Plant Diversity II: Seed Plants
advertisement

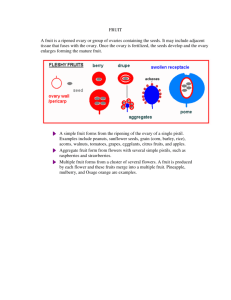
NAME: Lab Worksheet Lab Topic 16 Plant Diversity II: Seed Plants Biology 211 Fall 2005 Use the following as a resource as you complete the lab assignment. ATLAS FIGURES AND COLOR PLATES IN LAB MANUAL Exercise 16.1 Gymnosperms Lab Study A Divisions of Gymnosperms Atlas pages 74-81; Color plates 38, 39, 40, 41 and 42. Exercise 16.2 Angiosperms Lab Study A Flower Morphology: Atlas pages 92-96; Color plate 43, and 44, Lab Study C Angiosperm Life Cycle: Atlas page 82; Color plate 48 (ovule) and 49 (pollen tube). Lab Study D Fruits and Dispersal: Atlas pages 97-98; Color plate 44, 45, 46, and 47. IN-LAB ASSIGNMNENT Exercise 16.1 Gymnosperms Lab Study A Divisions of Gymnosperms (1.25 pt) 1. Review Introduction section, page 428. Complete Procedure, Results and Discussion sections, p. 429. Use the following resources: a) live material on display b) Color plates at the back of the lab manual (see list above) c) Following web sites Cycads http://waynesword.palomar.edu/ww0803.htm#cycads http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/401/Cycadophyta/Zamiaceae/Dioon/Dioon_holmgrenii_ MC.html http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/401/Cycadophyta/Stangeriaceae/Stangeria/S_eriopus_D W.html http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/401/Cycadophyta/Zamiaceae/Dioon/Dioon_spinulosum/ Dioon_spinulosum_habit_DW.html Gingkos http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/401/Ginkgophyta/Ginkgoaceae/Ginkgo_biloba/ http://waynesword.palomar.edu/ww0803d.htm (Picture of Ginkgos on OSU campus!) Gnetophyta -Ephedra http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/401/Gnetophyta/Ephedra/E_nevadensis_habit_DW.ht ml Gnetum http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/courses/systematics/Phyla/Gnetophyta/Gnetophyta.html Welwitschia http://waynesword.palomar.edu/welwit.htm http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/images/401/Gnetophyta/Welwitschia_mirabilis/ Table 16.2 Divisions of Gymnosperms Divisions Examples Sketch of examples; include any reproductive structures Discussion 1. (0.25 pt) Identify one of the conifers on display using the taxonomic key found on OSU tree identification website: http://oregonstate.edu/trees/ (Just for fun, identify one of the mystery trees found on the website!). Conifer number: _____ Species name: ____________ Exercise 16.2 Angiosperms Lab Study A Flower Morphology (1.75 pts) 1. Review Introduction, p. 433-434. Note that the correct general term for the female part is pistil, not carpel. 2. Complete procedure and results, pp. 435-436. Table 16.3 Flower Morphology and Pollinators Features 1. Peruvian lily Plant names Number of petals Number of sepals Number of stamens Number of pistils Monocot or dicot Sketch of the ovules in the ovary The ovules develop into what? The ovary develops into what? Color Scent (+/-) Nectar (+/-) Shape (including corolla shape: tubular, star, etc.) Special features (landing platform, guidelines, nectar spur, etc.) Predicted pollinator (Hint: use the key on p, 438) Lab Study B Pollinators (Skip this exercise). Lab Study C Angiosperm Life Cycle (2.00 pts) 2. Snapdragon 3. composite A. Complete Procedure, Results and Discussion sections, p. 439-442. Results 1. 2. a) Labeled sketch of your prepared microscope slide from procedure 1. b) Labeled sketch of your prepare microscope slide from procedure 2. 3. Table 16.4 Results of Pollen Germination Studies Plant name 30 min (+/-) 60 min (+/-) Challenge question (0.5 pt) Pollen germinates in the lab for some species and not at all for others. In some species, a biochemical signal is required from the stigma to initiate germination. If the pollen has not germinated after 30 minutes, design an experiment to test the hypothesis that a substance in the stigma is necessary for pollen germination. Discussion 1. 2. B. Once your group feels that it understands the angiosperm life cycle, get together with another group and teach the angiosperm life cycle to the other group, which will listen and evaluate your presentation. Instructor’s initials ______________ Lab Study D Fruits and Dispersal (0.75 pt) 1. Complete Procedure and Results sections, p. 443. NOTE: Use the modified Key to Fruits found on the last page this worksheet, instead of the one in you lab manual. 2. Turn in Table 16.5. Work with a second group and identify three dry fruits, and three fleshy fruits. Hint: review Results 3, p.443. Table 16.5 Fruit Types and Dispersal Mechanisms Plant name Fruit type 1. dry fruit Dispersal Methods 2. dry fruit 3. dry fruit 4. fleshy fruit 5. fleshy fruit 6. fleshy fruit Challenge question (0.5 pt) The history of life has been punctuated by several extinctions, based on evidence from the fossil record. The impact of a meteorite may have wiped out the dinosaurs and many forms of marine lifer at the end of the Cretaceous period. Fossils indicate that plants were much less severely affected by this and other mass extinctions. Speculate on what adaptations may have enabled plants to withstand these disasters better than animals? Justify your hypotheses. Practice exam questions 1. Microspore is to ______________________ as _______________________ is to embryo sac. 2. Important terrestrial adaptations that evolved exclusively in seed plants include all the of the following except a. pollination b. transport of water through vascular tissue c. retention of the gametophyte plant within the sporophyte d. dispersal of new plants by seeds e. retention of spores by the parent sporophyte Clean and reorganize your workspace for the next lab group. Remove slides from microscopes and turn nosepiece to lowest objective. _____________ Instructor’s initials Just for Fun http://waynesword.palomar.edu/ww0601.htm 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. The World's Oldest Living Thing The Oldest Germinated Seed The World's Oldest Living Fossil The World's Most Massive Living Thing The World's Tallest Tree The World's Hardest & Heaviest Wood The World's Smallest Flowering Plant The World's Smallest And Largest Fruit The World's Largest Hitchhiking Fruit The World's Largest Vegetable The World's Smallest And Largest Seed The World's Smallest And Largest Leaves The World's Largest Flying Seed Longest Distance Traveled By Drift Seed World's Fastest Reproducing Plants The World's Fastest Growing Plants The Fastest Trapdoor On A Plant The World's Deadliest Plants Most Painful Botanical Encounters World's Most Valuable Plant Jewels Dislaimer: Authenticity Of Coconut Pearls Most Complex Plant-Insect Relationship The World's Largest Stinking Flowers 23. Plant & Animal Adaptation Hyperlinks 24. Go To Diversity Of Flowering Plants KEY TO COMMON FRUITS 1A. Simple fruits (one ovary) 1a. Fruits fleshy 2a. Fruits with a single seed enclosed in a hard pit...............................................................DRUPE 2b. Fruits with more than one seed, the seeds are not enclosed in a hard pit 3a. Fruits derived from the ovary only; endocarp fleshy or slimy..................................BERRY (berries with a thin skin are called TRUE BERRIES; berries with leathery skin containing oil are called HESPERIDIUMS= citrus family) 3b. Fruits derived from the ovary plus other parts of the flower; therefore, ovary wall seen as “core” around seeds. 4a. Fruits with relatively hard rind (= squash family).................................................PEPO 4b. Fruits without a hard rind.................................................................................... POME 1b. Fruits dry 5a. Fruits not splitting at maturity 6a. Fruits with a wing................................................................................... .............SAMARA 6b. Fruits without a wing 7a. Fruits with a hard shell surrounding the seed .........................................................NUT 7b. Fruits without a hard shell 8a. Fruit wall fused to the seed coat.............................. ....... ..GRAIN (CARYOPSIS) 8b. Fruit wall with seed loosely attached.......................................................ACHENE 5b. Fruits splitting in various ways at maturity 9a. Fruits splitting through multiple seams or forming a cap that come off or has a row of pores near the top.................................................................................................CAPSULE 9b. Fruits splitting along lengthwise along the edges 10a. Fruits splitting along one edge only............................................................FOLLICLE 10b. Fruits splitting along both edges...................................................................LEGUME 1B. Compound fruits Imore than one ovary) 11a. Fruit formed from ovaries of many flowers........................................... ............MUTIPLE FRUIT 11b. Fruit formed from several ovaries in one flower ........................................AGGREGATE FRUIT Revised 9/2005