GCSE Revision - Describing Music
advertisement
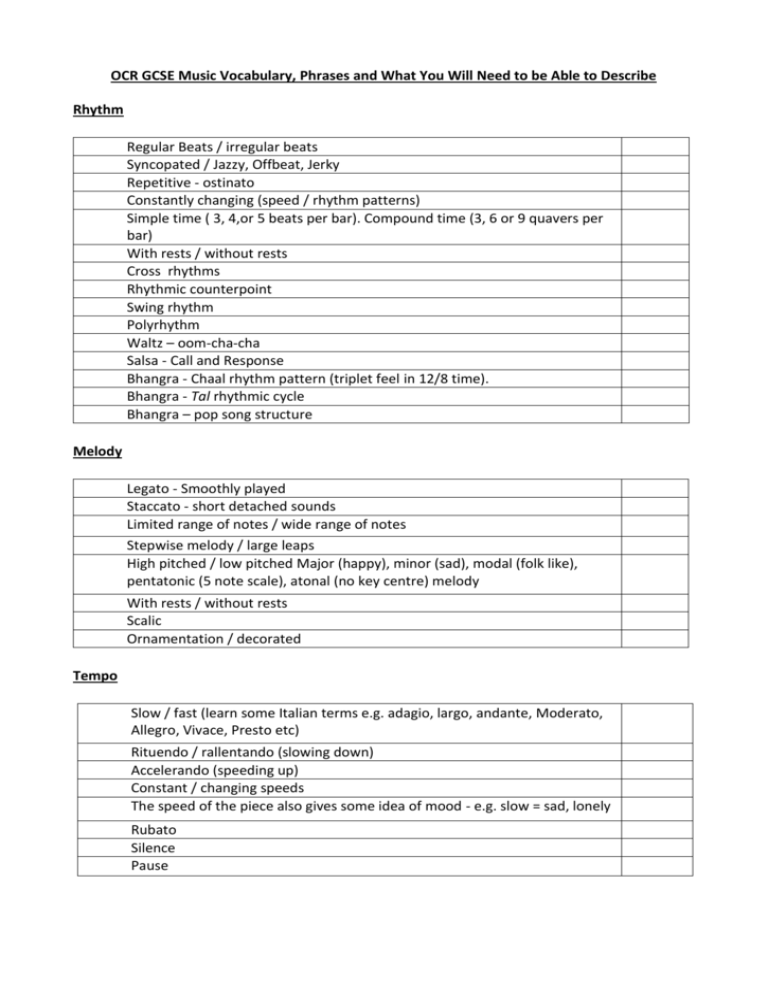
OCR GCSE Music Vocabulary, Phrases and What You Will Need to be Able to Describe Rhythm Regular Beats / irregular beats Syncopated / Jazzy, Offbeat, Jerky Repetitive - ostinato Constantly changing (speed / rhythm patterns) Simple time ( 3, 4,or 5 beats per bar). Compound time (3, 6 or 9 quavers per bar) With rests / without rests Cross rhythms Rhythmic counterpoint Swing rhythm Polyrhythm Waltz – oom-cha-cha Salsa - Call and Response Bhangra - Chaal rhythm pattern (triplet feel in 12/8 time). Bhangra - Tal rhythmic cycle Bhangra – pop song structure Melody Legato - Smoothly played Staccato - short detached sounds Limited range of notes / wide range of notes Stepwise melody / large leaps High pitched / low pitched Major (happy), minor (sad), modal (folk like), pentatonic (5 note scale), atonal (no key centre) melody With rests / without rests Scalic Ornamentation / decorated Tempo Slow / fast (learn some Italian terms e.g. adagio, largo, andante, Moderato, Allegro, Vivace, Presto etc) Rituendo / rallentando (slowing down) Accelerando (speeding up) Constant / changing speeds The speed of the piece also gives some idea of mood - e.g. slow = sad, lonely Rubato Silence Pause Harmony Simple Triads - chords without 7ths and 9ths Complex chords / harmony (chords with additional notes added = 7ths, 9ths etc) Major, minor, modal, atonal, consonance, dissonance (clashing sounds) Diatonic Cadences Modulation Transpose Pedal Drone Chord pattern Arpeggio Figured bass Dynamics Constant / changing Crescendo - getting louder Decrescendo / diminuendo - getting quieter. Learn some Italian terms – Piano (p) - softly, Forte (f) - loudly, Mezzo forte (mf) - moderately loudly, Mezzo piano (mp) - moderately soft, fortissimo (ff) - very loud, pianissimo (pp)- very soft. Subito (sub p) – suddenly quiet Accent / sforzando (sfz) Instrumentation Mention specific instrument names Mention family groups - Brass / Woodwind / Percussion / Strings. Explain the role of instruments - e.g. which instruments provide the melody, harmony, bass line, accompaniment. Compare instrument groups together - e.g. imitating same melody, question and answer, melody and harmony etc. Specific ensembles Accompaniment Styles Supporting the melody and providing chordal, arpeggio accompaniment Mention family groups - Brass / Woodwind / Percussion / Strings. Adding harmony parts to the melody Improvising sections between the melody - instrument or voice Imitating the melody / playing the same music. Unaccompanied - a cappella Tonality (also see harmony) A piece may be in a MAJOR key (sounds happy) or MINOR key (sounds sad) based on a Major or Minor scale May also be chromatic, pentatonic or whole-tone scale Music not based on a type of scale is called ATONAL - e.g. Twentieth Century Transposed Modal Pitch May be High, Medium or Low Try to identify any intervals between notes - either between two notes played after each other in a melody - MELODIC, or between two notes played simultaneously - HARMONIC, by counting up from the bottom note to the top note. 3rd and 6ths sound pleasant, 2nds and 7ths sound unpleasant, 4ths and 5ths sound bare tonic (1), sub-dominant (4th) dominant (5th) Octave (higher, lower, in octaves) Range Register Tones Semi - tones Tessitura - the most musically acceptable and comfortable timbre for a given voice Sharp, flats, naturals Unison Inversion Blues Scale Blue notes Pentatonic Texture General words used to describe music include - light, heavy, thin, rich, soft and hard. MONOPHONIC - one sound e.g. a piece for a solo violin POLYPHONIC - many sounds - where there are several instruments playing together and there are several layers of sound. HOMOPHONIC- block chords, as in a hymn CONTRAPUNTAL - two or more tunes being played together which form some interesting harmonies. Melody and accompaniment Time Signature A time signature is a group of two numbers written near the beginning of almost all music. The top number says how many beats there are in every bar The bottom number is a type of code which tells you what kind of beat to count in. A bottom number of 4 tells you to count in crotchet beats. 8 tells you to count in quaver beats. SIMPLE time signatures are where the beat is a non-dotted note which can be divided into twos. COMPOUND - time signatures are where the beat is a dotted note that can be divided into threes. The most common time signatures are: Jig – 3/4 or 6/8 Slip jig 9/8 Reel – 4/4 Waltz – 3/4 Salsa – 4/4 (2/4) Tango – 2/4 Line dancing – 4/4 Disco – 4/4 Club dance – 4/4 Timbre Timbre means 'sound quality' The difference in sound say between a trumpet and a violin Try to identify as many different sounds as you can. Learn to identify the sounds of different instruments in the same family eg Strings - violin, cello, double bass Word painting Use adjectives such as metallic, shimmering, bright Structure Structure or form describes the order in which sections of it are repeated or not. BINARY form (AB) consisting of a section (A) followed by a section (B) TERNARY form (ABA) Waltz – intro – ABA – Coda Disco – song structure (intro, verse, chorus, middle 8, outro) Salsa - Intro-verse (sometimes several) - break - montuno (improvisations, call and response) – mambo – montuno – ending. Irish Jig and Reel – AB (Binary) or AABB Line dancing - Verse and chorus structure often with equal length sections. A sequence of steps can be extended by adding a tag (few extra counts), or a bridge (longer section). Expression The expression of the music, or in other words how it is played. Many Italian words are used to describe the expression of the music. These include : Animato - in an agitated manner, Con Brio - with vigour, Con Moto with movement, Dolce - sweetly, Grazioso - gracefully, - Legato - smoothly, Mesto - sadly, Pesante - heavily, Subito - suddenly, Tutti - everyone plays or sings, Vivo - lively. Articulation Legato – smooth Staccato - short, detached Tremolo Pizzicato - plucked (strings) Arco - with bow (strings) Col legno - with the wood of the bow