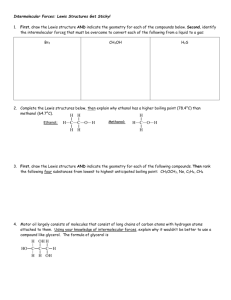
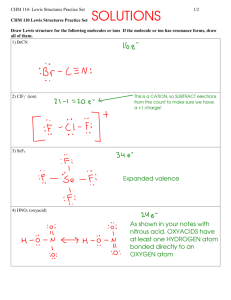
300 Chemistry Problems Bonding Do on separate paper or in your

300 Chemistry Problems Bonding
Do on separate paper or in your notebook
1. Predict the type of bonding that will occur between each of the following pairs of elements
(ionic, polar covalent, nonpolar covalent), using the following electronegativity values: H
2.1, Li 1.0, C 2.5, N 3.0, O 3.5, F 4.0, Mg 1.2, Cl 3.0, K 0.8, Ca 1.0, and Br 2.8. Note any patterns since you will not always have electronegativity values readily available.
H and Br
Br and Br
C and O
F and Cl
Li and O
K and Cl
H and N
F and F
Ca and O
Li and F
Mg and F
C and H
N and O
2. Draw the Lewis structures for each of the following ionic compounds:
KF
MgF
2
Li
2
O
AlCl
3
NaI
Na
2
S
RbI
K
2
O
NaBr
AlF
3
BaO
3. Draw the Lewis structures for each of the following covalently bonded compounds:
H
2
F
2
Se
HCl
CF
4
O
2
NF
3
H
2
CO
2
SiH
4
N
2
BH
3
4. Draw Lewis structures for each of the compounds below (level 1 … straightforward):
H
2
F
2
O
2
N
2
CO
2
H
2
O
HF
CH
3
OH
H
2
S
NH
3
I
2
CF
4
CHCl
3
SO
3
CCl
4
BF
3
SiO
2
5. Draw Lewis structures for the compounds below (level 2 … some are a little more challenging):
PBr
3
N
2
H
2
C
2
H
4
BSF
C
2
H
5
OH
N
2
F
4
CO
NO
2
F
SiS
2
C
2
H
2
BeF
2
BH
3
NF
3
C
2
H
6
CS
2
H
2
Te
C
2
H
4
Cl
2
SO
2
HCN
Cl
2
CO
H
2
CCl
2
FNO
C
4
H
10
OCl
2
SeF
2
6. Draw the Lewis structures for the following polyatomic ions:
Ammonium
Perchlorate
Sulfate
Nitrate
Thiocyanate
Hydronium (H
3
O
+1
)
7. Go back to questions 4, 5, and 6 and identify any substances that have coordinate covalent bonds.
8. Go back to questions 4, 5, and 6 and name the three dimensional geometry of each, draw a
3D picture of it, and label the appropriate bond angle.
9. Go back to questions 4 and 5 and state whether each molecule is polar or nonpolar.
10. Go back to questions 4 and 5 and identify the most noticeable type of intermolecular forces present in each substance.
11. For each of the following substances, determine the dominant type of intermolecular force. You may find it useful to draw Lewis structures for some of these:
Nitrogen
Carbon tetrachloride
Water
Sulfur monoxide
Boron trihydride
N
2
H
2
SiH
2
O
Ammonia (nitrogen trihydride)
Carbon dioxide
Phosphorous trichloride
Ethane (C
2
H
6
)
Acetone (CH
2
O)
Methanol (CH
3
OH)
12. Explain why ethyl alcohol (C
2
H
5
OH) has a higher boiling point than methyl alcohol
(CH
3
OH).
13. Rank the following in order from lowest to highest anticipated boiling point: C
2
H
4
, CH
4
,
Ne, H
3
COCH
3
.
14. Motor oil consists of molecules that consist of long chains of carbon atoms with hydrogen atoms attached to them. Using your knowledge of IMFs, explain why it wouldn’t be better to use a compound like glycerol (formula is CHOH(CH
2
OH)
2
).
15. Review problems
Identify each compound’s type of bonding: carbon dioxide, magnesium sulfate, water, dihydrogen monosulfide, sodium fluoride, calcium oxide.
16. Give the Lewis structures for: CH
4
, NH
3
, O
2
, Li
2
O, NaF, and Li
3
N.
17. For each of the following compounds, draw a Lewis structure, sketch a 3D shape showing the bond angle(s), name the geometry, identify whether or not the molecule is polar:
BCl
3
, PBr
3
, SiCl
4
, CH
2
, N
2
, NF
3,
CO, SO
2
, SO
3,
O
3
, SO
3
.
d. Rank each group of substances in order from lowest to highest boiling point:
.
C
2
H
4
, CH
4
, H
3
COCH
3
.
C
2
H
5
OH, CH
3
OH
.
HCN, CH
4
, H
2
O
.
He, Ne, CO
2
, NH
3
.
HF, CH
2
O, SiH
2
O
For additional practice:
Relevant sections in book are Chapter 12 and section 14.1
Additional practice problems can be found on p. 394-397 (1-7, 9-12, 30-37, 39-42, 47-50