Jeopardy #2
advertisement

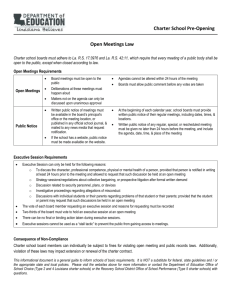
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. The war where American fought against the British (American Revolution) The amendment ending slavery (13th) The war in America fighting over slavery (Civil War) The year the UN was formed (1945, after the WW2) Most powerful court (Supreme court of Canada) How many judges does the supreme court have? (9) How do they get their position? (appointed by the PM) What are two reasons we discussed that provinces can restrict mobility? (welfare and unemployment rates) 9. The rights that state people have rights to life, liberty and security (natural) 10. The rights laid out in the Charter (civil rights) 11. the rights protecting people from being unfairly discriminated against (human) 12. unwritten laws thought to be understood (common laws) 13. the PM the signed the Bill of Rights (Diefenbaker) 14. What document was created by the UN and signed Dec. 10, 1948 (Universal Declaration of Human Rights) 15. The clause that allows provinces/territories to enact legislation that may violate the Charter (notwithstanding clause) 16. These rights limit the power government has on people (civil) 17. Which PM signed the Constitution Act, 1982? (Trudeau) 18. Which is harder to change, Charter or the Bill of Rights? (Charter) 19. The clause that can limit rights (reasonable limits clause) 20. What province is famous for using the notwithstanding clause? (Quebec) 21. What does franchise mean? (right to vote) 22. What is entrenched in the Constitution? (Charter) 23. Section 2 of the Charter outlines what? (The 4 fundamental freedoms) 24. What fundamental freedom states we are free to practice religion or not? (Freedom of Conscience and Religion) 25. What are Canada’s official languages? (English and French) 26. When it comes to human rights, it is illegal to (discriminate) 27. Making a judgment about a person ( prejudice) 28. Making a judgment about a group (stereotyping) 29. Chantal can’t play baseball because she’s a girl. This is an example of (prejudice) 30. All Asians are good at math. This is an example of (stereotyping) 31. Why aren’t aboriginals “existing rights” laid out in the Charter? (The government and aboriginals couldn’t agree) 32. 2 ways the Charter is enforced (strike down/read down, and apply to the courts) 33. Which has more legal impact, strike down or read down? (strike down) 34. Acting upon prejudice thoughts (discrimination) 35. Why does human rights law change? (because society is changing) 36. Not hiring a woman because she is pregnant, is an example of (discrimination) 37. Section 15 deals with (Equality Rights) 38. Which Section deals with equality of the sexes? (28) 39. A restriction is reasonable if (“ it is good for the group” and “demonstrably justifiable in a free and democratic society”) 40. When a person knowingly discriminates (intentional discrimination) 41. The name of Canada’s Human Rights Legislation (Canada’s Human Rights Act) 42. Provincial and Territorial human rights codes are based on (Universal Declaration of Human Rights) 43. What is the first step when you feel your human rights have been violated? (file a complaint) 44. Changes in a constitution (amendments) 45. Why does the government have censorship laws? (to protect the vulnerable) 46. Name and discuss and subgroup of the UN 47.