Energy
advertisement

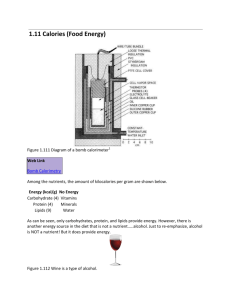
Energy Review – matter is defined as anything that has mass and volume – anything that you can weigh and takes up space. Is sunlight matter? Can you weight it? Does it take up space? You can’t see the air in the room, but it does have mass and volume that could be measured. Sunlight is not matter; it’s energy. Energy – the capacity to do work or give off heat Forms of Energy: Light energy Heat energy Electrical energy Nuclear energy Kinetic energy – the energy of motion Potential energy – stored energy (the potential to move) If I set a book on the edge of a table it has potential energy. If I push it off of the table that potential energy is converted in to kinetic energy. Name all of the sources of energy in the classroom: fluorescent lights, sunlight, potential energy, kinetic energy, electricity, batteries… A calorie is a unit of energy. We tend to associate calories with food, but they apply to anything containing energy. Specifically, a calorie is the amount of energy, or heat, it takes to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius (1.8 degrees Fahrenheit). One calorie is equal to 4.184 joules, a common unit of energy used in the physical sciences. Most of us think of calories in relation to food, as in "This can of soda has 200 calories." It turns out that the calories on a food package are actually kilocalories (1,000 calories = 1 kilocalorie). The word is sometimes capitalized to show the difference, but usually not. A food calorie contains 4,184 joules. A can of soda containing 200 food calories contains 200,000 regular calories. Other countries do use joules to describe food energy. The number of calories in a food is a measure of how much potential energy that food possesses. A gram of carbohydrates has 4 calories, a gram of protein has 4 calories, and a gram of fat has 9 calories. Foods are a compilation of these three building blocks. So if you know how many carbohydrates, fats and proteins are in any given food, you know how many calories, or how much energy, that food contains. Temperature Notes Let’s talk about temperature now. Temperature is not a measure of heat! It is the measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample. Heat is the amount of energy transferred between two objects of different temperatures. Think about it – it takes more heat energy to melt a big block of ice than a small block of ice, but they melt at the same temperature. Heat cannot be measured, only changes in heat. We’ll come back to that. As you know, we use a thermometer to measure temperature. There are three different temperature scales that you might see used in chemistry. Fahrenheit: This is the one that you’re probably most familiar with since it is used in the USA. Water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F. The development of the Fahrenheit scale was fairly arbitrary. One scientist who made very good thermometers back in the 16th century was named Gabriel Fahrenheit. As a consequence, his thermometers, and his temperature scale became widely used. Celsius: You might have also seen this one. It is used in the rest of the world. Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C. This temperature scale was not arbitrary at all. A Swedish astronomer named Anders Celsius developed it in the 16th century to be more compatible with the metric system. He marked the temperatures where water froze and boiled on a thermometer, and then divided the distance between the points in to 100 even graduations. Kelvin: This one is used a lot in chemistry, but not in every day life. As you might guess, it was named after a man named Lord Kelvin. The Kelvin scale was built so that there would not have to be any negative temperature measurements. An increase of 1K is the same as an increase of 1°C. 0K is absolute zero – the temperature where there is no heat present at all and the motion of all particles ceases. This temperature has not been reached anywhere yet. Conversion Factors: K = °C + 273 °C = (°F – 32) * (5/9) °F = °C * (9/5) + 32 Ex) Dry ice, solid carbon dioxide, sublimes at -78.5°C. What is this in Kelvin? K = °C + 273 = -78.5°C + 273 = 194.5 K Ex) Pure aspirin melts at 135°C. What is this in Kelvin? K = °C + 273 = 135°C + 273 = 408 K Ex) The temperature of the surface of the sun is about 6573 K. What is this in Celsius? °C = K - 273 = 6573 K - 273 = 6300 °C Ex) Human body temperature is 98.6°F. What is this in Kelvin? °F = (°C+ 32) * (9/5) 98.6 = (x + 32) * 9/5) = 22.8 °C K = °C + 273 = 273 + 22.8 = 295.8K Temperature Comparisons: The lowest ever recorded temperature on Earth was about -130°F in Antarctica. The highest ever recorded temperature on Earth was about 134°F in Death Valley.



![Temperature Notes [9/22/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006907012_1-3fc2d93efdacd086a05519765259a482-300x300.png)



