Understanding Health and Wellness

Understanding Health and Wellness
“Your Total Health”
Lesson Plan 1 / Chapter 1
Page 3-9
1. Objective: students will be able to identify the three parts of health. Students will be able to explain the difference between health and wellness. Lastly, students will be able to describe how the mind and the body are connected.
2. Student Activity - Using the letters in your first name, spell out something positive about yourself. (You have 5 minutes) Write going downward. Example: A- athletic, N - nice, D dedicated, E- exciting, R - responsible, S - studious, O - observant, N - nonjudgmental.
Question - why is it easier to think of negative things about oneself than positive things?
How much time do you think you would need to write down the negative things about yourself?
3. Read page 4
“Three Parts of Good Health” Question – what is Samantha suffering from?
She is suffering from all three parts of the Health Triangle – Physically she is too tired to do anything, Mentally she cannot focus in class, and socially she is arguing with friends.
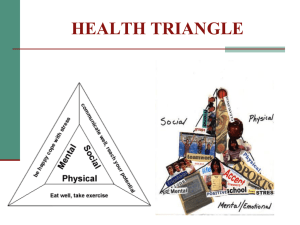
4. Show Health and Wellness Power Point . Talk about the Health Triangle. Figure 1.1 ( You need all three sides to complete the triangle, and each side supports the other two sides to make up your total health).
Physical Health – how you take care of the body.
Mental/Emotional Health – how you take care of the mind or brain, and how you control your emotions.
Social Health
– how you get along with others.
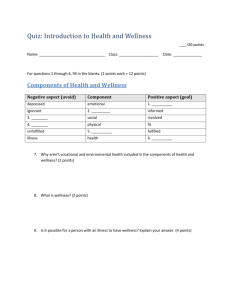
5. (5 points) - “How Healthy Are You”
List 5 conditions or behaviors that indicate your present health (it does not have to be all positive, it could be negative also).
Example ; nice, patient, exercise daily, eat a well balanced meal, sleep to much, eat too much fatty foods, etc.
6. (5 points) - Journal #1 (page 4)
Write a short paragraph describing how a person with “total health” might look and act. What might this person’s lifestyle be like?
7.
(10 points) - Assignment: Fill out the Personal “Health Inventory, Understanding Health and
Wellness” Worksheet.
8.
(10 points) - Homework - Put pictures that describe your current health on the health triangle.
9.
Wellness – a state of well-being or balanced health over a longer period of time.
Example: exercise over a long period of time will help a person to decrease fat and stay physically healthy. A person who eats a lot of fatty foods without exercise will increase their chances for obesity, heart disease, and other health problems.
10.
Mind-Body Connection – is how your emotions affect your physical and overall health and how your overall health affects your emotions.
Recap:
Define:
Health - combination of Physical/Emotional & Mental/ Social Health (social well being).
Wellness - Behavior that has a positive effect over time. (a state of well being or balanced health over a longer period of time)
Social - How you get along with others. (how you relate to people at home, at school, and everywhere else in your world)
Physical - how you take care of your body. (involves the condition of your body)
Mental & Emotional - how you take care of your mind. (Mental health refers to your ability to solve problems and handle the daily events in your life. Emotional health involves feelings, such as happiness, sadness, and anger and dealing with them in a positive way).
Mind-Body Connection – is how your emotions affect your physical and overall health and how our overall health affects your emotions.
Discussion: Physical/Mental & Emotional Health/ Social Health page 4-6.
END
Understanding Health and Wellness
Lesson Plan #2 “Skills for Building Health”
Page 10-17
Due: Health Triangle homework (10 pts)
Collect Course Disclosures
Review - Health/Wellness/Physical/Mental & Emotional/Social Health, Body Connection
Remind - Journals are due when we reach intervals of 4.
Objective:
In this lesson you will be able to identify ten basic skills that you need for good overall health.
You will be able to explain why these skills are important and describe how to use these skills for total health and wellness. Students will be able to apply the health skill of advocacy to encourage teens to be physically active.
Journal #2 - List three things that have influenced your health. Are these influences positive or negative? Why?
Read
“ Accessing Information” “Sources of Information” page 10-11.
TV, radio, computers, newspaper, and magazine.
Go over Figure 1.3 “Ten Building Blocks for Total Health”.
Reliable – the source is trustworthy and dependable. Tell me some myths about health.
Example your muscles turn to fat when you stop exercising, or exercise stunts your growth.
Self-Management – are practicing healthful behaviors and managing stress – you make many decisions for yourself now instead of depending so much on your parents.
Example: Getting mad, saying things we wished we hadn’t.
Stress the body’s response to real or imagined dangers and other life events.
Example – scary movies, sporting events when the game is on the line, speaking in front of an audience, amusement parks just before you fall or when coach announces that you have a test today.
Stress Management – means identifying sources of stress and learning how to handle them in ways that promote good mental/emotional health.
Example – how do you prepare for a test, game, speaking event, etc.
Analyzing Influences – Internal influences, such as your likes, dislikes, feelings, and interests, affect your decisions.
Example –
External influences, such as the opinions of others and media messages, affect your decisions as well.
Example – name brands vs. generic brands (which ones do you buy and why?). Fast foods vs. healthy foods, what do you do and why?
Communication Skills – You must be able to speak well and listen carefully, too.
Speaking skills help you express your ideas and feelings in healthful ways. Listening skills let you understand the messages other people send you.
Interpersonal Communication – the sharing of thoughts and feelings with other people.
Example – how many of you have ever been misunderstood? What happened? How could you have avoided this miscommunication?
Conflict Resolution Skills
Conflict – a disagreement between people with opposing viewpoints, interests, or needs.
Example – sports teams (BYU vs. Utah) can they see a game together without an argument?).
Conflict Resolution Skills – the ability to end a disagreement or keep it from becoming a larger conflict.
Conflict Resolution Tips:
1.
Take a time-out to let everyone calm down.
2.
Allow each person to tell his or her side of the story.
3.
Let each person ask questions of the other.
4.
Keep thinking of creative ways to resolve the conflict.
Refusal Skills - ways to say no effectively.
1.
Say No.
2.
Tell Why Not.
3.
Offer other ideas.
4.
Promptly leave.
Saying no to behavior that you do not want to be part in:
1.
Use the right body language.
2.
Use the right tone.
3.
Use direct eye contact.
4.
Serious facial expression.
5.
Firmly but not angry tone of voice.
Advocacy – taking action in support of a cause. Make a positive change by writing letters to a newspaper editor, collect signatures, and talk to government leaders.
Assignment: “Building Health Skills” (10 points)
Understanding Health and Wellness
Lesson Plan #3
“What Affects Your Health?”
Page 18-22
Review - Health/Wellness/Physical/Social/Mental & Emotional, Body Connection, Accessing
Information, Reliable, Self Management, Stress, Stress Management, Analyzing Influences,
Interpersonal Communication, Conflict, Conflict-Resolution Skills, Refusal Skills, Advocacy.
Assessment Quiz Health and Wellnes
Objective: Students will be able to explain why heredity is a health factor that you cannot control. Students will also be able to explain the role that environment plays in your total health.
Students will identify internal and external influences that affect health choices and be able to access reliable information to evaluate an advertised product.
Journal #3 – List three things you have inherited from your family.
Discussion: from journal 3.
Heredity
– is the passing of traits from parents to their biological children.
Discussion: What traits have you inherited from your family?
Example: Height, hair, eye color, skin, speech, laugh, frown. Do you act like them in telling your younger brother and sister what to do? Are you artistic, mechanical, musical, athletic, or have favorite foods like them. Do you say what they say? Walk like them, or notice your body imitates them when you are mad. How do you discipline those you are babysitting? Is it the same way you were disciplined? Is your personality like Dad or Mom? Are you laid back, a busy body, or always on the move like them?
What family illnesses do you have?
Example: glasses, cancer, diabetes, fragile bones, bad knees, etc.
Environment – all living and nonliving things around you.
Physical Environment – includes the home you live in, the school you go to, the air and water around you, and the climate.
Does your neighborhood have an effect on you?
Example: What type of people live where you live? What type of cars do people have where you live? What about their yard - what does everyone have in the front and backyard?
What do most kids play or play with in your neighborhood - basketball, football, skateboard, trampolines, scooters, bikes, and swing sets, etc. What kind of music does your neighborhood listen to? Is your neighborhood dangerous during the day or at night?
Social Environment – include family members and others in your life, such as friends, classmates and neighbors. Also includes the services available to you, such as schools, health care, and recreation.
Does your school have an effect on you?
Example: Dress, music, hair styles, speech, fads. people.
Cultural Background – the beliefs, customs, and traditions of a specific group of
Does your culture have an effect on you?
Example: What type of foods do you eat? Language do you speak in the home? Sports you play or exercises you do? What do you eat that no one else eats? You are fast food society.
What about language from certain areas such as Texas, Hawaii, Canada, Boston, or even Utah.
Media Influence
TV, radio, movies, magazines, newspapers, books, billboards, and the internet help you make wise health choices.
Evaluate – determine the quality of, everything you see, hear, or read.
Class Assignment - Make a poster using one of the following: Physical, Mental & Emotional, and Social, draw and example of people or things depicting one part of the Health Triangle. The idea is to influence people in healthy choices.
Assignment – (10 points) “Effects on Your Health”
Lesson Plan #4 Health Risks and Your Behavior”
Review and Discussion for the Test.
Journal #4 - What have you learned about overall Health?
Review - Health/Wellness/Physical/Social/Mental & Emotional, Body Connection,
Accessing Information, Reliable, Self Management, Stress, Stress Management,
Analyzing Influences, Interpersonal Communication, Conflict, Conflict-Resolution
Skills, Refusal Skills, Advocacy, Heredity, Environment.
Objective:
Students will be able to describe how risks and risk behaviors can affect your health.
Students will be able to explain that risk behaviors have consequences and identify ways to avoid or reduce risk.
Risk
– is the chance that something harmful may happen to your health and wellness.
Risk Behaviors – which are actions or choices that may harm you or others.
- ones we have to take. Example riding the bus, getting into a car, crossing the street.
- ones we do not have to take. Example; cliff diving, riding without seatbelts, riding a bike without a helmet, smoking cigarettes because it can lead to lung cancer, taking dares.
Consequences – are the results of actions. What are some actions that will only affect you? (Not studying for a test). What are some actions that may affect others? (Picking a fight with another person).
Cumulative Risk – when one risk factor adds to another to increase danger. Example: running in the halls by yourself and when the halls are busy.
Prevention – taking steps to avoid something.
Tips to reducing risk:
1.
Plan ahead
2.
Think about consequences.
3.
Resist negative pressure from others.
4.
Stay away from risk takers.
5.
Pay attention to what you are doing.
6.
Know your limits.
7.
Be aware of dangers.
Abstinence – the conscious, active choice not to participate in high-risk behaviors.
Physical Health – avoiding risk behaviors will help prevent illness and injuries.
Mental/Emotional Health – taking steps to reduce risks, you can feel good about making responsible health choices.
Social Health – practicing abstinence from risk behaviors and reducing unavoidable risks can help keep others safe.
Review for Test, Hand out study sheet.