file
advertisement

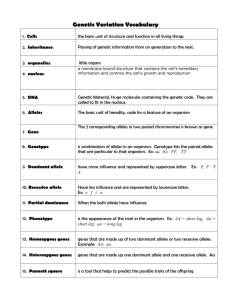
Name: ________________________________ Genetics Study Guide Complete with a parent signature for five bonus points on your test. Modified True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement true. ____ 1. A hybrid is the offspring of parents that have different alleles for a trait. _________________________ ____ 2. A pea plant that is heterozygous for tall stems has the alleles Tt. _________________________ ____ 3. The sex cells produced by meiosis have twice the number of chromosomes as the parent cells. _________________________ ____ 4. Chromosomes carry genes from parents to offspring. _________________________ ____ 5. A mutation in a sex cell can be passed to offspring. _________________________ ____ 6. Even if a gene has multiple alleles, a person cannot have more than three of those alleles. _________________________ ____ 7. A trait such as height or skin color that has many different phenotypes is often controlled by a single gene. _________________________ ____ 8. A person's environment can affect his or her genotype for certain traits, such as height. _________________________ ____ 9. Sex-linked traits that are controlled by recessive alleles are more likely to show up in males. _________________________ ____ 10. A male is represented by a square in a pedigree. _________________________ Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 11. Which term refers to physical characteristics that are studied in genetics? a. traits b. offspring c. generations d. hybrids ____ 12. The different forms of a gene are called a. alleles. b. factors c. masks. d. traits. ____ 13. Scientists call an organism that has two different alleles for a trait a a. hybrid. b. trait. c. purebred. d. factor. ____ 14. What does the notation TT mean to geneticists? a. two dominant alleles b. two recessive alleles c. at least one dominant allele d. one dominant and one recessive allelle ____ 15. What does the notation Tt mean to geneticists? a. two dominant alleles b. two recessive alleles c. at least one recessive allele d. one dominant allele and one recessive allelle ____ 16. What is probability? a. the actual results from a series of events b. the likelihood that a particular event will occur c. the way the results of one event affect the next event d. the number of times a coin lands heads up ____ 17. What does a Punnett square show? a. all the possible outcomes of a genetic cross b. only the dominant alleles in a genetic cross c. only the recessive alleles in a genetic cross d. all of Mendel's discoveries about genetic crosses ____ 18. If a homozygous black guinea pig (BB) is crossed with a homozygous white guinea pig (bb), what is the probability that an offspring will have black fur? a. 25 percent b. 50 percent c. 75 percent d. 100 percent ____ 19. An organism's genotype is its a. genetic makeup b. feather color c. physical appearance d. stem height ____ 20. An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait is a. codominant. b. tall. c. homozygous. d. heterozygous. ____ 21. A heterozygous organism has a. three different alleles for a trait. b. two identical alleles for a trait. c. only one allele for a trait. d. two different alleles for a trait. ____ 22. What does codominance mean in genetics? a. Both alleles are dominant. b. Both alleles are recessive. c. The alleles are neither dominant nor recessive. d. Each allele is both dominant and recessive. ____ 23. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? a. Chromosomes are carried from parents to offspring on hybrids. b. Genes are carried from parents to offspring on chromosomes. c. Hybrid pairs of chromosomes combine to form offspring. d. Codominant genes combine to form new hybrids. ____ 24. When sex cells combine to produce offspring, each sex cell will contribute a. one fourth of the normal number of chromosomes. b. half the normal number of chromosomes. c. the normal number of chromosomes. d. twice the normal number of chromosomes. ____ 25. What is a mutation? a. any change that is harmful to an organism b. any change in a gene or chromosome c. any change that is helpful to an organism d. any change in the phenotype of a cell ____ 26. A mutation is harmful to an organism if it a. changes the DNA of the organism. b. changes the phenotype of the organism. c. reduces the organism's chances for survival and reproduction. d. makes the organism better able to avoid predators. ____ 27. What are multiple alleles? a. more than two genes that control a trait b. three or more forms of a gene that code for a single trait c. three or more chromosomes that determine a trait d. more than two codominant genes in a chromosome ____ 28. What is the blood type of a child born to two parents with the genotypes IAIA and IBIB for blood type? a. Type A b. Type B c. Type AB d. Type O ____ 29. What factors can affect a person's height? a. genes only b. environmental factors only c. both genes and environmental factors d. the sex chromosomes a person inherits ____ 30. Which combination of sex chromosomes results in a male human being? a. XX b. YY c. XY d. either XX or YY ____ 31. Why are sex-linked traits more common in males than in females? a. All alleles on the X chromosome are dominant. b. All alleles on the Y chromosome are recessive. c. A recessive allele on the X chromosome will produce the trait in a male. d. Any allele on the Y chromosome will be codominant with the matching allele on the X chromosome. ____ 32. A carrier is a person who has a. one recessive and one dominant allele for a trait. b. two recessive alleles for a trait. c. two dominant alleles for a trait. d. more than two alleles for a trait. ____ 33. How does a geneticist use pedigrees? a. to create genetic crosses b. to replicate identical strings of DNA c. to prove that sex-linked traits are caused by codominant alleles d. to trace the inheritance of traits over generations of families ____ 34. Hemophilia is caused by a(n) a. recessive allele on the X chromosome. b. extra chromosome. c. dominant allele. d. codominant allele. ____ 35. Down syndrome most often occurs when a. a person inherits a recessive allele. b. chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis. c. sickle-shaped cells become stuck in blood vessels. d. blood fails to clot properly. ____ 36. What genetic disorder results in abnormally shaped blood cells? a. hemophilia b. Down syndrome c. cystic fibrosis d. sickle-cell disease ____ 37. Which genetic disorder causes the body to produce unusually thick mucus in the lungs and intestines? a. hemophilia b. Down syndrome c. cystic fibrosis d. sickle-cell disease ____ 38. What procedure helps doctors diagnose a genetic disorder before a baby is born? a. genetic engineering b. selective breeding c. amniocentesis d. cloning ____ 39. What is a karyotype? a. blood from a newborn baby b. a picture of a baby before it is born c. a picture of the chromosomes in a cell d. fluid that surrounds a baby before it is born ____ 40. Which form of selective breeding crosses genetically different individuals in an attempt to keep the best traits of both parents? a. genetic engineering b. inbreeding c. hybridization d. cloning ____ 41. What is the purpose of the Human Genome Project? a. to identify the DNA sequence of every gene in the human genome b. to clone every gene on a single chromosome in human DNA c. to splice every gene on a single chromosome in human DNA d. to inbreed the best genes on every chromosome in human DNA Completion Complete each sentence or statement. 42. If a ____________________ allele is present, its trait will appear in the organism. 43. A chart used to predict results of genetic crosses is known as a(n) ____________________. 44. Alleles that are neither dominant nor recessive produce an inheritance pattern known as ____________________. 45. Genes are located on structures called ____________________. 46. The process in which a parent cell divides twice to produce sex cells is called ____________________. 47. The three alleles of the single gene that controls blood type are said to be ____________________ alleles. 48. A(n) ____________________ is a used to track the occurrence of a trait in a family. 49. A person who has the genetic disorder called ____________________ bleeds easily. 50. Down syndrome is caused by the presence of an extra ____________________. 51. A doctor performs a procedure called ____________________ to get cells from the fluid that surrounds a developing baby. Short Answer 52. What do the circles in the pedigree represent? What do the squares represent? 53. Which pairs of individuals in the pedigree have children? 54. Which individuals neither have the trait nor are carriers? Essay 55. A woman gives birth to a son. Two years later, she gives birth to another son. What is the probability that her third child will be a girl? Explain your reasoning. 56. Is it possible for a son to inherit an allele on an X chromosome from his father? Explain why or why not.