Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb)
advertisement
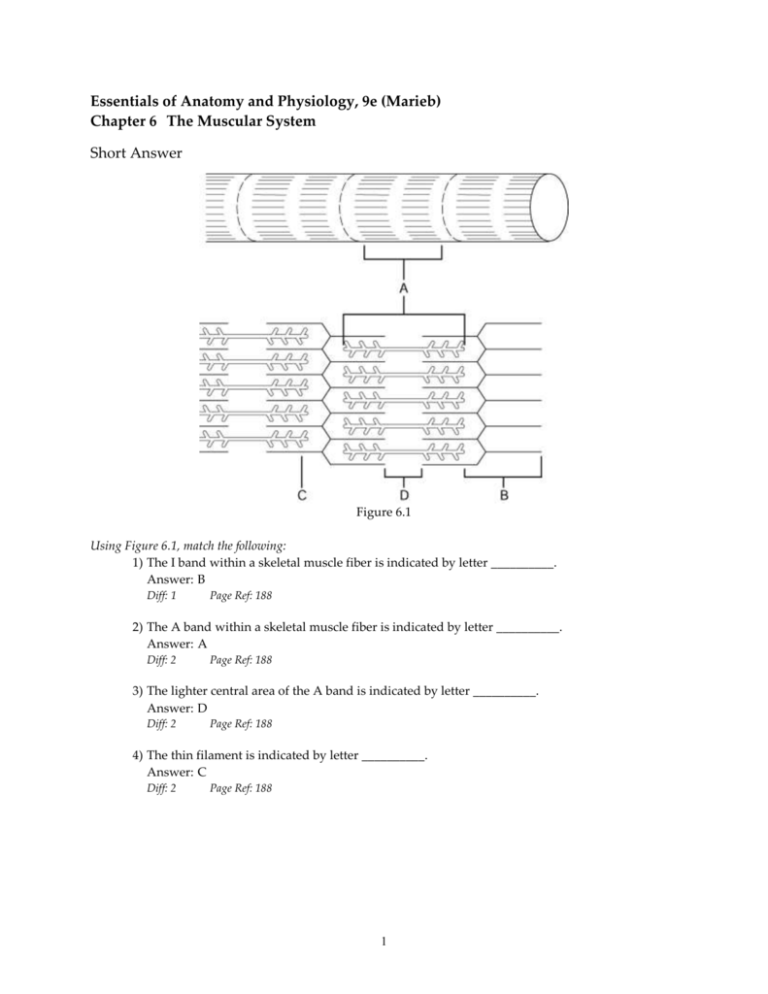
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 6 The Muscular System Short Answer Figure 6.1 Using Figure 6.1, match the following: 1) The I band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated by letter __________. Answer: B Diff: 1 Page Ref: 188 2) The A band within a skeletal muscle fiber is indicated by letter __________. Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 188 3) The lighter central area of the A band is indicated by letter __________. Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 188 4) The thin filament is indicated by letter __________. Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: 188 1 Figure 6.2 Using Figure 6.2, match the following: 5) The connective tissue "overcoat" that wraps the entire muscle is indicated by letter __________. Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 185 6) The connective tissue that wraps a fascicle, or bundle of muscle fibers, is indicated by letter __________. Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: 185 7) The muscle fiber is indicated by letter __________. Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 185 8) The endomysium that wraps individual muscle fibers is indicated by letter __________. Answer: B Diff: 1 Page Ref: 185 Fill in the blank or provide a short answer: 9) Only __________ muscle cells are cylindrical and multinucleated. Answer: skeletal Diff: 1 Page Ref: 184 10) The muscle tissue that normally exhibits voluntary contractions is __________ muscle. Answer: skeletal Diff: 1 Page Ref: 185 11) Only __________ muscle cells possess intercalated discs. Answer: cardiac Diff: 1 Page Ref: 186 2 12) Skeletal muscle is often attached to bone by strong, cordlike structures called __________. Answer: tendons Diff: 1 Page Ref: 185 13) The __________ zone of a sarcomere contains no actin filaments while the skeletal muscle is at rest (noncontractile state). Answer: H Diff: 1 Page Ref: 187; 189 14) The heads of the myosin myofilaments are called __________ when they link the thick and thin filaments together during skeletal muscle contraction. Answer: cross bridges Diff: 1 Page Ref: 189 15) The gap between the motor neuron and the muscle fiber it supplies at the neuromuscular junction is called the __________. Answer: synaptic cleft Diff: 1 Page Ref: 189 16) When a skeletal muscle is fully contracted, the __________ are closer to the thick filaments. Answer: Z discs Diff: 2 Page Ref: 192 17) The only energy source that can be used to directly power muscle activity is __________. Answer: ATP Diff: 2 Page Ref: 195 18) A smooth, sustained contraction is called __________. Answer: tetanus Diff: 1 Page Ref: 194 19) The __________ of a muscle is attached to the immovable or less movable bone. Answer: origin Diff: 1 Page Ref: 198-199 20) The movement that is commonly seen in a ball-in-socket joint, that includes a combination of flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction, is called __________. Answer: circumduction Diff: 2 Page Ref: 199 21) The muscle that has the major responsibility for causing a particular movement is the __________. Answer: prime mover Diff: 1 Page Ref: 202 22) The arrangement of fascicles in orbicularis oris is __________. Answer: circular Diff: 1 Page Ref: 204; 207 3 23) The muscle referred to as the "smiling" muscle because it raised the corners of the mouth upward is the __________. Answer: zygomaticus Diff: 2 Page Ref: 207 24) The __________ muscle runs deep to the external oblique muscle. Answer: internal oblique Diff: 1 Page Ref: 209 25) The quadriceps femoris muscle group is composed of the three vastus muscles and the __________ muscle. Answer: rectus femoris Diff: 2 Page Ref: 214 26) An inherited disease that causes muscles to degenerate and atrophy is known as __________. Answer: muscular dystrophy Diff: 2 Page Ref: 221 Multiple Choice 1) Muscle tissue that has involuntary regulation of contraction is: A) cardiac muscle only B) smooth muscle only C) skeletal muscle only D) cardiac muscle and smooth muscle E) cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 185-186 2) The muscle tissue type that consists of single, very long, cylindrical, multinucleate cells with very obvious striations is: A) cardiac muscle only B) smooth muscle only C) skeletal muscle only D) cardiac and smooth muscle E) cardiac and skeletal muscle Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: 183-185 4 Figure 6.3 3) The type of muscle tissue pictured in Figure 6.3 is: A) skeletal muscle B) voluntary C) striated D) found only in the heart E) smooth muscle Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: 184 4) The plasma membrane of a muscle cell is called the: A) sarcolemma B) sarcomere C) myofilament D) sarcoplasm E) sarcoplasmic reticulum Answer: A Diff: 3 Page Ref: 187 5) Which of the following does not describe cardiac muscle tissue: A) uninucleate B) striations C) involuntary D) rhythmic contractions E) attached to bones Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: 186 6) What type of membrane wraps a fascicle: A) endomysium B) epimysium C) aponeuroses D) perimysium E) tendons Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 185 5 7) Which of the following is NOT a function of the muscular system: A) production of movement B) maintenance of posture C) stabilization of joints D) generation of heat E) hematopoiesis Answer: E Diff: 1 Page Ref: 187 8) A sarcomere is: A) the nonfunctional unit of skeletal muscle B) the contractile unit between two Z discs C) the area between two intercalated discs D) the wavy lines on the cell, as seen in a microscope E) a compartment in a myofilament Answer: B Diff: 2 Page Ref: 187 9) Which one of the following is composed of myosin protein: A) thick filaments B) thin filaments C) all myofilaments D) Z discs E) light bands Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 187-189 10) Place these structures of the skeletal muscle in order from largest to smallest: 1. fascicle 2. myofilament 3. muscle fiber (cell) 4. myofibril 5. sarcomere A) 1, 3, 4, 5, 2 B) 1, 4, 3, 2, 5 C) 2, 5, 4, 3, 1 D) 3, 1, 2, 4, 5 E) 3, 2, 5, 4, 1 Answer: A Diff: 3 Page Ref: 185-189 11) The axon terminals of a nerve cell and the sarcolemma of a skeletal muscle cell join at the: A) motor unit B) neuromuscular junction C) synaptic cleft D) action potential E) myofibril Answer: B Diff: 3 Page Ref: 189 6 12) Which one of the following functions do calcium ions perform during skeletal muscle contraction: A) increase the action potential transmitted along the sarcolemma B) release the inhibition on Z discs C) expose myosin binding sites on the actin D) cause ATP binding to actin E) bind to regulatory proteins on the myosin filaments, changing both their shape and their position on the thick filaments Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: 193 13) The mechanical force of contraction is generated by: A) shortening of the thick filaments B) shortening of the thin filaments C) a sliding of thin filaments past thick ones D) the "accordian-like" folding of thin and thick filaments E) the temporary disappearance of thin filaments Answer: C Diff: 2 Page Ref: 192 14) Acetylcholine is: A) an ion pump on the postsynaptic membrane B) a source of energy for muscle contraction C) a component of thick myofilaments D) an oxygen-binding protein E) a neurotransmitter that stimulates skeletal muscle Answer: E Diff: 1 Page Ref: 189 15) The gap between the axon terminal of a motor neuron and the sarcolemma of a skeletal muscle cell is called the: A) motor unit B) sarcomere C) neuromuscular junction D) synaptic cleft E) cross bridge Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 189 16) Neurotransmitters are released upon stimulation from a nerve impulse by the: A) myofibrils B) motor unit C) thick filaments D) axon terminals of the motor neuron E) sarcolemma of the muscle cell Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 189 7 17) An elaborate and specialized network of membranes in skeletal muscle cells that function in calcium storage is the: A) sarcolemma B) mitochondria C) intermediate filament network D) myofibrillar network E) sarcoplasmic reticulum Answer: E Diff: 1 Page Ref: 189 18) During skeletal muscle contraction, myosin cross bridges attach to active sites of: A) myosin filaments B) actin filaments C) Z discs D) thick filaments E) the H zone Answer: B Diff: 1 Page Ref: 192 19) The major function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle contraction is to: A) make and store phosphocreatine B) synthesize actin and myosin myofilaments C) provide a source of myosin for the contraction process D) regulate intracellular calcium concentration E) store ATP Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 189 20) The striations that give skeletal muscle its characteristic striped appearance are produced, for the most part, by: A) a difference in the thickness of the sarcolemma B) the arrangement of myofilaments C) the sarcoplasmic reticulum D) the T tubules E) the "cocked" positions of the heads of the thick filaments Answer: B Diff: 2 Page Ref: 189 21) Which of these events must occur first to trigger the skeletal muscle to generate an action potential and contract: A) sodium ions rush into the cell B) acetylcholine (ACh) causes temporary permeability to sodium C) diffusion of potassium ions out of the cell D) operation of the sodium-potassium pump E) acetylcholinesterase (AchE) breaks down acetylcholine (ACh) Answer: B Diff: 3 Page Ref: 189-190 8 22) A skeletal muscle twitch differs from a tetanic contraction in that: A) the tetanic contraction is considered abnormal, while the twitch is a normal muscle response B) the tetanic contraction is caused by a single stimulus, while the twitch is caused by very rapid multiple stimuli C) the muscle twitch is prolonged and continuous while a tetanic contraction is brief and "jerky" D) the muscle twitch occurs only in small muscles while a tetanic contraction occurs in large muscle groups E) the muscle twitch is a brief and "jerky" movement, while the tetanic contraction is prolonged and continuous Answer: E Diff: 3 Page Ref: 194 23) Creatine phosphate (CP) functions within the muscle cells by: A) forming a temporary chemical compound with myosin B) forming a chemical compound with actin C) inducing a conformational change in the myofilaments D) storing energy that will be transferred to ADP to resynthesize ATP as needed E) storing energy that will be transferred to ATP to resynthesize ADP as needed Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 195 24) The condition of skeletal muscle fatigue can be best explained by: A) the all-or-none law B) the inability to generate sufficient quantities of ATP due to feedback regulation of synthesis C) insufficient intracellular quantities of ATP due to excessive consumption D) a total lack of ATP E) inadequate numbers of mitochondria Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: 195-196 25) Which one of the following muscle actions would NOT be classified as an ISOTONIC contraction: A) pushing against a stationary wall B) lifting a glass of water to your mouth C) writing a letter D) tying your shoe E) throwing a ball Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 197 9 26) Anaerobic glycolysis occurs without: A) ATP B) oxygen C) lactic acid D) carbon dioxide E) glucose Answer: B Diff: 3 Page Ref: 195 27) Which of these pathways to regenerate ATP during muscle activity is the fastest: A) direct phosphorylation of ADP by creatine phosphate B) aerobic respiration C) anaerobic glycolysis and lactic acid formation D) oxidative phosphorylation E) both aerobic respiration and anaerobic glycolysis Answer: C Diff: 3 Page Ref: 195 28) The insertion of the gluteus maximus is the: A) sacrum B) tibia C) ilium D) calcaneus E) femur Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: 211 29) Which of the following muscles closes the jaw: A) the buccinator B) the masseter C) the frontalis D) the sternocleidomastoid E) the masseter and the temporalis Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: 207 30) Sandra is playing the piano for her recital. Which muscle is not involved in the movement of her hands and/or fingers: A) flexor carpi radialis B) flexor carpi ulnaris C) extensor digitorum D) extensor digitorum longus E) extensor carpi radialis Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 219 10 31) Which of the following muscles inserts on the calcaneus: A) the semitendinosus B) the sartorius C) the tibialis anterior D) the soleus E) the iliopsoas Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 214; 219 32) Which one of the following does NOT compress the abdomen: A) internal oblique B) external oblique C) transversus abdominis D) latissimus dorsi E) rectus abdominis Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 209 33) A muscle located on the ventral (anterior) side of the body is the: A) pectoralis major B) occipitalis C) gastrocnemius D) gluteus medius E) latissimus dorsi Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 208 34) A nursing infant develops a powerful sucking muscle that adults also use for whistling or blowing a trumpet called the: A) platysma B) masseter C) zygomaticus D) buccinator E) temporalis Answer: D Diff: 1 Page Ref: 207 35) Which of these muscles is not responsibile for flexion or extension of the arm? A) biceps brachii B) triceps brachii C) brachialis D) platysma E) latissimus dorsi Answer: D Diff: 3 Page Ref: 210; 211 11 36) A muscle group that works with and assists the action of a prime mover is a(n): A) antagonist only B) fixator only C) synergist only D) antagonist and synergist E) antagonist and fixator Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: 202 37) Which of the following muscles is not involved in dorsiflexion and/or plantar flexion of the foot: A) gastrocnemius B) tibialis anterior C) extensor digitorum longus D) soleus E) iliopsoas Answer: E Diff: 3 Page Ref: 212; 214 38) Which one of the following is the action of the orbicularis oris: A) closes, purses, and protrudes the lips B) pulls the lower lip down and back C) draws the eyebrows together D) allows blinking, squinting, and various other protective mechanisms for the eye E) closes the jaw Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 207 39) Paralysis of which of the following would make an individual unable to flex the thigh: A) biceps femoris B) vastus medialis C) vastus lateralis D) vastus intermedius E) iliopsoas and rectus femoris Answer: E Diff: 2 Page Ref: 212; 214 40) Which one of the following muscles is involved in abduction of the arm at the shoulder joint: A) deltoid B) biceps brachii C) triceps brachii D) latissimus dorsi E) pectoralis major Answer: A Diff: 2 Page Ref: 210 12 41) Which of the following muscles adducts the thigh: A) peroneus muscles B) gluteus maximus C) sartorius D) quadriceps group E) adductor muscles Answer: E Diff: 1 Page Ref: 214 42) While doing "jumping jacks" during an exercise class, your arms and legs move laterally away from the midline of your body. This motion is called: A) extension B) flexion C) abduction D) adduction E) circumduction Answer: C Diff: 1 Page Ref: 199 43) Which of the following muscles are antagonists: A) biceps brachii and triceps brachii B) bicpes femoris and biceps brachii C) vastus medialis and vastus lateralis D) masseter and temporalis E) gastrocnemius and soleus Answer: A Diff: 3 Page Ref: 211 44) Paralysis of which of the following would make an individual unable to flex the knee: A) hamstring muscle group B) gluteal muscle group C) gastrocnemius D) sartorius E) iliopsoas Answer: A Diff: 3 Page Ref: 214 45) Which one of the following is NOT a criteria generally used in naming muscles: A) relative size of the muscle B) number of origins of the muscle C) shape of the muscle D) method of attachment of the muscle to bone E) action of the muscle Answer: D Diff: 2 Page Ref: 204 13 True/False 1) Skeletal muscle is considered involuntary because it is the only type of muscle usually subject to conscious control. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 183; 185 2) The epimysium covers individual muscle fibers. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 185 3) Skeletal muscles need nerve stimulation for contraction to occur. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 189 4) A nerve cell and all the muscle cells that it stimulates are referred to as a motor unit. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 189 5) A contraction in which a skeletal muscle does not shorten but its tension increases is called isometric. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 197 6) Cardiac muscle fibers are relatively short, tapering cells within a single centrally located nucleus. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 186 7) The neurotransmitter used by the nervous system to activate skeletal muscle cells is acetylcholine. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 189 8) Thick filaments are made of a protein called actin. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 189 9) One of the important functions of skeletal muscle is to generate heat. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 187 10) Lactic acid results from aerobic respiration. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 195 11) A sustained partial contraction of skeletal muscle is called muscle tone. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 197 14 12) An aponeurosis is a ropelike piece of muscle fascia that forms indirect connections to muscles of the leg. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 185 13) A muscle twitch results when the muscle is stimulated so rapidly that no evidence of relaxation is seen. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 194 14) The effect of the neurotransmitter on the muscle cell membrane is to temporarily modify its permeability of ions such as Na+ and K+. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 189-190 15) When a muscle fiber contracts, the I bands diminish in size, the H zones disappear, and the A bands move closer together but do not diminish in length. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 192 16) The insertion of the biceps brachii muscle is on the radius. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 211 17) A prime mover of the arm that acts in adduction is the deltoid. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 210 18) The deepest muscle of the abdominal wall is the transversus abdominis. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 209 19) Dorsiflexion and plantar flexion are synergistic actions. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 202 20) Plantar flexion at the ankle joint is accomplished by the tibialis anterior muscle. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 214 21) The bicpes brachii muscle is named for the two heads that orginiate from the shoulder girdle. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 211 22) There are 206 skeletal muscles in the human body. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 198 23) Supination and pronation refer to up and down movements of the foot at the ankle. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 202 15 Matching Match the following: 1) The distance between two Z discs Diff: 2 Page Ref: 187-188 2) Otherwise known as thick filaments Diff: 2 Page Ref: 189 B) myosin filaments C) actin filaments D) Z discs 3) Contains only the actin filaments Diff: 2 A) I band E) sarcomere Page Ref: 187-188 F) H zone 4) Both actin and myosin are found in this band G) A band Diff: 1 Page Ref: 187-188 5) The type of filament that is studded with myosin heads Diff: 1 Page Ref: 189 6) Tiny contractile unit that shortens during muscle contraction Diff: 2 Page Ref: 187; 192 7) Actin filaments are anchored to these disclike membranes Diff: 1 Page Ref: 189 8) Lighter central portion of the A band Diff: 2 1) E 7) D Page Ref: 187 2) B 8) F 3) A 4) G 16 5) B 6) E Match the following: 9) Serves as the actual "go" signal for muscle contraction Diff: 2 Page Ref: 193 B) acetylcholine 10) Neurotransmitter substance released at motor end plates by the motor neuron Diff: 2 F) aerobic respiration Page Ref: 189 G) anaerobic respiration 12) A metabolic pathway that produces water, carbon dioxide, and ATP, and provides for a large amount of ATP per glucose because oxygen is used Diff: 3 C) enzymes D) potassium ions E) calcium ions Page Ref: 189 11) Normally stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum Diff: 2 A) creatine phosphate H) sodium ions Page Ref: 195 13) A reserve, high-energy compound used to convert ADP to ATP by the transfer of a high-energy phosphate group Diff: 2 Page Ref: 195 14) Destroys acetylcholine (ACh) Diff: 2 9) E Page Ref: 190 10) B 11) E 12) F 17 13) A 14) C Match the following: 15) Type of movement that decreases the angle of the joint Diff: 2 Page Ref: 199 16) Type of movement that results when the forearm rotates laterally so that the palm faces anteriorly Diff: 2 Page Ref: 202 17) The movement of a limb toward the body midline Diff: 2 A) supination B) extension C) pronation D) rotation E) adduction F) flexion G) abduction Page Ref: 199 18) Type of movement that increases the angle of the joint Diff: 2 Page Ref: 199 19) The movement of a bone around its longitudinal axis Diff: 2 Page Ref: 199 20) The movement of a limb away from the body midline Diff: 2 Page Ref: 199 21) Type of movement that results when the forearm rotates medially so the palm faces posteriorly Diff: 2 Page Ref: 202 22) Primary action of the deltoid Diff: 2 Page Ref: 210 23) Primary action of the adductor muscles Diff: 2 Page Ref: 214 24) Primary action of the erector spinae Diff: 2 Page Ref: 210 25) Primary action of the rectus abdominis Diff: 2 Page Ref: 209 18 15) F 21) C 16) A 22) G 17) E 23) E 18) B 24) B 19) D 25) F 20) G Essay 1) Compare skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles as to their body location, microscopic anatomy, regulation of contraction, speed of contraction, and rhythmicity. Answer: Body location—skeletal muscle is attached to bones or to skin (some facial muscles); cardiac muscle is located in the walls of the heart; smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow visceral organs (other than the heart). Microscopic anatomy—skeletal muscle consists of very long, cylindrical, multinucleated cells with very obvious striations; cardiac muscle consists of branching chains of cells that are uninucleated and possess striations; smooth muscle consists of single fusiform uninucleated cells that lack striations. Regulation of contraction—skeletal muscle is voluntary via nervous system controls, but this normal voluntary control can be overridden by involuntary reflex arcs (as explained in later chapters); cardiac muscle is involuntary via the heart pacemaker, nervous system controls, and hormones; smooth muscle is involuntary via nervous system controls, hormones, other chemicals, and stretching. Speed of contraction—skeletal muscle is slow to fast; cardiac muscle is slow; smooth muscle is the slowest. Rhythmicity—skeletal muscle is arrhythmic; cardiac muscle is rhythmic; smooth muscle is sometimes rhythmic. Diff: 3 Page Ref: 183-186 2) Describe the events that occur from the time that a motor neuron releases acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction until muscle cell contraction occurs. Answer: Acetylcholine is released, which diffuses through the synaptic cleft and attaches to receptors on the sarcolemma. The sarcolemma permeability to sodium ions increases briefly, causing sodium ions to rush into the muscle cell, which changes the electrical conditions of the resting sarcolemma. An action potential is initiated and sweeps over the entire sarcolemma. Calcium ions are released from storage areas inside the sarcoplasmic reticulum of the muscle cell. They attach to the myofilaments, which triggers the sliding of the myofilaments and causes a muscle cell contraction. Diff: 3 Page Ref: 189-192 3) List the seven criteria that are used in naming muscles and give an example of each. Answer: 1. Direction of the muscle fibers (e.g., external oblique) 2. Relative size of the muscle (e.g., maximus, minimus, longus) 3. Location of the muscle (e.g., temporalis, frontalis) 4. Number of origins (e.g., biceps, triceps, quadriceps) 5. Location of the muscle's origin and insertion (e.g., the sternocleidomastoid muscle has its origin on the sternum [sterno] and clavicle [cleido] and inserts on the mastoid process of the temporal bone) 6. Shape of the muscle (e.g., the deltoid muscle is roughly triangular—deltoid means "triangular") 7. Action of the muscle (e.g., the adductor muscles of the thigh all bring about its adduction, and the extensor muscles of the wrist all extend the wrist) Diff: 3 Page Ref: 202; 204 19 4) What is the effect of aging on skeletal muscles? Answer: With aging, the amount of connective tissue in muscle increases and the amount of skeletal muscle tissue decreases, thus the muscles become stringier (more sinewy). Since skeletal muscle represents a larger portion of body weight, it begins to decline in elderly persons as this normal loss of muscle mass occurs. Another result of the loss in muscle mass is a decrease in muscle strength—strength decreases by about 50% by the age of 80. Regular exercise can help offset the effects of aging on the muscular system, and frail elders who begin to "pump iron" can rebuild muscle mass and significantly increase their functional strength. Diff: 3 Page Ref: 221 5) Explain the steps in the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction, following the spreading of an action potential along the sarcolemma. Answer: An action potential triggers the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium ions into the sarcoplasm of the muscle cell. The calcium ions bind to regulatory proteins on the actin filaments, changing both their shape and their position on the actin filaments. This action allows myosin receptor sites on the thin actin filaments to become exposed. The myosin heads attach to the myosin binding sites on the actin filaments. Energized by ATP, the myosin heads swivel toward the center of the sarcomere, attaching and detaching several times. In the process the thin actin filaments are pulled toward the center of the sarcomere. As this event occurs simultaneously in sarcomeres throughout the cell, the muscle cell shortens. When the action potential ends, the calcium ions are reabsorbed back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum storage areas, causing the regulatory proteins to resume their original shape and position. Since the myosin heads now have nothing to attach to, the muscle cell relaxes and returns to its original length. Diff: 3 Page Ref: 192-193 6) Fascicle arrangements produce skeletal muscles with different structures and functional properties, and determine their individual range of motion and power. List the seven different fascicle arrangements of human skeletal muscles and give a specific example of each: Answer: 1. Circular—orbicularis oris, orbicularis oculi 2. Convergent—pectoralis major 3. Parallel—sartorius 4. Unipennate—extensor digitorum longus 5. Multipennate—deltoid 6. Fusiform—biceps brachii 7. Bipennate—rectus femoris Diff: 3 Page Ref: 204-206 7) List the "five golden rules" of gross skeletal muscle activity. Answer: 1. With few exceptions, all muscles cross at least one joint. 2. Typically, the bulk of the muscle lies proximal to the joint crossed. 3. All muscles have at least two attachments: the origin and the insertion. 4. Muscles can only pull: they never push. 5. During contraction, the muscle insertion moves toward the origin. Diff: 3 Page Ref: 198 20 8) Explain how isometric and isotonic contractions differ, using examples of each. Answer: 1. Isometric contractions are contractions in which the muscles do not shorten. An example of an isometric contraction is pushing against a wall with bent elbows. The muscles cannot shorten since the wall doesn't move. 2. Isotonic contractions occur when muscles shorten and movement occurs due to the sliding of the myofilaments. Flexion and extension of the arm are just two examples of isotonic contractions. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 197 9) Explain the difference between a motor unit and a neuromuscular junction. Answer: 1. The motor unit is the one neuron and all of the skeletal muscle cells it stimulates. 2. The neuromuscular junction occurs between the axon terminals of one neuron and the sarcolemma of a skeletal muscle cell. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 189 10) Explain how muscle movements mature in a baby, using examples of each. Answer: 1. Muscle development proceeds in a cephalic/caudal direction. For instance, babies can raise their heads before they can walk. 2. Muscle control proceeds in a proximal/distal direction. For instance, babies can perform gross movements like wave "bye-bye" before they can use the pincher grasp to pick up a pin. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 221 21





