Senior Comprehensive Exams
advertisement

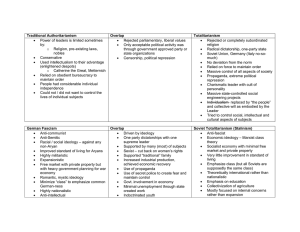
American key terms 1. Political socialization 2. Universal suffrage 3. Checks and balances vs. Separation of powers 4. Electoral college 5. Judicial review 6. Unitary vs. Confederal system 7. Layered Cake or Dual federalism 8. Marble Cake or Cooperative federalism 9. Picket-Fence or Centralized Federalism 10. Necessary and proper clause 11. Establishment vs. Free exercise clause 12. Writ of habeas corpus 13. Affirmative action 14. Civil rights vs. Civil liberties 15. De facto vs. De jure segregation 16. Plurality vs. Majority 17. Federalist 10 18. Primary and Front loading 19. Soft vs. Hard money 20. Reapportionment vs. Redistricting 21. Trustee vs. Instructed Delegate representation 22. Filibuster 23. Conference committee 24. Advice and consent 25. Impeachment 26. Bureaucracy 27. Iron triangle vs. Issue Network 28. Judicial activism vs. Judicial Restraint 29. Justiciable controversy vs. Political questions 30. Efficacy Theory key terms 1. Political theory 2. Human nature 3. Liberty (positive vs. negative) 4. Communism vs. Socialism 5. Capitalism 6. Anarchism 7. Fascism 8. republicanism 9. Natural rights 10. Social contract 11. Conservatism 12. Authoritarianism 13. Consent 14. Liberalism 15. Progressivism 16. Democracy 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. Republic Representative democracy Libertarianism Ideology Totalitarianism Polity Plato Aristotle Cicero Machiavelli Hobbes Locke Rousseau Marx Comparative Politics key terms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. Authoritarianism Totalitarianism Parliamentary Systems vs. Presidential Systems Political Culture Fascism Socialism Proportional Representation vs. Single Member District Democratization Political Ideology Theocracy Civil Society State vs. Nation Colonialism Nationalism Pluralism Ideology Development/ Dependency Vote of Confidence Coalition Government Ethnic conflict Coup Revolution Neo-Colonialism Corporatism/ Neo-Corporatism Devolution Stability State capacity Social Movements Constitution Capitalism World Politics key terms 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. Sovereignty Realism Liberalism Constructivism Marxism Terrorism Anarchy Norms Globalization Hegemon Security Dilemma Democratic Peace Theory Balance of Power Prisoner’s Dilemma Collective Action Problems State Protectionism Unilateralism vs. Multilateralism Deterrence Hard vs. Soft Power Non-governmental Organizations IMF/ World Bank Genocide United Nations International Court of Justice Imperialism Appeasement Diplomacy International law Human Rights Methods 1) Explain the difference between a qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods approach. If I give you a research question could you tell me which approach would be best? 2) Explain the difference between positivism/post-positivism, social contructivism, and pragmatism. 3) Be able to derive hypotheses from a research question. Identify the dependent, independent and intervening variables. 4) List the key components of an introduction to a research paper. What is the purpose of a Review of the Literature section? What is included in a Methods section? 5) If I give you a variable and how it is coded be able to tell me whether it is binomial, ordinal, or continuous (Ratio). 6) Be able to interpret a frequency table and tell me the best measure of central tendencies (mode, median, mean, standard deviation). 7) Be able to look at a line, bar, pie chart and interpret them. What is a box plot and a histogram, when would I use these? 8) Explain the process of re-coding variables. Why is it a bad idea? Why do people do it anyway? 9) Discuss the difference between a sample and a population. 10) Discuss the difference is between reliability and validity. 11) What is a correlation coefficient? What does it tell me? What doesn’t it tell me? 12) What is a regression coefficient, what does it tell me what doesn’t it tell me? 13) Why is statistical significance so important?