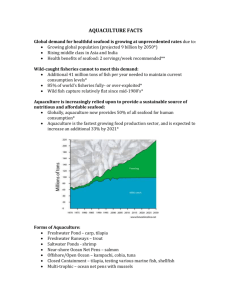
1 Aquaculture, the practice of growing finfish and shellfish under
advertisement

Part I GRAMMAR TEST Multiple choice ex. 1) Mary sometimes (A study B studies C is studying D was studied E to study) at home. 2) At the moment I (A has worked B work C works D am working E are working) in Forlì. 3) We left home early on Saturday morning and we (A will drive B drive C drives D drove E are going to drive) to the station. 4) Marie Curie (A discovers B has discovered C discovered D will discover E was discovering) radium in 1898. 5) The phone rang while I (A am making B make C was making D made E will make) a cake. 6) (A Did you see B Have you seen C Will you see D Do you see E Are you going to see) Tom one hour ago? 7) Somebody (A has taken B is taking C takes D take E was taking) my bag! I can’t find it! 8) Ann’s broken her arm. How (A will B did C has D does E was) she break it? She fell onto some rocks. 9) Pam (A lives B has lived C is living D doesn’t live E live) in Dublin for five years. 10) I (A didn’t go B would have gone C wouldn’t have gone D went E hadn’t gone) to the museum if I had known it was shut. 11) What’s the matter Paul? I’ve got a headache. Oh, I(A ‘ll get B am going to get C was D to take E give) you an aspirin! 12) I can play (A – B a C the D an E some) guitar. 13) We’ll go to the mountains on Friday unless it (A will rain B rain C won’t rain D rains E doesn’t rain). 14) There’s someone outside in an orange car. It (A must B need C can’t D mustn’t E couldn’t) be Susan. She’s the only person I know with an orange car. 15) If I won a lot of money I ( A‘ll buy B ‘d buy C bought D buy E ’d have bought) a big house. 16) You (A needn’t have B needn’t C have to D can E need) go to the shop. We have enough food. 17)The weather was terrible (A despite B in case C so D because of E owing to) we couldn’t go out. 18) The work (A will B is going to C was D will be E did) finished tomorrow. 19) (A How much B How far C How old D How long E How big) did the war continue? For six years. 20) The first Apple computers (A was produced B are produced C are producing D were produced E produced) in the 1970’s. 21) I’m going to the hairdresser’s to (A cut my hair B had my hair cut C have my hair cut D have cut my hair E my hair). 22) Let’s meet (A in B to C at D on E out) the cinema! 23) We enjoyed (A to sit B sit C sitting D sat E will sit) in the garden. 24) My sister promised (A help B helps C to help D helping E will help) me. 25) He told me he (A want B would C don’t D would have E won’t) wait for me! 26) What does Julie (A look/ B like C look like D see E prefer)? She is tall with brown hair. 27) They asked where (A did Ann live? B Ann lived C Ann live D does Ann live? E was Ann living?) 28) The factory (A who B whose C what D which E where) closed last week was well-known. 29) (A Whose B Who C When D What E How much) car is that? It’s my mother’s! 30) I really need your help, so don’t (A let me in/ B let me through C let me off D let me up E let me down). Soluzioni: 1 b 2 d 3 d 4 c 5 c 6 a 7 a 8 b 9 b 10 c 11 a 12 c 13 d 14 a 15 b 16 b 17 c 18 d 19 d 20 d 21 c 22 c 23 c 24 c 25 b 26 c 27 b 28 d 29 a 30 e Part II Reading Comprehension Read the following passage and then choose the most appropriate answer to the questions below: 1 Aquaculture, the practice of growing finfish and shellfish under controlled conditions, is not a new concept. The Japanese, Chinese, Romans, Egyptians, and Mayan Indians of South America farmed fish for food and recreation prior to 2000 BC. They constructed ponds and raised fish much as fish are raised today. Both freshwater and saltwater fish are currently raised commercially throughout the world. Other fisheries-related products, such as shrimp, crayfish, oysters, clams, and frogs, are also raised commercially. Although many fish are reared commercially, the vast majority of fishery food products eaten in the United States are produced from wild stocks captured in natural waters, not farmed. 2 Fishery food products are a potential answer to the growing problem of world dietary animalprotein shortages. Feed conversion rates of fish are higher than other common commercial animal protein sources because: (a) fish can utilize foods that are not used by most land animals; and (b) they require less energy from their foods to live. Moreover, fish can use the entire threedimensional environment of ponds, from top to bottom and sideways, for living space, while terrestrial animals are confined to the two-dimensional surface of the ground. The potential for commercial production and the lure of high profits have accelerated the interest in fish farming and other types of aquaculture. 3 There are many different kinds of Aquaculture, because there are a lot of different species. Catfish, crayfish, tilapia, for example, need warm fresh water to grow while salmon and trout must be raised in cold fresh water. On the other hand, in brackish or salt water, oysters, mussels, cod and flounder are bred. 4 Aquaculture must use water which is perfectly cleaned, low in chemicals (arsenic, boron, fluoride) otherwise it could be harmful to the survival of aquatic organisms. Moreover, three different forms of Aquaculture can take place: ponds (dikes), pens (large enclosures) and recirculating tanks (where “recirc” systems are employed to clean and reuse water). 5 Once the water source and systems are in place, the water is 'fertilised' with algae to create a natural environment for the growth of fish and other organisms. Fish spend one to two years in sea cages. When the fish are released into the sea, the production of table fish has started. During this growth phase, the fish farmer monitors the fish carefully and adjusts the quantity and quality of feed in line with water temperature and other biological conditions. At an age of two to three years, the fish are harvested after having reached sizes demanded in the markets. Finally thanks to modernday transport amenities, harvested fish reach their consumers at the most three days after being harvested. 1) What do we learn from Paragraph 1? A) Aquaculture is an idea of recent origin B) Aquaculture wasn’t present in the past C) Aquaculture was born 2000 years ago D) Aquaculture isn’t possible if there isn’t a pond E) Aquaculture isn’t a new project 2) What do we learn from paragraph 2? A) The interest for Aquaculture is increasing B) The interest for Aquaculture isn’t growing C) The interest for Aquaculture is decreasing D) The interest for Aquaculture is low E) The interest for Aquaculture is the same 3) What do we learn from paragraph 3? A) The type of Aquaculture depends on the fish to be raised B) The type of Aquaculture depends on the weather C) The type of Aquaculture depends on fish farmers D) The type of Aquaculture depends on the cost of the fishery E) The type of Aquaculture depends on the number of fish bred 4) What do we learn from paragraph 4? A) Aquaculture must employ fresh water with a lot of chemicals B) Aquaculture must use perfectly cleaned water C) Aquaculture can’t use perfectly cleaned water D) Aquaculture can use water which isn’t cleaned E) Aquaculture shouldn’t use perfectly cleaned water 5) What’s the best title for this article? A) Fish farmers And The Law B) Aquaculture And Agriculture C) The Science Of Aquaculture D) Fish Farmers And Consumers E) The Negative Side Of Aquaculture 6) What’s the most appropriate translation for “clams” (Paragraph 1)? A) orate B) merluzzi C) triglie D) vongole E) cozze 7) What’s the most appropriate translation for “reared” (Paragraph 1)? A) venduti B) controllati C)disinfettati D) pescati E) allevati 8) What’s the most appropriate translation for “brackish” (Paragraph 3)? A) fangose B) salmastre C) pulite D) dolci E) depurate 9) What’s the most appropriate translation for “pens” (Paragraph 4)? A) fiumi B) mari C) laghetti D) corsi d’acqua E) ruscelli 10) What’s the most appropriate translation for “environment” (Paragraph 5)? A) ambiente B) mercato C) crescita D) domanda E) reticolato Soluzioni: 1 e 2 a 3 a 4 b 5 c 6 d 7 e 8 b 9 c 10 a