the current infrastructure and to make recommendations. Based on the outside vendor’s report, budget will be proposed and submitted to the Superintendent to submit to the Board of Education to accommodate the most necessary recommendations to maintain a reliable infrastructure. The LEA technology staff (i.e. Network Administrator, Computer Consultants (one per building) and Technicians) will continue to support the infrastructure to ensure its operation and will continue to support the end users. Each April/May, the outside computer vendor will be contracted to evaluate the infrastructure. 37 Goal 3: Ensure that K-12 educational institutions have the capacity, infrastructure, staffing and equipment to meet academic and business needs for effective and efficient operations. The following must be addressed: Bullet 3: Describe the specific provisions the agency intends to make for the interoperability of the technologies. (Interoperability is the capability of the technology to be acquired to function compatibly with technologies that exist or will be acquired in the near future at the local and state level.) In the RFP submitted to the outside computer vendor, the LEA will ensure that all recommendations completed are compatible with the ELPS infrastructure and the CEN to ensure the interoperability and functionality of new technology acquired. Any technology purchases must be compatible and functional with the existing infrastructure. The outside computer vendor’s audit would be completed annually and the purchases would be based on the budget allocated each year. The LEA will continue to provide training for the appropriate staff to ensure the knowledge level necessary to support the infrastructure of the district. The LEA will continue to maintain the number of staff members currently supporting the district. The Technology Committee has recommended acquiring an additional consultant and technician. 38 Goal 4: Ensure that K-12 resources are available for all students, regardless of race, ethnicity, income, geographical location or disability, so they can become technologically literate by the end of eighth grade and achieve their academic potential. The following must be addressed: Bullet 1: Describe how the LEA will ensure that students with special needs will have those needs addressed through technology; Objective Strategy Students with identified special needs will have access to those technologies determined necessary for that student to benefit from instruction. Accountability Measure Students with identified special needs will have access to the same technology as regular education students. Assistive technology assessments will be used to determined individual needs and appropriate augmentative devices. Funding through local and grant sources will ensure the procurement of identified devices. 39 Students with identified special needs’ IEPs will include the assistive technology supports deemed appropriate. Progress on goals and objectives are communicated to parents on the same schedule as regular education progress reports. Timeline Progress reports/report cards 6 to 8 times a year Annual reviews for students with identified special needs include review of accommodations necessary to ensure access including technology and the effectiveness of those technologies. Goal 4: Ensure that K-12 resources are available for all students, regardless of race, ethnicity, income, geographical location or disability, so they can become technologically literate by the end of eighth grade and achieve their academic potential. The following must be addressed: Bullet 2: Describe how the LEA will encourage innovative practices to support equity and reduce performance gaps based on race, national origin, sex and physical or mental disability. Objective All teachers will have all students apply innovative technology practices in learning specific subject area matter. Strategy Accountability Measure Teachers will have access to periodic staff development experiences incorporating innovative technology practices. Teachers will have the opportunity to meet with their school’s technology consultant who will assist them in the application of innovative technology practices. The LEA will provide the necessary resources for technology workshops, conferences, and consultations. 40 Teachers will complete a technology competencies checklist as part of their summative evaluation (Teachers will complete an online survey to measure their technology competencies) Students will complete written reports and/or demonstration products utilizing appropriate technology practices in various subject areas. On an annual basis, the LEA will incorporate into the proposed school budget monies earmarked for technology in the subject area program budgets. Timeline Annually Dependent on project(s) due dates as established by the classroom/ subject area teacher. Annually in November Network Update Costs Building Purchase Network Status Report Switches Drops ELHS ELHS ELHS 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 Budgeted $1500 $1500 $1500 Yes $15,000 $3,000 $15,000 $5,000 $12,000 Yes Planned to be ELHS Back-up System $8,000 ELHS Server $15,000 Replacement $15,000 Planned to be $15,000 Yes (3 each year @ $5,000) Haynes Drops $7,500 Yes Computer Needs to Meet State Standards (3 per students) School # Cost Source NCS 0 0 Per Pupil, PTA and Revenue Haynes 18 $9,000 Per Pupil, PTA and Revenue Flanders 40 $20,000 Per Pupil, PTA and Revenue ELMS 61 $30,500 Per Pupil ELHS 89 $44,500 Per Pupil School NCS Haynes Flanders ELMS ELHS School NCS Haynes Flanders Computer Needs to Meet State Standards (3 per students) # Cost Source 5 $2,500 Per Pupil, PTA and Revenue 5 $2,500 Per Pupil, PTA and Revenue 5 $2,500 Per Pupil, PTA and Revenue 15 $7,500 Per Pupil 15 $7,500 Per Pupil # 1 1 1 Video Conferencing Unit Cost Source $20,000 District Budget $20,000 District Budget $20,000 District Budget 41 Goal 4: Ensure that K-12 resources are available for all students, regardless of race, ethnicity, income, geographical location or disability, so they can become technologically literate by the end of eighth grade and achieve their academic potential. The following must be addressed: Bullet 3: Describe how the LEA will ensure that all students will become technologically literate by the end of eighth grade; Objective All students will learn the technology competencies as indicated on the most recent CSDE and ISTE Technology Frameworks, being incorporated into East Lyme’s revised subject area curriculum guides Strategy Accountability Measure Students in grades K to 12 are exposed to a Library Media/ Learning Resources Program with accompanying goals, learner outcomes, and assessment activities. East Lyme Middle School will continue to require students in grades 5 through 8 to take Technology Education courses Students in grades 9 through 12 will continue to have available electives and Technology Education courses such as Graphic Design, Video Production, Animation Graphics, Web Design and CAD (presently there are 26 courses offered) The District’s Technology Committee will continue to evaluate the high school’s program of study to reflect the technology skills that students should possesses for a particular course 42 Students are expected to attain the learner outcomes as stipulated for their specific grade level in the Technology Education Curriculum Guide, the Library Media/ Learning Resources Program Guide, and the Technology Competencies List as measured by the completion of the specified activities and assessments The Library Media/ Learning Resources Program goals are aligned with the CSDE’s most recent Library Media Resources Framework All grade 5 through 12 technology courses will have aligned goals and student outcomes with accompanying student assessments, activities and product requirements for success. Timeline Library Media/ Learning Resources Program Guide is completed for grades K through 4 and 9 through 12; 5 through 8 is currently being revised with completion expected by June of 2007. Approximately 80% of the Library Media/ Learning Resource Guide and course guides are completed. Completion of the majority of the program and course guides by Sept. 2006. The Technology Consultants ensure that all East Lyme High School graduates achieve advanced technology literacy measured by both department and schoolwide rubrics. 43 Goal 4: Ensure that K-12 resources are available for all students, regardless of race, ethnicity, income, geographical location or disability, so they can become technologically literate by the end of eighth grade and achieve their academic potential. The following must be addressed: Bullet 4: Describe how the LEA will ensure equal access to all students, teachers, staff and administrators. Objective All students, teachers, staff and administrators will have equal access to technology appropriate for their grade level, subject area or responsibilities. Strategy Accountability Measure See Goal 3; the district is committed to improving access and technology availability in an equitable manner for staff and students. All curriculum and program guides are district-wide with learner expectations developed for all students regardless of their race, ethnicity, income or disability. 44 Implementation of Technology Education and Library Media/ Learning Resources Program activities and assessments will be monitored by building principals or their designees. Timeline Equipment equalization by June of 2009 Curriculum Guide implementation by Sept. 2007 Goal 5: Develop a continuous process of evaluation and accountability for the use of educational technology as: a teaching and learning tool, a measurement and analysis tool for student achievement, and a fiscal management tool. The following must be addressed: Bullet 1: Describe how the LEA will evaluate and make changes to this plan on a yearly basis; Objective The plan will be adjusted based on student achievement. Strategy: Accountability Measure Teacher’s will demonstrate that students have achieved technology competencies by completion of end of unit projects with accompanying documentation. 45 At each grade level, the technology consultant will meet with teachers. The success of the project completion will be determined by competencies cited in Goal 1. Timeline Throughout the school year Goal 5: Develop a continuous process of evaluation and accountability for the use of educational technology as: a teaching and learning tool, a measurement and analysis tool for student achievement, and a fiscal management tool. The following must be addressed: Bullet 2: Describe how the LEA will provide access for students to take on-line tests, when available, that facilitate their involvement and the compilation of results; Objective The LEA will ensure that there is one computer per every three students and a high speed reliable network. Strategy: Accountability Measure Encourage the use of endorsed College Board on-line test registration and test preparation for SAT, SAT subject tests, and AP tests. The LEA will develop a committee to plan and ensure that the East Lyme School District pilots appropriate online testing. The pilot program will make certain that both teachers and students are prepared to take the State or National assessment instruments when they become available. 46 Teachers will be provided with professional development and curriculum support for developing and implementing valid online testing instruments/ assessments. The Curriculum Council and other LEA curriculum specialists will continue to research and evaluate the online assessment instruments as they relate to student achievement. In addition, curriculum specialists and the Curriculum Council will evaluate the test results to see if the tests are accurately measuring the students’ knowledge. Timeline On-going. Goal 5: Develop a continuous process of evaluation and accountability for the use of educational technology as: a teaching and learning tool, a measurement and analysis tool for student achievement, and a fiscal management tool. The following must be addressed: Bullet 3: Describe how the LEA will provide professional development to enable teachers and administrators to use data from the CMT’s, CAPT and district- or classroom-based formative and summative assessments to improve instruction; Objective Professional development is determined, in part, based on the student performance results on CMT and CAPT. Strategy: Accountability Measure Teachers use the assessment data to adjust instruction to accommodate individual student needs. School Improvement Plans (SIP) with accompanying action plans are developed by SIP teams in each building in conjunction with the building principals. 47 Principals periodically report and summarize information regarding SIP programs and adjustments. Timeline Throughout the school year. Goal 5: Develop a continuous process of evaluation and accountability for the use of educational technology as: a teaching and learning tool, a measurement and analysis tool for student achievement, and a fiscal management tool. The following must be addressed: Bullet 4: Describe how the LEA will create, maintain or improve electronic resources to ensure administrative needs are addressed and solutions developed; and Objective The LEA has implemented electronic resources to compare and profile student information. Strategy: Accountability Measure This is maintained on an ongoing basis with student test data monitored electronically in grades K-12. 48 Principals monitor Timeline On-going Goal 5: Develop a continuous process of evaluation and accountability for the use of educational technology as: a teaching and learning tool, a measurement and analysis tool for student achievement, and a fiscal management tool. The following must be addressed: Bullet 5: Describe how the LEA will implement technology initiatives to improve student achievement. Objective The District will provide professional development for teachers and paraprofessionals regarding the latest initiatives in technology. Strategy: Accountability Measure Access resources in our region such as LEARN technology offerings and professional development offerings as advised by the district-wide steering committee. 49 The district professional development days will include specific technology programming depending on teacher and student needs. Timeline Annual Goal 6: Develop a schema of current and future financing requirements to support the LEA’s Technology Plan. The following must be addressed: Bullet 1: Describe how the LEA will meet current and future funding requirements to support plan implementation A phase-in plan is in place to improve our district network. The plan increases the number of switches and drops, improves our back up capabilities, replaces servers and out-of-date or nonrepairable CPUs using current levels of funding that are increased yearly. Also included in our spending plan is a periodic network check up by a contracted vendor. Where the current level of funding is insufficient, the plan calls for specific budget allocation increases to meet these needs. Since the total impact of these requests is relatively small, the expectation is that they will be granted by the Board of Education. Principals will be expected to allocate from their per pupil allocations a minimum level of support for hardware and software acquisition and replacement as stated in the district’s Technology Long Range Plan. 50 Goal 6: Develop a schema of current and future financing requirements to support the LEA’s Technology Plan. The following must be addressed: Bullet 2: Describe how the LEA will develop policies and procedures related to maintenance of hardware, software, infrastructure and security. Policies and procedures currently exist. This plan includes the expectation that current technology staff will continue to be available to make repairs, maintain the network, review and recommend software acquisition, train staff on software use, and deliver professional development. The network administrator will analyze and implement the recommendations of the contracted vendor and the results of their periodic network check up. 51 Goal 6: Develop a schema of current and future financing requirements to support the LEA’s Technology Plan. The following must be addressed: Bullet 3: Describe how the LEA will meet current and future funding requirements to keep the technology updated. As indicated in Bullet 1, the plan includes updating and replacement provisions to meet this need. In addition, the Technology Committee meets regularly (once a month) and includes in its discussions, plans and proposals how to keep our network and technology services current and effective. Funding proposals are forwarded to central office and building administrative personnel for consideration, support and implementation. 52 Goal 7: Develop a telecommunications services plan that will support both instructional needs and administrative requirements. The following must be addressed: Bullet 1: Clear goals and a realistic strategy for using telecommunications and information technology to improve education or library services; Objective : The goal of the East Lyme School District is to integrate global communications, distance learning, and resource sharing using telecommunications for advanced student achievement and learning of new knowledge and the world they live in. Strategy To have students use technology to communicate with and learn from others in numerous learning activities and course objectives throughout the K-12 curriculum. To join consortiums and or form partnerships with others in academia, K-12, business, and libraries for the purposes of resource sharing of materials, staff and information. To fully participate in the CEN and all the resources available. To promote the use of Connecticut Digital Library and its databases. To seek partnerships for distance learning opportunities to enhance the curriculum and to accomplish curriculum objectives. To offer on-line courses to high school students in curricula areas that are not offered locally. 53 Goal 7: Develop a telecommunications services plan that will support both instructional needs and administrative requirements. The following must be addressed: Bullet 2: A professional development strategy to ensure that staff know how to use these new technologies to improve education or library services. Objectives/ Activities/ Strategies 2006-07 During the 2006-2007 school year, the East Lyme Public Schools K-12 Library Media/Learning Resources Guide will be completed and plans for implementation will ensue. Objectives/ Activities/ Strategies 2006-2007, 2007-2008, 2008-2009 An annual Professional Development Brochure will provide the staff opportunities to be involved in workshops that incorporate computer and other technologies as applied to student learning and classroom instruction, communications and data management as indicated in CT ED Laws (Sec. 10-220a). Monitoring/Evaluation Procedure During the Fall of 2006, the revised guide will be distributed to all Library Media Specialists and Technology Consultants. Discussion will ensue regarding building level implementation. Monitoring/Evaluation Procedure The technology workshops are all CEU-able; therefore, attendance is monitored as well as completion of program offering outcomes by central office administration. Technology competency plans will be part of each certified staff’s growth plan, and monitored by the certified staff’s evaluator. A Technology Competencies Checklist will be provided for each staff member. Based on a self-evaluation and in consultation with the building Technology Consultant, individual PD plans will be developed on an annual basis (aligning technology plans and subject area expectations). 54 Goal 7: Develop a telecommunications services plan that will support both instructional needs and administrative requirements. The following must be addressed: Bullet 3: An assessment of the telecommunications services, hardware, software and other services that will be needed to improve education or library services; Continue to meet Department of Information Technology network and telecommunication standards for full participation in the CEN. Conduct an annual review either locally or with an outside contractor to determine the readiness of our telecommunication services, hardware, and software as required by the Universal Service Fund for E-Rate participation. 55 Goal 7: Develop a telecommunications services plan that will support both instructional needs and administrative requirements. The following must be addressed: Bullet 4: A sufficient budget to acquire and support the non-discounted elements of the plan: the hardware, software, professional development and other services that will be needed to implement the strategy. As Goal 6 indicates, budgeted funds are earmarked for specific purchases to acquire the hardware, software, professional development and other services, such as the periodic network evaluation by a contracted vendor. Title II grant funds will also be used to support professional development activities for staff members and technology committee members. Where necessary, our finance plan includes the preparation of requests for additional funds for specific purposes. Current levels of funding which include per pupil allocations to buildings by level are planned to remain constant with cost of living increases as appropriate from year to year. 56 Goal 7: Develop a telecommunications services plan that will support both instructional needs and administrative requirements. The following must be addressed: Bullet 5: An evaluation process that enables the school or library to monitor progress toward the specific goals (of the eligible entity) and make mid-course corrections in response to new developments and opportunities as they arise. The District Technology Committee meets monthly to address immediate issues and plan for the future. Media specialists, computer consultants, and an administrator from central office serve on the committee. This standing committee reports to the District Curriculum Council quarterly and delivers an annual report stating goals and needs for the coming year, and then later, how the committee is progressing toward those goals. The computer consultants (one from each building) and the network administrator also meet each month to deal with technical problems and implementation of curriculum. At the elementary and middle school levels, each computer consultant monitors classroom technology activity through grade-level meetings, computer lab use, and individual teacher meetings. Grade-level specific goals are reviewed and integrated lessons are planned so that the outcomes are addressed. The media specialist is responsible for collaborating with teachers to ensure that the student technology competencies listed in the K-12 Library Media/ Learning Resources Guide and the District Technology Plan are integrated into instruction. At the high school level, each course has specific technology outcomes embedded into it. By the end of four years, each student has to have met the technology requirements for graduation. Guidance counselors ensure that students are taking the appropriate courses. Teachers monitor student’s technology skills and knowledge when assessing their work in the content/curriculum areas such as learning activities that resulting in student projects, reports, communications, literacy, research, and problem solving. The school monitors each student’s progress towards achieving advanced technology competencies through department and school-wide rubrics. Midcourse corrections or the need for additional learning are monitored by the teacher and supported with professional development provided by the computer consultant. Students receive additional group and individual support by the library media specialist. 57 Objectives/ Activities/ Strategies 2006-2007, 2007-2008, 2008-2009 To integrate global communications, distance learning, and resource sharing using telecommunications for advanced student achievement and learning of new knowledge and the world they live in. 2006-2007 2007-2008 2008-2009 Monitoring/Evaluation Procedure Provide staff development for teachers in World Languages and Social Studies. Expand staff development opportunities for teachers in additional subject areas: Language Arts, Math and Science. To provide follow-up PD based on a needs assessment to enhance the integration of global communication, distance learning and resource sharing. Develop, monitor and evaluate student products to assure that students used technology to communicate with and learn from others in numerous learning activities and course objectives throughout the K-12 curriculum. Provide staff opportunities to be involved in workshops that incorporate computer and other technologies. Teachers who participate in 2005-2006 staff development apply new skills to advance student learning and classroom instruction, communications and data management as indicated in CT ED Laws (Sec. 10-220a). Expand staff development opportunities for teachers by having technology consultants providing inservices based on a needs assessment. Teachers apply learned skills in 2007-2008 to advance student learning. Technology workshops that advance student learning are all CEU-able; therefore, attendance is monitored as well as completion of program offering outcomes by central office administration. A Technology Competencies Checklist will be provided for each staff member. Based on a selfevaluation and in consultation with the building Technology Consultant, individual PD plans will be developed on an annual basis. Technology plans and subject area expectations will be aligned annually. Technology competency plans will be part of each certified staff’s growth plan, and monitored by the certified staff’s evaluator. (continued on next page) 58 Objectives/ Activities/ Strategies 2006-2007, 2007-2008, 2008-2009 To join consortiums and or form partnerships with others in academia, K-12, business, and libraries for the purposes of resource sharing of materials, staff and information. 2006-2007 To fully participate in the CEN and all the resources available and train staff on resources. To seek partnerships for distance learning opportunities to enhance the curriculum and to accomplish curriculum objectives. Offer on-line courses to high school students in World Languages. Continue to offer on-line courses to high school students in curricula areas that are not offered locally. 2007-2008 2008-2009 Monitoring/Evaluation Procedure The District technology Committee will monitor the development and implementation of efforts to meet these expectations. The Committee’s Annual report will be reviewed by the district administrative team to determine what activities should be continued and improved and what activities need to be terminated. 59 Technology Funding Sources and Costs Professional Development Planned The National Study for School Evaluation (NSSE) Teacher Technology On-line Survey conducted in February, 2006 identified areas in need of further training by level: elementary, middle school, high school. Initial analysis of this survey’s results identified the following items the staff at each level identified as the items they felt least competent in: Elementary: “I can design an assignment in which students evaluate the accuracy, relevance, appropriateness, and bias of electronic information sources.” “I can use students’ test results from computer-based assessments to evaluate student learning from software.” “I can create my own World Wide Web pages to be accessed by my students as part of a lesson.” Middle School: “I can design a lesson in which students create web pages to share their reports or writings outside the classroom.” “I can create my own World Wide Web pages to be accessed by my students as part of a lesson.” “I can teach students to create digital portfolios of their learning using media such as HyperStudio or the Web.” “I can teach a lesson addressing district and state standards as well as the ISTE National Educational Technology Standards for Students.” “I can protect privacy and security when publishing students’ writing or images on the web.” High School: “I can design a lesson in which students create web pages to share their reports or writings outside the classroom.” “I can create my own World Wide Web pages to be accessed by my students as part of a lesson.” “I can use students’ test results from computer-based assessments to evaluate student learning from software.” “I can protect privacy and security when publishing students’ writing or images on the Web.” “I can teach students to create digital portfolios of their learning using media such as HyperStudio or the web.” The District Technology Committee will discuss these needs and identify additional technology skills and various applications that require training. At the building level, computer consultants poll teachers regarding 60 PD activities. Included in our curriculum development process is an expectation that the integration of appropriate technology is a component of all discipline areas. An outgrowth of these processes is the identification of technology implementation expectations that have PD implications. The District-wide Technology Committee is a body that facilitates the identification and scheduling of PD and interacts with the District’s Professional Development Steering Committee. The Steering Committee is responsible for advising the District’s Leadership Team and assists in coordinating and implementing PD activities on designated days. During 2006-2008 years, the Professional Development focus will be on: Training new teachers on how to use our network and the software applications dictated by the curriculum/grade level they teach Digital Portfolios at ELHS and ELMS Web page development by students and staff at ELHS and ELMS Use students’ test results from computer-based assessments to evaluate student learning from software at ELHS and ELMS 61 ANNUAL BUDGET SUMMARY YEAR 2006-2007 NOTE: DUPLICATE THIS PAGE FOR EACH YEAR AS NEEDED o List the professional development and technologies to be acquired during each year of the agency’s plan. o Note: At least 25% of the funds allocated to an LEA through the Title II-D ED Tech Program, must be allocated for professional development activities. (Current estimates indicate that Title II D funding will be reduced by ~40% in 2006-07 year from the 2005-06 level.) o Estimate the cost of the professional development and technologies in the appropriate column(s) from which the agency intends to take the funds. o Describe how your district/charter coordinates or aligns the other federal, state, local funds with district/charter consolidated plans and/or individual schools' School Improvement Plans. Acquired Technologies and Professional Development Ed Tech Competitive/ Title II-D Ed Tech Formula/ Title II-D State Bond Funds Capital E-Rate NCLB/other than Title II-D Other (Specify) Network Report $1,500 Operational Budget Switches $15,000 Operational Budget Server Replacement $15,000 Operational Budget Drops $7,500 Operational Budget New Computers $35,000 Operational Budget Replacement Computers $22,500 Operational Budget P.D. provided after hours by on-site tech staff P.D. provided during school hours by on-site tech staff TOTAL $2,065 Costs included in Operational Budget $2,065 $96,500 62 ANNUAL BUDGET SUMMARY YEAR 2007-2008 NOTE: DUPLICATE THIS PAGE FOR EACH YEAR AS NEEDED o List the professional development and technologies to be acquired during each year of the agency’s plan. o Note: At least 25% of the funds allocated to an LEA through the Title II-D ED Tech Program, must be allocated for professional development activities. (Current estimates indicate that Title II D funding will be reduced by ~40% in 2006-07 year from the 2005-06 level.) o Estimate the cost of the professional development and technologies in the appropriate column(s) from which the agency intends to take the funds. o Describe how your district/charter coordinates or aligns the other federal, state, local funds with district/charter consolidated plans and/or individual schools' School Improvement Plans. Acquired Technologies and Professional Development Ed Tech Competitive/ Title II-D Ed Tech Formula/ Title II-D State Bond Funds Capital E-Rate NCLB/other than Title II-D Other (Specify) Network Report $1,500 Operational Budget Switches $15,000 Operational Budget Back Up System $8,000 Operational Budget Server Replacement $15,000 Operational Budget New Computers $35,000 Operational Budget Replacement Computers $22,500 Operational Budget P.D. provided after hours by on-site tech staff P.D. provided during school hours by on-site tech staff Video Conferencing Equipment TOTAL $2,065 Costs included in Operational Budget $20,000 Operational Budget $2,065 $117,000 63 ANNUAL BUDGET SUMMARY YEAR 2008-2009 NOTE: DUPLICATE THIS PAGE FOR EACH YEAR AS NEEDED o List the professional development and technologies to be acquired during each year of the agency’s plan. o Note: At least 25% of the funds allocated to an LEA through the Title II-D ED Tech Program, must be allocated for professional development activities. (Current estimates indicate that Title II D funding will be reduced by ~40% in 2006-07 year from the 2005-06 level.) o Estimate the cost of the professional development and technologies in the appropriate column(s) from which the agency intends to take the funds. o Describe how your district/charter coordinates or aligns the other federal, state, local funds with district/charter consolidated plans and/or individual schools' School Improvement Plans. Acquired Technologies and Professional Development Ed Tech Competitive/ Title II-D Ed Tech Formula/ Title II-D State Bond Funds Capital E-Rate NCLB/other than Title II-D Other (Specify) Network Report $1,500 Operational Budget Switches $12,000 Operational Budget Video Conferencing Equipment Server Replacement $20,000 Operational Budget New Computers $35,000 Operational Budget Replacement Computers $22,500 Operational Budget P.D. provided after hours by on-site tech staff P.D. provided during school hours by on-site tech staff TOTAL $15,000 Operational Budget $2,065 Costs included in Operational Budget $2,065 $106,000 64 CHILDREN’S INTERNET PROTECTION ACT (CIPA) CERTIFICATION Schools and libraries that plan on receiving E-Rate discounts on Internet access and/or internal connection services after July 1, 2002, need to be in compliance with the CIPA. CIPA compliance means that schools and libraries are filtering their internet services and have implemented formal internet safety policies (also frequently known as Acceptable Use Policies). Information on the CIPA requirements is located at http://E-Ratecentral.com/CIPA/cipa_policy_primer.pdf. I, Paul Smotas , certify that one of the following conditions (as indicated below) exists in Name of Superintendent/Director East Lyme Public Schools LEA X My district/agency is E-Rate compliant; or My district/agency is not E-Rate compliant. (Check one additional box below): Every “applicable school*” has complied with the CIPA requirements in subpart 4 of Part D of Title II of the ESEA**. Not all “applicable schools*” have yet complied with the requirements in subpart 4 of Part D of Title II of the ESEA**. However, the LEA has received a one-year waiver from the U.S. Secretary of Education under section 2441(b)(2)(C) of the ESEA for those applicable schools not yet in compliance. The CIPA requirements in the ESEA do not apply because no funds made available under the program are being used to purchase computers to access the Internet, or to pay for direct costs associated with accessing the Internet, for elementary and secondary schools that do not receive E-Rate services under the Communications Act of 1934, as amended. *An applicable school is an elementary or secondary school that does not receive E-Rate discounts and for which Ed Tech funds are used to purchase computers used to access the Internet, or to pay the direct costs associated with accessing the Internet. **http://www.ed.gov/legislation/ESEA02/pg37.html Signature of Superintendent/Director Date 65 APPENDIX A: Educational Technology Planning Toolkit It is recommended that the following companion documents be utilized when developing local educational technology plans: Educational Technology Planning CSDE Position Statement on Educational Technology National Educational Technology Plan CT Educational Technology BLOG CT Administrator Technology Standards CT Teacher Technology Competencies CT PreK-12 Computer Technology Competency Standards for Students CT Education Network (CEN) CT Commission for Educational Technology (CET) SETDA Toolkit contains resources for eLearning, 8th Grade Technology Literacy Assessment and technology embedded curriculum development. CAPSS E-Learning Position Statement CAPSS Educational Technology Position Statement E-Rate Central A Guide For Assessing Technology A Critical Issue: Developing a School or District Technology Plan Educational Technology Planning NCrtec; Leadership and Learning with Technology Southwest Educational Development Laboratory Profiler; free online technology assessment tool and tutorial enGauge; a framework for effective technology use and planning ICT Literacy Skill maps Interactive School Technology and Readiness Assessment Site http://www.state.ct.us/sde/board/ed_technology.pdf http://www.nationaledtechplan.org/default.asp http://cteducationaltechnology.blogspot.com/ http://www.state.ct.us/sde/dtl/technology/CATSv2.pdf http://www.state.ct.us/sde/dtl/technology/CTTCt.pdf http://www.state.ct.us/sde/dtl/technology/StudentCompv2.pdf http://www.ct.gov/cen/site/default.asp http://www.ct.gov/ctedtech/site/default.asp?cenPNavCtr=|#30930 http://www.setda.org/Toolkit2004/evaluation_07_resources_readings.ht m#assessment http://www.capss.org/E-learningpositionpaper.doc http://www.capss.org/CAPSStechnologypositionstatement2.pdf http://E-Ratecentral.com http://nces.ed.gov/pubs2003/2003313.pdf http://www.ncrel.org/sdrs/areas/issues/methods/technlgy/te300.htm http://www.tcet.unt.edu/tek-plan.htm http://www.ncrtec.org/pd/llwt/ http://www.sedl.org/pubs/tec26/flash.html http://profiler.hprtec.org/ http://www.ncrel.org/engauge/ http://www.21stcenturyskills.org/index.php?option=com_content&task= view&id=31&Itemid=33 http://www.iste.org/inhouse/starchart/index.cfm?Section=STaRChart&C FID=1752780&CFTOKEN=91033516 57 APPENDIX B : Technology Plan Review Guide Technology Plan Review Guide Reviewer ___________________ LEA ____________________ Complete? (Y/N) additional information required/comments LEA Profile Technology Committee Needs Assessment Goal 1 Goal 2 Goal 3 Goal 4 Goal 5 Goal 6 Goal 7 Goal 8 Technology Funding Sources I _________________________verify that _______________________ has successfully completed all of the requirements as stated in the Signature of Reviewer Name of LEA technology plan template. 58