Health Basics
advertisement

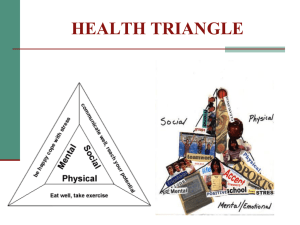
Health Basics Health – The balancing act of keeping ones Physical, Mental/Emotional, and Family – Social parts of life balanced and all working together Health Triangle – A way to represent ones balanced health. If one point is out of balance it can and most likely will disrupt a persons health. Balanced Triangle = Equilateral Triangle = HEALTHY Physical Health – The condition of a person’s body Example: eating healthfully, exercising, and getting enough rest Mental/Emotional Health – The condition of a person’s mind and how that person expresses feelings Example: having challenging conversations, taking time to understand one’s feeling and expressing them in a healthful manner Family – Social Health – How a people deal with other people in their life Example: listening when others speak, getting and keeping friends Unbalanced Triangle = Obtuse/Acute Triangle = UNHEALTHY Physical Menta l Social Factor that Affect your Health Status Health Status – The sum of the positive and negative influences on a person’s health and well-being. 10 Factors that Affect your Health Status A) Health Knowledge The information and understanding a person has about health B) Access to Health Information, Products and Services C) A person’s Behavior D) The way a person responds to Culture, Media, and Technology Name 4 Types of Media: 1 2 3 4 Give 2 examples of Technology A B Culture – The arts, beliefs, and customs that make up a way of life for a group of people What are your family’s beliefs about: Drinking Alcohol – Smoking – E) Skills in Communicating, Resisting, and Conflict Resolving F) The Decisions we make G) H) I) J) Your Advocacy Skills Your Heredity The Quality of the Environment one lives Random Events that happen throughout life Wellness Wellness – The quality of life that results from a person’s health status Wellness Scale – Shows the range in quality of life. The quality can range from Optimal Wellness, to Premature Death. Optimal Wellness – A person is living at a very high level of health status with few risks, if any, risk factors Influences on your Health How to Analyze Influences on Health 1) Identify people and things that might influence you Examples – Friends, Family, Famous People (Politicians, Movie People, Sports), Doctors, Clergy, Media, Technology, and Your Culture 2) Evaluate how the influence might affect your health behaviors and decisions Guidelines for Analyzing Influences on Health a) Does the influence promote healthful behavior b) Does the influence promote safe behavior c) Does the influence promote legal behavior d) Does the influence behavior that shows respect to myself and others e) Does the influence behavior that follows the guidelines of responsible adults f) Does the influence behavior that demonstrates good character 3) Choose the positive influences on your health 4) Protect yourself from negative influences on health Advertisements Advertisements (Ads) are designed to get the public to purchase a product or service. Questions to help evaluate Ads 1) What is being advertised 2) Where and when did the Ad appear 3) Why was this particular type of media selected 4) Who appears to be the target of the Ad 5) What advertising appeal(s) were used 6) What does the Ad want me to believe 7) What do I know to be fact 8) Will the Ad promote my health 9) It is legal for me to use of have 10) Will its use promote self respect, and respect of others 11) Does it follow my family guidelines 12) Does it demonstrate good character 10 “Hooks” or Appeals that Advertisers use to get the Consumer (a.k.a. You) To Purchase Their Products 1) Brand Loyalty – Convinces a person that they need to buy a particular brand again and again. a. Example – Car companies 2) False Image - Convinces people that they will have a better image if they buy and use the product. a. Example – any ad that uses before and after pictures 3) Bandwagon – Implies that everyone is using the product and to be in the “in” you need to “jump on the Bandwagon.” a. Example – Your Friends and Family use this Product so should you. 4) Humor – uses a catchy slogan, jingle, or cartoon to help people remember the certain product or service. a. Example – Free Credit report.com 5) Glittering Generality – exaggerated appeal that uses emotions. a. Example – SPCA 6) Scientific Evidence – uses data from labs and surveys to convince people to use the product. a. Example – 4 out of 5 doctors say … 7) Progress - “The latest version” to convince people to use product. a. Example – “New and Improved” 8) Reward - use some type of enticement to get people to buy a product. a. Example – Buy one get one (BOGO) 9) Sex – convinces people that if they use the product they will become more attractive and alluring. a. Example – Acne medicine 10) Testimonial – uses a spokesperson to sell the product. b. Example – Direct TV in Hi - Def